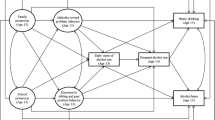
Ill-timed and excessive use of alcohol is associated with multiple and irreversible disabilities. The relationship between perinatal alcohol use and developmental disabilities, including fetal alcohol syndrome, is well documented. Empirical evidence also links alcohol use to a host of other developmental and physical problems among the offspring of drinkers and among drinkers themselves. Toward advancing the science of how to reduce alcohol abuse risks, this study developed and tested family and computer-based approaches for preventing alcohol use among a community sample of inner-city minority youth. Original findings from 4-year follow-up data obtained from over 90% of the study sample document continued positive program outcomes and shed light on cognitive problem solving, peer, and family mediators of alcohol use risk and protective factors among target youth.

Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Bahr, S. J., Marcos, A. C., and Maughan, S. I. (1995). Family, educational, and peer influences on the alcohol use of female and male adolescents. J. Stud. Alcohol 56: 457–469.
Bandura, A. (1986). Social foundations of thought and action: A social cognitive theory, Prentice Hall, Englewood Cliffs, NJ.
Blum, R. W., Beuhring, T., Shew, M. L., Bearing, L. H., Sieving, R. E., and Resnick, M. D. (2000). The effects of race/ethnicity, income, and family structure on adolescent risk behaviors. Am. J. Public Health 90: 1879–1884.
Bonnie, R. J., and O’Connell, M. E. (eds.). (2004). Reducing underage drinking: A collective responsibility, The National Academies Press, Washington, DC.
Bosworth, K. (Spring 2003). Application of computer technology to drug abuse prevention. In Bukowski, W., and Slaboda, Z. (eds.), Handbook of drug abuse theory, science, and practice, New York: Plenum Publishing.
Bosworth, K., Espelage, D., and DuBay, T. (1998). A computer-based violence prevention intervention for young adolescents: Pilot study. Adolescence 33: 785–795.
Botvin, G. J., Baker, E., Dusenbury, L., Botvin, E. M., and Diaz, T. (1995). Long-term follow-up results of a randomized drug abuse prevention trial in a White middle-class population. JAMA 273: 1106–1112.
Brezina, T. (2000). Delinquent problem solving: An interpretive framework for criminological theory and research. J. Res. Crime Delinq 37: 3–30.
Brick, J. (ed.) (2004). Handbook of the medical consequences of alcohol and drug abuse, Haworth Press, New York.
Brody, G. H., Flor, D. L., and Gibson, N. M. (September 1999). Linking maternal efficacy beliefs, developmental goals, parenting practices, and child competence in rural single-parent African American families. Child Dev. 70:1197–1208.
Brook, J. S., Brook, D. W., Gordon, A. S., Whiteman, M., and Cohen, P. (1990). The psychological etiology of adolescent drug use: A family interactional approach. Genet. Soc. Gen. Psychol. Monogr. 116: Whole No. 2.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (1999). Youth Risk Behavior Surveillance System. Retrieved July 16, 2004, from http://www.cdc.gov/nccdphp/dash/yrbs/index.htm
Coles, C. D., Platzman, K. A., Raskind-Hood, C. L., Brown, R. T., Falek, A., and Smith, L. E. (1997). A comparison of children affected by prenatal alcohol exposure and attention deficit, hyperactivity disorder. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 21: 150–161.
Domel, S. B., Thompson, W. O., Baranowski, T., and Smith, A. F. (1994). How children remember what they have eaten. J. Am. Diet Assoc. 94: 1267–1272.
Eggert, L. L., Thompson, E. A., Herting, J. R., and Nicholas, L. J. (1994). Prevention research program: Reconnecting at-risk youth. Issues Ment. Health Nurs. 15: 107–135.
Garmezy, N. (1985). Stress-resistant children: The search for protective factors. In Stevenson J. E. (ed.), Recent research in developmental psychopathology, Elsevier, New York, pp. 213–233.
Hawkins, J. D., Arthur, M. W., and Catalano, R. F. (1994). Preventing substance abuse. Crime and Justice 8: 197–277.
Hawkins, J. D., Catalano, R. F., and Miller, J. Y. (1992). Risk and protective factors for alcohol and other drug problems in adolescence and early adulthood: Implications for substance abuse prevention. Psychol. Bull. 112: 64–105.
Hingson, R. W., and Howland, J. (2002). Comprehensive community interventions to promote health: Implications for college-age drinking problems. J. Stud. Alcohol. (Suppl. No. 14): 226–240.
Jessor, R., and Jessor, S. L. (1977). Problem behavior and psychosocial development: A longitudinal study of youth, Academic Press, New York.
Johnson, K., Strader, T. N., Berbaum, M., Bryant, D., Bucholtz, G., Collins, D., and Noe, T. (1996). Reducing alcohol and other drug use by strengthening community, family, and youth resiliency: An evaluation of the Creating Lasting Connections Program. J. Adolesc. Res. 11: 36–67.
