Abstract
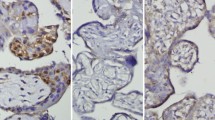
The placenta is a regulator organ for many metabolic activities between mother and fetus. Therefore, fetal growth is directly related to the placental development. Placental development is a series of events that depend on the coordinated action of trophoblasts’ proliferation, differentiation and invasion. Studies on cell cycle related proteins which control these events are fairly limited. How placental tissue proliferation is affected by diabetes is not exactly known yet. Therefore in this study, the immunohistochemical localizations of cell cycle related proteins like PCNA, Ki67, cyclin D3, p27 and p57 in the differentiation, proliferation and apoptosis mechanisms of normal and diabetic placentas were investigated. Information on cell cycle related proteins that control these events is limited and how they are affected in diabetes mellitus is not fully understood yet. Therefore, in this study, to understand the role of cell cycle regulators in diabetic placentas we aimed to determine the spatio-temporal immunolocalizations of cell cycle regulators in diabetic and normal human term placentas. Term placentas were obtained from diabetic women and from normal pregnancies with informed consent following caesarean deliveries. Placental samples were stained via immunohistochemistry with PCNA, Ki67, cyclin D3, p27 and p57 antibodies and were examined by light microscopy. When compared to control placentas, PCNA, Ki67 and cyclin D3 staining intensities significantly increased in villous parts of diabetes group. Moreover, Ki67 and cyclin D3 stainings also significantly increased in basal plates and chorionic plate respectively. In chorionic plates, p27 and p57 staining intensities significantly decreased in diabetic group. p57 staining also significantly decreased in villous parts of diabetic placentas. Placental abnormalities seen in diabetic placentas could be associated with proliferation and cell cycle arrest mechanisms’ alterations occurred in diabetes mellitus.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acar N, Korgun ET, Cayli S, Sahin Z, Demir R, Ustunel I (2008) Is there a relationship between PCNA expression and diabetic placental development during pregnancy? Acta Histochem 110(5):408–417
Alemzadeh RWD (2004) Diabetes Mellitus. In: Behrman RE, Kliegman RM, Jenson HB (eds) Nelson textbook of pediatrics, 17th edn. Elsevier Saunders, Pennsylvania, pp 1947–1972
Bacus S, Flowers JL, Press MF, Bacus JW, McCarty KS Jr (1988) The evaluation of estrogen receptor in primary breast carcinoma by computer-assisted image analysis. Am J Clin Pathol 90(3):233–239
Bamberger A, Sudahl S, Bamberger CM, Schulte HM, Loning T (1999) Expression patterns of the cell-cycle inhibitor p27 and the cell-cycle promoter cyclin E in the human placenta throughout gestation: implications for the control of proliferation. Placenta 20(5–6):401–406
Benirschke K, Kaufmann P, Baergen RN (2006) Pathology of the human placenta, 5th edn. Springer, New York
Black SM, DeVol JM, Wedgwood S (2008) Regulation of fibroblast growth factor-2 expression in pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells involves increased reactive oxygen species generation. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 294(1):C345–C354
Bravo R, Macdonald-Bravo H (1987) Existence of two populations of cyclin/proliferating cell nuclear antigen during the cell cycle: association with DNA replication sites. J Cell Biol 105(4):1549–1554
Burant CF (2004) Medical management of type two diabetes, 5th edn. McGraw-Hill, New York
Burleigh DW, Stewart K, Grindle KM, Kay HH, Golos TG (2004) Influence of maternal diabetes on placental fibroblast growth factor-2 expression, proliferation, and apoptosis. J Soc Gynecol Investig 11(1):36–41
Charnock-Jones DS, Kaufmann P, Mayhew TM (2004) Aspects of human fetoplacental vasculogenesis and angiogenesis. I. Molecular regulation. Placenta 25(2–3):103–113
Danihel L, Gomolcak P, Korbel M, Pruzinec J, Vojtassak J, Janik P, Babal P (2002) Expression of proliferation and apoptotic markers in human placenta during pregnancy. Acta Histochem 104(4):335–338
De Falco M, Fedele V, Cobellis L, Mastrogiacomo A, Giraldi D, Leone S, De Luca L, Laforgia V, De Luca A (2004) Pattern of expression of cyclin D1/CDK4 complex in human placenta during gestation. Cell Tissue Res 317(2):187–194
