Abstract
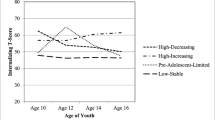
Children with disabilities tend to have higher levels of behavior problems than other children. Such problems have implications for psychopathology in the young adult years, with possible effects on life course opportunities such as employment and independent living. This investigation examines the developmental course of both internalizing and externalizing behavior problems by employing person-centered analyses to construct patterns of change in behavior problems in 169 children (54 % male) with early diagnosed disabilities, from age 3 to age 18. Early childhood predictors of these patterns indicated that more adverse patterns of both types of behavior problems were predicted by higher maternal depressive symptoms. Greater impacts on the family of having a child with a disability predicted more adverse patterns of internalizing behavior problems. More adaptive patterns of externalizing behavior problems were predicted by positive maternal sensitivity to a child’s distress. These findings suggest the need for early intervention focused on the family system.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abidin, R. R. (1990). Parenting Stress Index manual (2nd ed.). Charlottesville: Pediatric Psychology Press.
Abidin, R. R. (1995). Parenting Stress Index manual (3rd ed.). Odessa: Psychological Assessment Resources.
Achenbach, T. M. (1991). Manual for the Child Behavior Checklist/4-18 and 1991 Profile. Burlington: University of Vermont Department of Psychiatry.
Achenbach, T. M. (1992). Manual for the Child Behavior Checklist /2-3 and 1992 Profile. Burlington: University of Vermont Department of Psychiatry.
Ashman, S. B., Dawson, G., & Panagiotides, H. (2008). Trajectories of maternal depression over 7 years: Relations with child psychophysiology and behavior and role of contextual risks. Development and Psychopathology, 20, 55–77. doi:10.1017/S0954579408000035.
Bailey, D. B., Raspa, M., & Fox, L. C. (2012). What is the future of family outcomes and family-centered services? Topics in Early Childhood Special Education, 31, 216–223. doi:10.1177/0271121411427077.
Baker, B. L., Blacher, J., Crnic, K. A., & Edelbrock, C. (2002). Behavior problems and parenting stress in families of 3-year-old children with and without developmental delays. American Journal on Mental Retardation, 107, 433–444.
Baker, B. L., McIntyre, L. L., Blacher, J., Crnic, K., Edelbrock, C., & Low, C. (2003). Preschool children with and without developmental delay: Behaviour problems and parenting stress over time. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research, 47, 217–230. doi:10.1046/j.1365-2788.2003.00484.x.
Barnard, K. E. (1978). NCAST: Nursing Child Assessment Teaching Scale. Seattle: University of Washington.
Boyle, M. H., & Pickles, A. R. (1997). Influence of maternal depressive symptoms on ratings of childhood behavior. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 25, 399–412.
Carlson, E. A., Sroufe, L. A., & Egeland, B. (2004). The construction of experience: A longitudinal study of representation and behavior. Child Development, 75, 66–83.
Caspi, A., Henry, B., McGee, R. O., Moffitt, T. E., & Silva, P. A. (1995). Temperamental origins of child and adolescent behavior problems: From age three to age fifteen. Child Development, 66, 5568.
Caspi, A., Sugden, K., Moffitt, T. E., Taylor, A., Craig, I. W., Harrington, H., et al. (2003). Influence of life stress on depression: Moderation by a polymorphism in the 5-HTT gene. Science, 301, 386–389.
Cents, R. A. M., Diamantopoulou, S., Hudziak, J. J., Jaddoe, V. W. V., Hofman, A., Verhulst, F. C., & Tiemeier, H. (2013). Trajectories of maternal depressive symptoms predict child problem behaviour: The generation R study. Psychological Medicine, 43, 13–25. doi:10.1017/S0033291712000657.
Cherny, S. S., Fulker, D. W., Corley, R. P., Plomin, R., & DeFries, J. C. (1994). Continuity and change in infant shyness from 14 to 20 months. Behavior Genetics, 24, 365–379.
Chi, T. C., & Hinshaw, S. P. (2002). Mother-child relationships of children with ADHD: The role of maternal depressive symptoms and depression-related distortions. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 30, 387–400. doi:10.1023/A:1015770025043.
Cicchetti, D., & Rogosch, F. A. (1996). Equifinality and multifinality in developmental psychopathology. Development and Psychopathology, 8, 597–600.
