Abstract
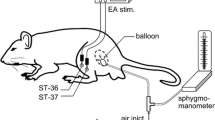
Previous studies demonstrated the efficacy of electro-acupuncture (EA) in relieving chronic visceral hypersensitivity (CVH) in IBS rats. However, ST25 which is a key acupoint for patients with IBS has not been reported in these experiments. Eight CVH rats were treated by EA at both ST25 and ST37 for 20 min, once daily for seven consecutive days, model rats (n = 8) and normal rats (n = 8) as controls. After the first EA treatment, the abdominal withdrawal reflex scores were investigated to evaluate the pain threshold. After seven EA treatments, the concentrations of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), 5-HT3 receptor (5-HT3R) and 5-HT4 receptor (5-HT4R) in colon tissue were assayed quantitatively by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. The results showed that EA improved the pain threshold of CVH rats, reduced the 5-HT concentration and increased the 5-HT4R concentration, but had no effect on the 5-HT3R concentration. Further studies are needed to optimize the choice of two-matching points for EA in the treatment of CVH rats.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saito YA, Schoenfeld P, Locke GR 3rd (2002) The epidemiology of irritable bowel syndrome in North America: a systematic review. Am J Gastroenterol 97:1910–1915
Forbes A, Jackson S, Walter C et al (2005) Acupuncture for irritable bowel syndrome:a blinded placebo-controlled trial. World J Gastroenterol 11:4040–4044
Rohrböck RB, Hammer J, Vogelsang H et al (2004) Acupuncture has a placebo effect on rectal perception but not on distensibility and spatial summation: a study in health and IBS. Am J Gastroenterol 99:1990–1997. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2004.30028.x
Fireman Z, Segal A, Kopelman Y et al (2001) Acupuncture treatment for irritable bowel syndrome. A double-blind controlled study. Digestion 64:100–103. doi:10.1159/000048847
Lowe C, Depew W, Vanner S (2000) A placebo-controlled, double-blind trial of acupuncture in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Gastroenterology 118:A3168
Schneider A, Weiland C, Enck P et al (2007) Neuroendocrinological effects of acupuncture treatment in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Complement Ther Med 15:255–263. doi:10.1016/j.ctim.2006.12.002
Xiao WB, Liu YL (2004) Rectal hypersensitivity reduced by acupoint TENS in patients with diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome: a pilot study. Dig Dis Sci 49:312–319. doi:10.1023/B:DDAS.0000017458.55517.33
Liu B, Hu YM, Tenner SM (2000) A randomized controlled trial of acupuncture for irritable bowel syndrome. Am J Gastroenterol 95:2498. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.2000.02657.x
Chan J, Carr I, Mayberry JF (1997) The role of acupuncture in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome: a pilot study. Hepatogastroenterology 44:1328–1330
Zhang LS, Shi Y (2004) ST25 in treatment of patients with intestinal tract diseases by acupuncture and moxibustion therapies. Jiangxi J Trad Chin Med 35:53–56
Wu HG, Wang JH, Chen HP et al (1996) Exploration of efficacy and immunological mechanism for IBS treated by herb-partition moxibustion. Zhongguo Zhen Jiu 16:43–45
Tian SL, Wang XY, Ding GH (2008) Repeated electro-acupuncture attenuates chronic visceral hypersensitivity and spinal cord NMDA receptor phosphorylation in a rat irritable bowel syndrome model. Life Sci 83:356–363. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2008.06.027
Tian XY, Bian ZX, Hu XG et al (2006) Electro-acupuncture attenuates stress-induced defecation in rats with chronic visceral hypersensitivity via serotonergic pathway. Brain Res 1088:101–108. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2006.03.014
Cui KM, Li WM, Gao X et al (2005) Electro-acupuncture relieves chronic visceral hyperalgesia in rats. Neurosci Lett 376:20–23. doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2004.11.018
Al-Chaer ED, Kawasaki M, Pasricha PJ (2000) A new model of chronic visceral hypersensitivity in adult rats induced by colon irritation during postnatal development. Gastroenterology 119:1276–1285. doi:10.1053/gast.2000.19576
Wu HG, Jiang B, Zhou EH et al (2008) Regulatory mechanism of electroacupuncture in irritable bowel syndrome: preventing MC activation and decreasing SP VIP secretion. Dig Dis Sci 53:1644–1651. doi:10.1007/s10620-007-0062-4
Gershon MD, Tack J (2007) The serotonin signaling system: from basic understanding to drug development for functional GI disorders. Gastroenterology 132:397–414. doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2006.11.002
McLean PG, Borman RA, Lee K (2007) 5-HT in the enteric nervous system: gut function and neuropharmacology. Trends Neurosci 30:9–13. doi:10.1016/j.tins.2006.11.002
Crowell MD, Shetzline MA, Moses PL et al (2004) Enterochromaffin cells and 5-HT signaling in the pathophysiology of disorders of gastrointestinal function. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 5:55–60
Dunlop SP, Coleman NS, Blackshaw E et al (2005) Abnormalities of 5-hydroxytryptamine metabolism in irritable bowel syndrome. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 3:349–357. doi:10.1016/S1542-3565(04)00726-8
Jin JG, Foxx-Orenstein AE, Grider JR (1999) Propulsion in guinea pig colon induced by 5-hydroxytryptamine (HT) via 5-HT4 and 5-HT3 receptors. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 288:93–97
Kozlowski CM, Green A, Grundy D et al (2000) The 5-HT(3) receptor antagonist alosetron inhibits the colorectal distention induced depressor response and spinal c-fos expression in the anaesthetised rat. Gut 46:474–480. doi:10.1136/gut.46.4.474
Hicks GA, Coldwell JR, Schindler M, Ward PA (2002) Excitation of rat colonic afferent fibres by 5-HT(3) receptors. J Physiol 544:861–869. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2002.025452
Greenwood-Van Meerveld B, Venkova K, Hicks G et al (2006) Activation of peripheral 5-HT4 receptors attenuates colonic sensitivity to intraluminal distension. Neurogastroenterol Motil 18:76–86. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2982.2005.00723.x
Coffin B, Farmachidi JP, Rueegg P et al (2003) Tegaserod, a 5-HT4 receptor partial agonist, decreases sensitivity to rectal distension in healthy subjects. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 17:577–585. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2036.2003.01449.x
Coelho A-M, Rovira P, Fioramonti J et al (2000) Antinociceptive properties of HTF 919 (tegaserod) a 5-HT4 receptor partial agonist on colorectal distension in rats. Gastroenterology 218:A835
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (973 program, No. 2009CB522904), and by China Postdoctoral Science Foundation funded project (No. 200801260 and No. 20080430117). Many thanks go to editors and reviewers of Neurochemical Research, Dr. Lin-ying Tan and Dr. Ci-Li Zhou of Shanghai University of T.C.M. for their invaluable suggestions and advice for revision of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, HR., Wang, XM., Zhou, EH. et al. Acupuncture at Both ST25 and ST37 Improves the Pain Threshold of Chronic Visceral Hypersensitivity Rats. Neurochem Res 34, 1914–1918 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-009-9972-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-009-9972-1