Abstract
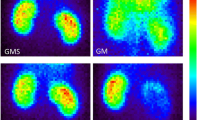
Erdosteine is a mucolytic agent having antioxidant properties through its active metabolites in acute injuries induced by pharmacological drugs. This study was designed to investigate the renoprotective potential of Erdosteine against gentamicin (GM)-induced renal dysfunction by using Technetium-99 m dimercaptosuccinic acid (Tc-99 m DMSA) uptake and scintigraphy in rats. For this purpose, male Wistar rats were randomly allotted into one of the four experimental groups: Control, Erdosteine, GM, and GM + Erdosteine groups. GM and GM + Erdosteine groups received 100 mg/kg GM intramuscularly for 6 days. In addition, Erdosteine and GM + Erdosteine groups received 50 mg/kg Erdosteine orally for 6 days. Renal function tests were assessed by serum blood urea nitrogen (BUN), creatinine levels, as well as scintigraphic and tissue radioactivity measurements with Tc-99 m DMSA. Renal oxidative damage was determined by renal malondialdehyde (MDA) levels, by antioxidant enzyme activities; superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT) and activities of oxidant enzymes; xanthine oxidase (XO) and myeloperoxidase (MPO). GM administration resulted in marked renal lipid peroxidation, increased XO and MPO activities and decreased antioxidant enzyme activities. GM + Erdosteine group significantly had lower MDA levels, higher SOD and CAT activities and lower XO and MPO activities, when compared to GM. Also GM + Erdosteine had lower levels of serum BUN, creatinine and higher renal tissue Tc-99 m DMSA uptake and radioactivity with respect to GM. In conclusion, our results supported a protective role of Erdosteine in nephrotoxicity associated with GM treatment.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ho JL, Barza M (1987) Role of aminoglycoside antibiotics in the treatment of intra-abdominal infection. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 31:485–491
Lerner SA, Schmitt BA, Seligsohn R, Matz GJ (1986) Comparative study of ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity in patients randomly assigned to treatment with amikacin or gentamicin. Am J Med 80:98–104
Rodriguez-Barbero A, Lopez-Novoa JM, Arevalo M (1997) Involvement of platelet-activating factor in gentamicin nephrotoxicity in rats. Exp Nephrol 5:47–54
Cuzzocrea S, Mazzon E, Dugo L, Serraino I, Di PR, Britti D, De SA, Pierpaoli S, Caputi A, Masini E et al (2002) A role for superoxide in gentamicin-mediated nephropathy in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 450:67–76
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JM (1984) Lipid peroxidation, oxygen radicals, cell damage, and antioxidant therapy. Lancet 1:1396–1397
Halliwell B (1997) Antioxidants and human disease: a general introduction. Nutr Rev 55:S44–S49
Dechant KL, Noble S (1996) Erdosteine. Drugs 52:875–881
Gurel A, Armutcu F, Cihan A, Numanoglu KV, Unalacak M (2004) Erdosteine improves oxidative damage in a rat model of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Eur Surg Res 36:206–209
Piepsz A (2002) Radionuclide studies in paediatric nephro-urology. Eur J Radiol 43:146–153
Yamada M (1991) Assessment of 99mTc-DMSA renography and uptake compared with creatinine clearance in rats with drug-induced nephrotoxicity—I. Gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity. Kaku Igaku 28:339–345
Yamada M (1991) Assessment of 99mTc-DMSA renography and uptake compared with creatinine clearance in rats with drug-induced nephrotoxicity—II. Cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity. Kaku Igaku 28:347–354
Draper HH, Hadley M (1990) Malondialdehyde determination as index of lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol 186:421–431
Prajda N, Weber G (1975) Malignant transformation-linked imbalance: decreased xanthine oxidase activity in hepatomas. FEBS Lett 59:245–249
Aebi (1974) Catalase. New York and London Academic Press
Sun Y, Oberley LW, Li Y (1988) A simple method for clinical assay of superoxide dismutase. Clin Chem 34:497–500
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Ekor M, Farombi EO, Emerole GO (2006) Modulation of gentamicin-induced renal dysfunction and injury by the phenolic extract of soybean (Glycine max). Fundam Clin Pharmacol 20:263–271
Farombi EO, Ekor M (2006) Curcumin attenuates gentamicin-induced renal oxidative damage in rats. Food Chem Toxicol 44:1443–1448
Inglesi M, Nicola M, Fregnan GB, Bradamante S, Pagani G (1994) Synthesis and free radical scavenging properties of the enantiomers of erdosteine. Farmaco 40:703–708
Miyake K, Kaise T, Hosoe H, Akuta K, Manabe H, Ohmori K (1999) The effect of erdosteine and its active metabolite on reactive oxygen species production by inflammatory cells. Inflamm Res 48:205–209
Hayashi K, Hosoe H, Kaise T, Ohmori K (2000) Protective effect of erdosteine against hypochlorous acid-induced acute lung injury and lipopolysaccharide-induced neutrophilic lung inflammation in mice. J Pharm Pharmacol 52:1411–1416
Kavutcu M., Canbolat O., Ozturk S., Olcay E., Ulutepe S., Ekinci C., Gokhun I.H., Durak I (1996). Reduced enzymatic antioxidant defense mechanism in kidney tissues from gentamicin-treated guinea pigs: effects of vitamins E and C. Nephron 72: 269–274
Rajeswari A, Varalakshmi P (2006) Low molecular weight heparin protection against oxalate-induced oxidative renal insult. Clin Chim Acta 370:108–114
Fadillioglu E, Yilmaz HR, Erdogan H, Sogut S (2003) The activities of tissue xanthine oxidase and adenosine deaminase and the levels of hydroxyproline and nitric oxide in rat hearts subjected to doxorubicin: protective effect of erdosteine. Toxicology 191:153–158
Parlakpinar H, Tasdemir S, Polat A, Bay-Karabulut A, Vardi N, Ucar M, Acet A (2005) Protective role of caffeic acid phenethyl ester (cape) on gentamicin-induced acute renal toxicity in rats. Toxicology 207:169–177
Lora-Michiels M, Anzola K, Amaya G, Solano M (2001) Quantitative and qualitative scintigraphic measurement of renal function in dogs exposed to toxic doses of Gentamicin. Vet Radiol Ultrasound 42:553–561
Bingham JB, Maisey MN, Joyce MR, Saxton HM (1978) Use of 99Tcm-DMSA as a static renal imaging agent. Contrib Nephrol 11:95–99
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cabuk, M., Gurel, A., Sen, F. et al. Renoprotective effect of Erdosteine in rats against gentamicin nephrotoxicity: a comparison of 99mTc-DMSA uptake with biochemical studies. Mol Cell Biochem 308, 35–42 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-007-9609-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-007-9609-0