Desoye G, Shafrir E (1996) The human placenta in diabetic pregnancy. Diabet Rev 4:70–89
Evers IM, Nikkels PG, Sikkema JM, Visser GH (2003) Placental pathology in women with type 1 diabetes and in a control group with normal and large-for-gestational-age infants. Placenta 24(8–9):819–825
Fox H (1969) Pathology of the placenta in maternal diabetes mellitus. Obstet Gynecol 34(6):792–798
Frohlich JD, Huppertz B, Abuja PM, Konig J, Desoye G (2012) Oxygen modulates the response of first-trimester trophoblasts to hyperglycemia. Am J Pathol 180(1):153–164
Fukunaga M (2002) Immunohistochemical characterization of p57(KIP2) expression in early hydatidiform moles. Hum Pathol 33(12):1188–1192
Genbacev O, McMaster MT, Fisher SJ (2000) A repertoire of cell cycle regulators whose expression is coordinated with human cytotrophoblast differentiation. Am J Pathol 157(4):1337–1351
Gerdes J, Lemke H, Baisch H, Wacker HH, Schwab U, Stein H (1984) Cell cycle analysis of a cell proliferation-associated human nuclear antigen defined by the monoclonal antibody Ki-67. J Immunol 133(4):1710–1715
Hiden U, Glitzner E, Ivanisevic M, Djelmis J, Wadsack C, Lang U, Desoye G (2008) MT1-MMP expression in first-trimester placental tissue is upregulated in type 1 diabetes as a result of elevated insulin and tumor necrosis factor-alpha levels. Diabetes 57(1):150–157
Inadera H, Tachibana S, Takasaki I, Tatematsu M, Shimomura A (2010) Hyperglycemia perturbs biochemical networks in human trophoblast BeWo cells. Endocr J 57(7):567–577
Jansson T, Ekstrand Y, Bjorn C, Wennergren M, Powell TL (2002) Alterations in the activity of placental amino acid transporters in pregnancies complicated by diabetes. Diabetes 51(7):2214–2219
Jaskulski D, Gatti C, Travali S, Calabretta B, Baserga R (1988) Regulation of the proliferating cell nuclear antigen cyclin and thymidine kinase mRNA levels by growth factors. J Biol Chem 263(21):10175–10179
Jones CJ, Fox H (1976) An ultrastructural and ultrahistochemical study of the placenta of the diabetic woman. J Pathol 119(2):91–99
Josko J, Mazurek M (2004) Transcription factors having impact on vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) gene expression in angiogenesis. Med Sci Monit 10(4):RA89–RA98
Kiyokawa H, Kineman RD, Manova-Todorova KO, Soares VC, Hoffman ES, Ono M, Khanam D, Hayday AC, Frohman LA, Koff A (1996) Enhanced growth of mice lacking the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor function of p27(Kip1). Cell 85(5):721–732
Korgun ET, Celik-Ozenci C, Acar N, Cayli S, Desoye G, Demir R (2006) Location of cell cycle regulators cyclin B1, cyclin A, PCNA, Ki67 and cell cycle inhibitors p21, p27 and p57 in human first trimester placenta and deciduas. Histochem Cell Biol 125(6):615–624
Kuhl C (1975) Glucose metabolism during and after pregnancy in normal and gestational diabetic women. 1. Influence of normal pregnancy on serum glucose and insulin concentration during basal fasting conditions and after a challenge with glucose. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 79(4):709–719
Kuruvilla AG, D’Souza SW, Glazier JD, Mahendran D, Maresh MJ, Sibley CP (1994) Altered activity of the system A amino acid transporter in microvillous membrane vesicles from placentas of macrosomic babies born to diabetic women. J Clin Invest 94(2):689–695
Laurini RN, Visser GH, van Ballegooie E, Schoots CJ (1987) Morphological findings in placentae of insulin-dependent diabetic patients treated with continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII). Placenta 8(2):153–165
Leach L, Gray C, Staton S, Babawale MO, Gruchy A, Foster C, Mayhew TM, James DK (2004) Vascular endothelial cadherin and beta-catenin in human fetoplacental vessels of pregnancies complicated by Type 1 diabetes: associations with angiogenesis and perturbed barrier function. Diabetologia 47(4):695–709
Leushner JR, Tevaarwerk GJ, Clarson CL, Harding PG, Chance GW, Haust MD (1986) Analysis of the collagens of diabetic placental villi. Cell Mol Biol 32(1):27–35
Levy R, Smith SD, Yusuf K, Huettner PC, Kraus FT, Sadovsky Y, Nelson DM (2002) Trophoblast apoptosis from pregnancies complicated by fetal growth restriction is associated with enhanced p53 expression. Am J Obstet Gynecol 186(5):1056–1061
