Abstract
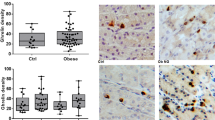
Currently, obesity is an important health problem in all countries, both developed and developing. Dietary habits and neurohormonal imbalances play a critical role in obesity. Circulating amounts of ghrelin, which is a neurohormonal hormone, decrease with obesity and increase with weight loss. Although it is known that both mRNA and peptide version of the ghrelin hormone are expressed in almost all tissues of both humans and animals, it is not known how obesity changes the expression of this hormone in the tissues, with the exception of the gastrointestinal system tissues. Therefore, the objective of the present study is to show how diet-induced obesity in rats changes ghrelin expression in all system tissues, and thus, to shed light on the etiopathology of obesity. The study included 12 male and 12 female 2-month-old Wistar albino species rats. The animals in the control group were fed on standard rat pellet, while those in the experiment group were fed ad libitum on a cafeteria-style diet for 2 months. When their body mass index reached 1 g/cm2, diet-induced obese (DIO) rats were sacrificed in a sterile environment after one night fasting. Ghrelin localizations in the tissues were studied immunohistochemically using avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) method, while tissue ghrelin amounts were analyzed using radioimmunoassay (RIA) method. When the ghrelin amounts in the urogenital system (with the exception of kidney tissues), sensory organs, respiratory system, immune system, skeletal muscle system, cardiovascular system, nervous system, and adipose tissue of rats analyzed by RIA method were compared to those in the control group, tissue ghrelin amounts in the DIO group were found lower. Immunohistochemical findings which showed a similar fall in ghrelin concentrations in the tissues were parallel to RIA results. In addition, ghrelin was shown to be synthesized in the cardiovascular system, heart muscle cells, tails of the sperms, hair follicles, lacrimal glands, tongue, and teeth of rats for the first time in this study and ghrelin syntheses in these tissues were found to decrease in obesity. Nutritional obesity is among the most common causes of obesity and the findings we have obtained through diet-induced obesity will contribute to the illumination of the etiopathology of obesity.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ford ES, Mokdad AH (2008) Epidemiology of obesity in the Western Hemisphere. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 93(Suppl 1):S1–S8
Katsiki N, Ntaios G, Vemmos K (2011) Stroke, obesity, and gender: a review of the literature. Maturitas 69:239–243
Selassie M, Sinha AC (2011) The epidemiology and aetiology of obesity: a global challenge. Best Pract Res Clin Anaesthesiol 25:1–9
Alvarez-Castro P, Sangiao-Alvarellos S, Brandón-Sandá I, Cordido F (2011) Endocrine function in obesity. Endocrinol Nutr 58:422–432
Suematsu M, Katsuki A, Sumida Y, Gabazza EC, Murashima S, Matsumoto K, Kitagawa N, Akatsuka H, Hori Y, Nakatani K, Togashi K, Yano Y, Adachi Y (2005) Decreased circulating levels of active ghrelin are associated with increased oxidative stress in obese subjects. Eur J Endocrinol 153:40
Sahin I, Aydin S, Ozkan Y, Dagli AF, Akin KO, Guzel SP, Catak Z, Ozercan MR (2011) Diet-induced obesity suppresses ghrelin in rat gastrointestinal tract and serum. Mol Cell Biochem 355:299–308
Kojima M, Hosoda H, Date Y, Nakazato M, Matsuo H, Kangawa K (1999) Ghrelin is a growth-hormone-releasing acylated peptide from stomach. Nature 402:656–660
Inui A, Asakawa A, Bowers CY, Mantovani G, Laviano A, Meguid MM, Fujimiya M (2004) Ghrelin, appetite, and gastric motility: the emerging role of the stomach as an endocrine organ. FASEB J 18:439–456
Wierup N, Svensson H, Mulder H, Sundler F (2002) The ghrelin cell: a novel developmentally regulated islet cell in the human pancreas. Regul Pept 107:63–69
Kojima M, Kangawa K (2011) The discovery of ghrelin: with a little luck and great passion. Peptides 32(11):2153–2154
Nishi Y, Yoh J, Hiejima H, Kojima M (2011) Structures and molecular forms of the ghrelin-family peptides. Peptides 32(11):2175–2182
Aydin S (2007) Discovery of ghrelin hormone: research and clinical applications. Turk J Biochem 32:76–89
Ariyasu H, Takaya K, Tagami T, Ogawa Y, Hosoda K, Akamizu T, Suda M, Koh T, Natsui K, Toyooka S, Shirakami G, Usui T, Shimatsu A, Doi K, Hosoda H, Kojima M, Kangawa K, Nakao K (2001) Stomach is a major source of circulating ghrelin, and feeding state determines plasma ghrelin-like immunoreactivity levels in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:4753–4758