Cicchetti, D., Rogosch, F. A., & Toth, S. L. (2000). The efficacy of toddler-parent psychotherapy for fostering cognitive development in offspring. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 28, 135–148. doi:10.1023/A:1005118713814.
Cox, M. J., & Paley, B. (2003). Understanding families as systems. Current Directions in Psychological Science, 12, 193–196. doi:10.1111/1467-8721.01259.
de Ruiter, K. P., Dekker, M. C., Verhulst, F. C., & Koot, H. M. (2007). Developmental course of psychopathology in youths with and without intellectual disabilities. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 48, 498–507. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.2006.01712.x.
Dekker, M. C., & Koot, H. M. (2003). DSM-IV disorders in children with borderline to moderate intellectual disability. I: Prevalence and impact. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 42, 915–922. doi:10.1097/01.CHI.0000046892.27264.1A.
Dekker, M. C., Koot, H. M., van der Ende, J., & Verhulst, F. C. (2002). Emotional and behavioral problems in children and adolescents with and without intellectual disability. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 43, 1087–1098. doi:10.1111/1469-7610.00235.
Dodge, K. A., & Pettit, G. S. (2003). A biopsychosocial model of the development of chronic conduct problems in adolescence. Developmental Psychology, 39, 349–371. doi:10.1037/0012-1649.39.2.349.
Downey, G., & Coyne, J. C. (1990). Children of depressed parents: An integrative review. Psychological Bulletin, 108, 50–76.
Dykens, E. M. (2000). Psychopathology in children with intellectual disability. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 41, 407–417. doi:10.1111/1469-7610.00626.
Eisenberg, N., Spinrad, T. L., & Smith, C. L. (2004). Emotion-related regulation: Its conceptualization, relations to social functioning, and socialization. In P. Philippot & R. S. Feldman (Eds.), The regulation of emotion (pp. 277–306). Mahwah: Erlbaum.
Eisenhower, A. S., Baker, B. L., & Blacher, J. (2005). Preschool children with intellectual disability: Syndrome specificity, behaviour problems, and maternal well-being. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research, 49, 657–671. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2788.2005.00699.x.
Emerson, E., Kiernan, C., Alborz, A., Reeves, D., Mason, H., Swarbrick, R., et al. (2001). The prevalence of challenging behaviors: A total population study. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 22, 77–93. doi:10.1016/S0891-4222(00)00061-5.
Fanti, K. A., & Henrich, C. C. (2010). Trajectories of pure and co-occurring internalizing and externalizing problems from age 2 to age 12: Findings from the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development study of early child care. Developmental Psychology, 46, 1159–1175. doi:10.1037/a0020659.
Fraley, R. C., Roisman, G. I., & Haltigan, J. D. (2013). The legacy of early experiences in development: Formalizing alternative models of how early experiences are carried forward over time. Developmental Psychology, 49, 109–126. doi:10.1037/a0027852.
Goodman, S. H., & Tully, E. (2008). Children of depressed mothers: Implications for the etiology, treatment, and prevention of depression in children and adolescents. In C. L. M. Keyes & S. H. Goodman (Eds.), Women and depression: A handbook for the social, behavioral, and biomedical sciences (pp. 241–282). New York: Guilford Press.
Green, V. A., O’Reilly, M., Itchon, J., & Sigafoos, J. (2005). Persistence of early emerging aberrant behavior in children with developmental disabilities. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 26, 47–55. doi:10.1016/j.ridd.2004.07.003.
Guerin, D. W., Gottfried, A. W., & Thomas, C. W. (1997). Difficult temperament and behaviour problems: A longitudinal study from 1.5 to 12 years. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 21, 71–90.
Hastings, R. P., & Taunt, H. M. (2002). Positive perceptions in families of children with developmental disabilities. American Journal on Mental Retardation, 107, 116–127.
Hauser-Cram, P., Warfield, M. E., Shonkoff, J. P., & Krauss, M. W. (2001). Children with disabilities: A longitudinal study of child development and parent well-being. Monographs of the Society for Research in Child Development, 66, 1–131. doi:10.1111/1540-5834.00151.
Hauser-Cram, P., Cannarella, A., Tillinger, M., & Woodman, A. (2013). Disabilities and development. In R. M. Lerner, A. Easterbrooks, & J. Mistry (Eds.), Developmental psychology (Handbook of psychology 2nd ed., Vol. 6, pp. 547–569). Hoboken: Wiley.
