Abstract
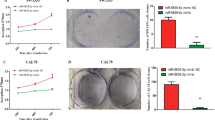
Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 1 (TIMP-1) is a glycosylated protein with multiple activities in the regulation of biological processes, such as cell growth and apoptosis as well as tumor invasion and metastasis. Bioinformatics analysis using TargetScan and miRanda suggested tissue inhibitors of TIMP-1 are among the targets of miR-1293. To confirm this, we cloned both wild-type and mutant TIMP-1 3′UTR fragments by overlap extension PCR, constructed the recombinant plasmids pGL3-TIMP-1-wt, -mut, and pcDNA 3.1(+)/TIMP-1-CDS and, respectively, co-transfected them into 293T cells with the miR-1293 inhibitor, mimics or the miR inhibitor-NC using a BTX ECM 2001 square-wave electroporator. We used a luciferase assay to investigate binding of miR-1293 to the 3′UTR of TIMP-1. Effects on the levels of the TIMP-1 protein were analyzed by Western blot experiments. The luciferase reporter assay showed a statistically significant (P < 0.05) upregulation of activity. Western blot analysis showed a significant increase of expression of the TIMP-1 gene co-transfected with the miR-1293 inhibitor, and demonstrated direct binding of miR-1293 to the 3′UTR of TIMP-1. In this study, we identified TIMP-1 as a novel direct target for miR-1293, which provides the basis for further study of the multifunctional mechanisms of miR-1293 and TIMP-1 in the regulation of a variety of diseases.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lambert E, Dassé E, Haye B, Petitfrère E (2004) TIMPs as multifacial proteins. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 49:187–198
Caterina NC, Windsor LJ, Bodden MK, Yermovsky AE, Taylor KB, Birkedal-Hansen H, Engler JA (1998) Glycosylation and NH2-terminal domain mutants of the tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 (TIMP-1). Biochim Biophys Acta 1388:21–34
Brew K, Nagase H (2010) The tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases (TIMPs): an ancient family with structural and functional diversity. Biochim Biophys Acta 1803:55–71
Avalos BR, Kaufman SE, Tomonaga M, Williams RE, Golde DW, Gasson JC (1988) K562 cells produce and respond to human erythroid-potentiating activity. Blood 71:1720–1725
Stetler-Stevenson WG (2008) Tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in cell signaling: metalloproteinase-independent biological activities. Sci Signal 1:re6
Oelmann E, Herbst H, Zühlsdorf M, Albrecht O, Nolte A, Schmitmann C, Manzke O, Diehl V, Stein H, Berdel WE (2002) Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 1 is an autocrine and paracrine survival factor, with additional immune-regulatory functions, expressed by Hodgkin/Reed–Sternberg cells. Blood 99:258–267
Yang L, Liu R, Wang X, He D (2013) Imbalance between matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP-1) and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-1 (TIMP-1) contributes to bladder compliance changes in rabbits with partial bladder outlet obstruction (PBOO). BJU Int. doi:10.1111/j.1464-410X.2012.11740.x
Würtz SØ, Schrohl AS, Sørensen NM, Lademann U, Christensen IJ, Mouridsen H, Brünner N (2005) Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 in breast cancer. Endocr Relat Cancer 12:215–227
Mohammed FF, Pennington CJ, Kassiri Z, Rubin JS, Soloway PD, Ruther U, Edwards DR, Khokha R (2005) Metalloproteinase inhibitor TIMP-1 affects hepatocyte cell cycle via HGF activation in murine liver regeneration. Hepatology 41:857–867
Porter JF, Sharma S, Wilson DL, Kappil MA, Hart RP, Denhardt DT (2005) Tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-1 stimulates gene expression in MDA-MB-435 human breast cancer cells by means of its ability to inhibit metalloproteinases. Breast Cancer Res Treat 94:185–193
Groblewska M, Siewko M, Mroczko B, Szmitkowski M (2012) The role of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and their inhibitors (TIMPs) in the development of esophageal cancer. Folia Histochem Cytobiol 50:12–19
Bloomston M, Shafii A, Zervos E, Rosemurgy AS (2005) TIMP-1 antisense gene transfection attenuates the invasive potential of pancreatic cancer cells in vitro and inhibits tumor growth in vivo. Am J Surg 189:675–679
Jung CJ, Iyengar S, Blahnik KR, Ajuha TP, Jiang JX, Farnham PJ, Zern M (2011) Epigenetic modulation of miR-122 facilitates human embryonic stem cell self-renewal and hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation. PLoS One 6:e27740
Zhang J, Luo N, Luo Y, Peng Z, Zhang T, Li S (2012) microRNA-150 inhibits human CD133-positive liver cancer stem cells through negative regulation of the transcription factor c-Myb. Int J Oncol 40:747–756
Shukla GC, Singh J, Barik S (2011) MicroRNAs: processing, maturation, target recognition and regulatory functions. Mol Cell Pharmacol 3:83–92
Yi R, Fuchs E (2011) MicroRNAs and their roles in mammalian stem cells. J Cell Sci 124:1775–1783
Lindow M (2011) Prediction of targets for microRNAs. Methods Mol Biol 703:311–317
Zhang Q, Sun H, Jiang Y, Ding L, Wu S, Fang T, Yan G, Hu Y (2013) MicroRNA-181a suppresses mouse granulosa cell proliferation by targeting activin receptor IIA. PLoS One 8:e59667
Huang Y, Zou Q, Song H, Song F, Wang L, Zhang G, Shen X (2010) A study of miRNAs targets prediction and experimental validation. Protein Cell 1:979–986
Perron MP, Provost P (2008) Protein interactions and complexes in human microRNA biogenesis and function. Front Biosci 13:2537–2547
Bartel DP (2004) MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116:281–297
Li J, Kong X, Zhang J, Luo Q, Li X, Fang L (2013) MiRNA-26b inhibits proliferation by targeting PTGS2 in breast cancer. Cancer Cell Int 13:7
Shen L, Li J, Xu L, Ma J, Li H, Xiao X, Zhao J, Fang L (2012) miR-497 induces apoptosis of breast cancer cells by targeting Bcl-w. Exp Ther Med 3:475–480
Rhoades MW, Reinhart BJ, Lim LP, Burge CB, Bartel B, Bartel DP (2002) Prediction of plant microRNA targets. Cell 110:513–520
Li L, Xu J, Yang D, Tan X, Wang H (2010) Computational approaches for microRNA studies: a review. Mamm Genome 21:1–12
Zhang R, Su B (2009) Small but influential: the role of microRNAs on gene regulatory network and 3′UTR evolution. J Genet Genomics 36:1–6
Long D, Chan CY, Ding Y (2008) Analysis of microRNA-target interactions by a target structure based hybridization model. Pac Symp Biocomput 64–74
Kang JG, Pripuzova N, Majerciak V, Kruhlak M, Le SY, Zheng ZM (2011) Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus ORF57 promotes escape of viral and human interleukin-6 from microRNA-mediated suppression. J Virol 85:2620–2630
Kang JG, Majerciak V, Uldrick TS, Wang X, Kruhlak M, Yarchoan R, Zheng ZM (2011) Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesviral IL-6 and human IL-6 open reading frames contain miRNA binding sites and are subject to cellular miRNA regulation. J Pathol 225:378–389
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to all staff at the study center who contributed to this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, P., Ma, Y., Wang, Y. et al. Identification of miR-1293 potential target gene: TIMP-1. Mol Cell Biochem 384, 1–6 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1775-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1775-7