Dagli AF, Aydin S, Karaoglu A, Akpolat N, Ozercan IH, Ozercan MR (2009) Ghrelin expression in normal kidney tissue and renal carcinomas. Pathol Res Pract 205:165–173
Gnanapavan S, Kola B, Bustin SA, Morris DG, McGee P, Fairclough P, Bhattacharya S, Carpenter R, Grossman AB, Korbonits M (2002) The tissue distribution of the mRNA of ghrelin and subtypes of its receptor, GHS-R, in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87:2988
Ghelardoni S, Carnicelli V, Frascarelli S, Ronca-Testoni S, Zucchi R (2006) Ghrelin tissue distribution: comparison between gene and protein expression. J Endocrinol Invest 29:115–121
Hosoda H, Doi K, Nagaya N, Okumura H, Nakagawa E, Enomoto M, Ono F, Kangawa K (2004) Optimum collection and storage conditions for ghrelin measurements: octanoyl modification of ghrelin is rapidly hydrolyzed to desacyl ghrelin in blood samples. Clin Chem 50:1077–1080
Gröschl M, Uhr M, Kraus T (2004) Evaluation of the comparability of commercial ghrelin assays. Clin Chem 50:457–458
Hsu SM, Raine L, Fanger H (1981) Use of avidin–biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase technique. J Histochem Cytochem 29:577–580
Cummings DE, Purnell JQ, Frayo RS, Schmidova K, Wisse BE, Weigle DS (2001) A preprandial rise in plasma ghrelin levels suggests a role in meal initiation in humans. Diabetes 50:1714–1719
Zorrilla EP, Iwasaki S, Moss JA, Chang J, Otsuji J, Inoue K, Meijler MM, Janda KD (2006) Vaccination against weight gain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:13226–13231
Monteiro MP (2011) Anti-ghrelin vaccine for obesity: a feasible alternative to dieting? Expert Rev Vaccines 10:1363–1365
Mori K, Yoshimoto A, Takaya K, Hosoda K, Ariyasu H, Yahata K, Mukoyama M, Sugawara A, Hosoda H, Kojima M, Kangawa K, Nakao N (2000) Kidney produces a novel acylated peptide, ghrelin. FEBS Lett 486:213–216
Kuloglu T, Dabak DO (2009) Determination of ghrelin immunoreactivity in kidney tissues of diabetic rats. Ren Fail 31:562–566
Tena-Sempere M, Barreiro ML, González LC, Gaytán F, Zhang FP, Caminos JE, Pinilla L, Casanueva FF, Diéguez C, Aguilar E (2002) Novel expression and functional role of ghrelin in rat testes. Endocrinology 143:717–725
Holly FJ, Lemp MA (1977) Tear physiology and dry eyes. Surv Ophthalmol 22:69–87
Garreis F, Gottschalt M, Schlorf T, Gläser R, Harder J, Worlitzsch D, Paulsen FP (2011) Expression and regulation of antimicrobial peptide psoriasin (S100A7) at the ocular surface and in the lacrimal apparatus. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 52:4914–4922
Aydin S, Erenler S, Kendir Y (2011) Effects of sodium octanoate, acylated ghrelin, and desacylated ghrelin on the growth of genetically engineered escherichia coli. J Med Biochem 30:328–333
Lin Y, Matsumura K, Fukuhara M, Kagiyama S, Fujii K, Iida M (2004) Ghrelin acts at the nucleus of the solitary tract to decrease arterial pressure in rats. Hypertension 43:977–982
Chung H, Chung HY, Bae CW, Kim CJ, Park S (2011) Ghrelin suppresses tunicamycin- or thapsigargin-triggered endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis in primary cultured rat cortical neuronal cells. Endocr J 58:409–420
Konturek PC, Brzozowski T, Walter B, Burnat G, Hess T, Hahn EG, Konturek SJ (2006) Ghrelin-induced gastroprotection against ischemia-reperfusion injury involves an activation of sensory afferent nerves and hyperemia mediated by nitric oxide. Eur J Pharmacol 536:171–178
Sehirli O, Sener E, Sener G, Cetinel S, Erzik C, Yeğen BC (2008) Ghrelin improves burn-induced multiple organ injury by depressing neutrophil infiltration and the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Peptides 29:1231–1240
Kodama T, Ashitani J, Matsumoto N, Kangawa K, Nakazato M (2008) Ghrelin treatment suppresses neutrophil-dominant inflammation in airways of patients with chronic respiratory infection. Pulm Pharmacol Ther 21:774–779
Chorny A, Anderson P, Gonzalez-Rey E, Delgado M (2008) Ghrelin protects against experimental sepsis by inhibiting high-mobility group box 1 release and by killing bacteria. J Immunol 180:8369–8377
Aydin S, Ozercan IH, Geckil H, Dagli F, Aydin S, Kumru S, Kilic N, Sahin I, Ozercan MR (2007) Ghrelin is present in teeth. J Biochem Mol Biol 40:368–372
Acknowledgment
The authors would like to extend their thanks to TUBITAK (project no: 106S350) and FUBAP (project no: 1445) for their financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aydin, S., Sahin, İ., Ozkan, Y. et al. Examination of the tissue ghrelin expression of rats with diet-induced obesity using radioimmunoassay and immunohistochemical methods. Mol Cell Biochem 365, 165–173 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-012-1256-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-012-1256-4