Jones, K. L., and Smith, D. W. (1973). Recognition of fetal alcohol syndrome in early infancy. Lancet 2: 999–1001.
Mattson, S. N., and Riley, E. P. (1996). Brain anomalies in fetal alcohol syndrome. In Abel, E. L. (ed.), Fetal alcohol syndrome: From mechanism to prevention, CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, pp. 51–68.
Murray, M., Swan, A. V., Bewley, B. R., and Johnson, M. R. D. (1993). The development of smoking during adolescence: The MRC/Derbyshire smoking study. Int. J. Epidemiol. 12: 185–192.
National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism (2000). Tenth special report to the U.S. Congress on alcohol and health: Highlights from current research (NIH publication No. 00-1583), U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Bethesda, MD.
National Institute on Drug Abuse [NIDA], National Institutes of Health (1997). Preventing drug use among children and adolescents: A research-based guide, Author, Rockville, MD.
Oetting, E. R., Beauvais, F., and Edwards, R. (1994). The American Drug and Alcohol Use Survey™, RMBSI, Fort Collins, CO.
Paperny, D. M. N. (1997). Computerized health assessment and education for adolescent HIV and STD prevention in health care settings and schools. Health. Educ. Behav. 24: 54–70.
Paperny, D. M., Aono, J. Y., Lehman, R. M., Hammar, S. L., and Risser, J. (1990). Computer-assisted detection and intervention in adolescent high-risk health behaviors. J. Pediatr. 116: 456–462.
Perry, C. L., Williams, C. L., Veblen-Mortenson, S., Toomey, T., Komro, K. A., Anstine, P. S., McGovern, P. G., Finnegan, J. R., Forster, J. L., Wagenaar, A. C., and Wolfson, M. (1996). Project Northland: Outcomes of a community-wide alcohol use prevention program during early adolescence. Am. J. Public Health 86: 956–965.
Rotheram-Borus, M. J. (2000). Expanding the range of interventions to reduce HIV among adolescents. AIDS 14: S33–S40.
Schinke, S. P., Di Noia, J., and Glassman, J. R. (2004a). Computer-mediated intervention to prevent drug abuse and violence among high-risk youth. Addict. Behav. 29: 225–229.
Schinke, S. P., and Schwinn, T. M. (2005). Gender-specific intervention for preventing drug abuse among girls: A computer-based approach. Am. J. Drug Alcohol Abuse 31:609–616.
Schinke, S. P., Schwinn, T. M., DiNoia, J., and Cole, K. C. (2004b). Reducing the risks of alcohol use among urban youth: 3-year effects of a computer-based intervention with and without parent involvement. J. Stud. Alcohol 65: 443–450.
Schinke, S. P., Schwinn, T. M., and Ozanian, A. J. (2005). Alcohol abuse prevention among high-risk youth: Computer-based intervention. J. Prev. Interv. Community 29: 117–130.
Streissguth, A. P., Bookstein, F. L., Sampson, P. D., and Barr, H. M. (1995). Attention: Prenatal alcohol and continuities of vigilance and attentional problems from 4 through 14 years. Dev. Psychopathol. 7: 419–446.
The National Center on Addiction and Substance Abuse at Columbia University (1999). Back to School 1999: National Survey of American Attitudes on Substance Abuse V: Teens and Their Parents, Author, New York.
U.S. Department of Education (2000). Progress in prevention: Report on the national study of local education agency activities under the Safe and Drug Free Schools Act (Doc. 2002–003), U.S. Dept. of Education, Office of the Under Secretary, Planning and Education Service, Rockville, MD.
Vega, W. A., and Gil, A. G. (1998). Drug use and ethnicity in early adolescence, Plenum Press, New York.
Wagenaar, A. C., Murray, D. M., Gehan, J. P., Wolfson, M., Forster, J. L., Toomey, T. L., Perry, C. L., and Jones-Webb, R. (2000). Communities mobilizing for change on alcohol: Outcomes from a randomized community trial. J. Stud. Alcohol 61: 1–11.
Williams, C. L., Perry, C. L., Farbakhsh, K., and Veblen-Mortenson, S. (1999). Project Northland: Comprehensive alcohol use prevention for young adolescents, their parents, schools, peers, and communities. J. Stud. Alcohol 13: 112–124.
ACKNOWLEDGMENT
This research was funded by research grant AA011924 from the National Institute of Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schinke, S., Schwinn, T. & Cole, K. Preventing Alcohol Abuse Among Early Adolescents Through Family and Computer-Based Interventions: Four-Year Outcomes and Mediating Variables. J Dev Phys Disabil 18, 149–161 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10882-006-9009-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10882-006-9009-5