Hebbeler, K., Spiker, D., Bailey, D., Scarborough, A., Mallik, S., Simeonsson, R., et al. (2007). Early intervention for infants and toddlers with disabilities and their families: Participants, services, and outcomes: Final report of the National Early Intervention Longitudinal Study. Menlo Park: SRI International.
Hinshaw, S. P. (2002). Process, mechanism, and explanation related to externalizing behavior in developmental psychopathology. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 30, 431–446. doi:10.1023/A:1019808712868.
Hodapp, R. M., & Dykens, E. M. (2005). Measuring behavior in genetic disorders of mental retardation. Mental Retardation and Developmental Disabilities Research Reviews, 11, 340–346. doi:10.1002/mrdd.20087.
Jones, B. L., Nagin, D. S., & Roeder, K. (2001). A SAS procedure based on mixture models for estimating developmental trajectories. Sociological Methods & Research, 29, 374–393. doi:10.1177/0049124101029003005.
Kim-Cohen, J., Moffitt, T. E., Taylor, A., Pawlby, S. J., & Caspi, A. (2005). Maternal depression and children’s antisocial behavior: Nature and nurture effects. Archives of General Psychiatry, 62, 173–181.
Kok, R., Linting, M., Bakermans-Kranenburg, M., van IJzendoorn, M. H., Jaddoe, V. W. V., Hofman, A., et al. (2013). Maternal sensitivity and internalizing problems: Evidence from two longitudinal studies in early childhood. Child Psychiatry and Human Development, 44, 751–765. doi:10.1007/s10578-013-0369-7.
Kraatz Keiley, M., Bates, J. E., Dodge, K. A., & Pettit, G. S. (2000). A cross-domain growth analysis: Externalizing and internalizing behaviors during 8 years of childhood. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 28, 161–179. doi:10.1023/A:1005122814723.
Lacourse, E., Cŏté, S., Nagin, D. S., Vitaro, F., Brendgen, M., & Tremblay, R. E. (2002). A longitudinal-experimental approach to testing theories of antisocial behavior development. Development and Psychopathology, 14, 909–924. doi:10.1017/S0954579402004121.
Leadbeater, B. J., & Hoglund, W. L. G. (2009). The effects of peer victimization and physical aggression on changes in internalizing from first to third grade. Child Development, 80, 843–859. doi:10.1111/j.1467-8624.2009.01301.x.
Leaper, C. (2002). Parenting boys and girls. In M. H. Bornstein (Ed.), Children and parenting (Handbook of parenting 2nd ed., Vol. 1, pp. 189–225). Mahwah: Erlbaum.
Lovejoy, M. C., Graczyk, P. A., O’Hare, E., & Neuman, G. (2000). Maternal depression and parenting behavior: A meta-analytic review. Clinical Psychology Review, 20, 561–592.
Lowe, K., Allen, D., Jones, E., Brophy, S., Moore, K., & James, W. (2007). Challenging behaviours: Prevalence and topographies. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research, 51, 625–636. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2788.2006.00948.x.
Mathiesen, K. S., Sanson, A., Stoolmiller, M., & Karevold, E. (2009). The nature and predictors of undercontrolled and internalizing problem trajectories across early childhood. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology, 37, 209–222. doi:10.1007/s10802-008-9268-y.
McCarthy, D. (1972). McCarthy Scales of Children’s Abilities. New York: Psychological Corp.
Miner, J. L., & Clarke-Stewart, K. (2008). Trajectories of externalizing behavior from age 2 to age 9: Relations with gender, temperament, ethnicity, parenting, and rater. Developmental Psychology, 44, 771–786. doi:10.1037/0012-1649.44.3.771.
Minuchin, P. (1985). Families and individual development: Provocations from the field of family therapy. Child Development, 56, 289–302. doi:10.2307/1129720.
Muthén, B., & Muthén, L. K. (2000). Integrating person-centered and variable-centered analyses: Growth mixture modeling with latent trajectory classes. Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, 24, 882–891.
Nagin, D. S. (1999). Analyzing developmental trajectories: A semiparametric, group-based approach. Psychological Methods, 4, 139–157. doi:10.1037/1082-989X.4.2.139.
Nagin, D. S. (2005). Group-based modeling of development. Cambridge: Harvard University Press.
National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Early Child Care Research Network. (2005). Duration and timing of poverty and children’s cognitive and social development from birth through third grade. Child Development, 76, 795–810.
Neece, C. L., Green, S. A., & Baker, B. L. (2012). Parenting stress and child behavior problems: A transactional relationship across time. American Journal on Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities, 117, 48–66.
O’Connor, E. E., Dearing, E., & Collins, B. A. (2011). Teacher-child relationship and behavior problem trajectories in elementary school. American Educational Research Journal, 48, 120–162. doi:10.3102/0002831210365008.
Perry, A., Harris, K., & Minnes, P. (2004). Family environments and family harmony: An exploration across severity, age, and type of DD. Journal on Developmental Disabilities, 11, 17–29.
Petrenko, C. L. M. (2013). A review of intervention programs to prevent and treat behavioral problems in young children with developmental disabilities. Journal of Developmental and Physical Disabilities, 25, 651–679. doi:10.1007/s10882-013-9336-2.
Richters, J. E. (1992). Depressed mothers as informants about their children: A critical review of the evidence for distortion. Psychological Bulletin, 112, 485–499. doi:10.1037/00332909.112.3.485.
Sameroff, A. (2009). The transactional model. In A. Sameroff (Ed.), The transactional model of development: How children and contexts shape each other (pp. 3–21). Washington, D.C.: American Psychological Association.
Schalock, R. L., Borthwick-Duffy, S. A., Bradley, V. J., Buntinx, W. H. E., Coulter, D. L., Craig, E. M., et al. (2010). Intellectual disability: Definition, classification, and systems of support (11th Ed.). Washington, D.C: American Association on Intellectual and Developmental Disability.
Shaw, D. S., Gilliom, M., Ingoldsby, E. M., & Nagin, D. S. (2003). Trajectories leading to school-age conduct problems. Developmental Psychology, 39, 189–200. doi:10.1037/0012-1649.39.2.189.
Shaw, D. S., Lacourse, E., & Nagin, D. S. (2005). Developmental trajectories of conduct problems and hyperactivity from ages 2 to 10. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 46, 931–942. doi:10.1111/j.1469-7610.2004.00390.x.
Sparrow, S. S., Balla, D. A., & Cicchetti, D. V. (1984). The Vineland Adaptive Behavior Scales-Interview form. Circle Pines: American Guidance Service.
Stein, R. E. K., & Jessop, D. J. (2003). The impact on family scale revisited: Further psychometric data. Journal of Developmental and Behavioral Pediatrics, 24, 9–16.
Stein, R. E. K., & Reissman, C. K. (1980). The development of an impact-on-family scale: Preliminary findings. Medical Care, 18, 465–472.
Sterba, S. K., Prinstein, M. J., & Cox, M. J. (2007). Trajectories of internalizing problems across childhood: Heterogeneity, external validity, and gender differences. Development and Psychopathology, 19, 345–366. doi:10.1017/S0954579407070174.
Sumner, G. A., & Spietz, A. (1995). NCAST Caregiver/Parent-child Interaction Feeding Manual. Seattle: NCAST Publications, University of Washington, School of Nursing.
Vazsonyi, A. T., & Huang, L. (2010). Where self-control comes from: On the development of self-control and its relationship to deviance over time. Developmental Psychology, 46, 245–257. doi:10.1037/a0016538.
Widaman, K. F. (2006). Best practices in quantitative methods for developmentalists: Missing data: What to do with or without them. Monographs of the Society for Research in Child Development, 71, 42–64. doi:10.1111/j.1540-5834.2006.00404.x.
Young, J. M., & Hauser-Cram, P. (2006). Mother-child interaction as a predictor of mastery motivation in children with disabilities born preterm. Journal of Early Intervention, 28, 252–263. doi:10.1177/105381510602800402.
Acknowledgments
We thank the participants of the Early Intervention Collaborative Study. This study was supported by grant R40 MC08956 from the Maternal and Child Health Bureau (Title V, Social Security Act), Health Resources and Services Administration, U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hauser-Cram, P., Woodman, A.C. Trajectories of Internalizing and Externalizing Behavior Problems in Children with Developmental Disabilities. J Abnorm Child Psychol 44, 811–821 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-015-0055-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-015-0055-2