Madsen H, Ditzel J (1984) Blood-oxygen transport in first trimester of diabetic pregnancy. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 63(4):317–320
Mandl M, Haas J, Bischof P, Nohammer G, Desoye G (2002) Serum-dependent effects of IGF-I and insulin on proliferation and invasion of human first trimester trophoblast cell models. Histochem Cell Biol 117(5):391–399
Maruo T, Ishihara N, Samoto T, Murakoshi H, Laoag-Fernandez JB, Matsuo H (2001) Regulation of human trophoblast proliferation and apoptosis during pregnancy. Early Pregnancy 5(1):28–29
Matsuoka S, Edwards MC, Bai C, Parker S, Zhang P, Baldini A, Harper JW, Elledge SJ (1995) p57KIP2, a structurally distinct member of the p21CIP1 Cdk inhibitor family, is a candidate tumor suppressor gene. Genes Dev 9(6):650–662
Nakayama K, Ishida N, Shirane M, Inomata A, Inoue T, Shishido N, Horii I, Loh DY (1996) Mice lacking p27(Kip1) display increased body size, multiple organ hyperplasia, retinal dysplasia, and pituitary tumors. Cell 85(5):707–720
Olvera M, Harris S, Amezcua CA, McCourty A, Rezk S, Koo C, Felix JC, Brynes RK (2001) Immunohistochemical expression of cell cycle proteins E2F-1, Cdk-2, Cyclin E, p27(kip1), and Ki-67 in normal placenta and gestational trophoblastic disease. Mod Pathol 14(10):1036–1042
Ozbey O, Sahin Z, Ozenci AM, Acar N, Ustunel I (2010) The effect of systemic corticosteroid treatment on the immunolocalisation of Notch-1, Delta, CD105 and CD166 in rat articular cartilage. Acta Histochem 112(5):424–431
Padmanabhan R, Shafiullah M (2001) Intrauterine growth retardation in experimental diabetes: possible role of the placenta. Arch Physiol Biochem 109(3):260–271
Pickup JC, Williams G (1997) Textbook of diabetes, vol 1, 2nd edn. Blackwell Science, Oxford
Pollard D, Earnshaw C (2002) Cell biology, 1st edn. Saunders, Philadelphia
Salge AK, Rocha KM, Xavier RM, Ramalho WS, Rocha EL, Guimaraes JV, Silva RC, Siqueira KM, Abdalla DR, Michelin MA, Murta EF (2012) Macroscopic placental changes associated with fetal and maternal events in diabetes mellitus. Clinics (Sao Paulo) 67(10):1203–1208
Scholzen T, Gerdes J (2000) The Ki-67 protein: from the known and the unknown. J Cell Physiol 182(3):311–322
Scott M, Bonnefin P, Vieyra D, Boisvert FM, Young D, Bazett-Jones DP, Riabowol K (2001) UV-induced binding of ING1 to PCNA regulates the induction of apoptosis. J Cell Sci 114(Pt 19):3455–3462
Sgarbosa F, Barbisan LF, Brasil MA, Costa E, Calderon IM, Goncalves CR, Bevilacqua E, Rudge MV (2006) Changes in apoptosis and Bcl-2 expression in human hyperglycemic, term placental trophoblast. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 73(2):143–149
Shams F, Rafique M, Samoo NA, Irfan R (2012) Fibrinoid necrosis and hyalinization observed in normal, diabetic and hypertensive placentae. J Coll Phys Surg Pak 22(12):769–772
Sherer DM, Divon MY (1996) Prenatal ultrasonographic assessment of the ductus arteriosus: a review. Obstet Gynecol 87(4):630–637
Smith SC, Price E, Hewitt MJ, Symonds EM, Baker PN (1998) Cellular proliferation in the placenta in normal human pregnancy and pregnancy complicated by intrauterine growth restriction. J Soc Gynecol Investig 5(6):317–323
Start RD, Cross SS, Clelland C, Silcocks PB, Rogers K, Smith JH (1992) Delay in fixation does not affect the immunoreactivity of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA). J Pathol 168(2):197–199
Sutton LN, Mason DY, Redman CW (1989) Isolation and characterization of human fetal macrophages from placenta. Clin Exp Immunol 78(3):437–443
Takahashi T, Caviness VS Jr (1993) PCNA-binding to DNA at the G1/S transition in proliferating cells of the developing cerebral wall. J Neurocytol 22(12):1096–1102
Taricco E, Radaelli T, Nobile de Santis MS, Cetin I (2003) Foetal and placental weights in relation to maternal characteristics in gestational diabetes. Placenta 24(4):343–347
Teasdale F (1981) Histomorphometry of the placenta of the diabetic women: class A diabetes mellitus. Placenta 2(3):241–251
Van Assche FA, Holemans K, Aerts L (2001) Long-term consequences for offspring of diabetes during pregnancy. Br Med Bull 60:173–182
Varastehpour A, Radaelli T, Minium J, Ortega H, Herrera E, Catalano P, Hauguel-de Mouzon S (2006) Activation of phospholipase A2 is associated with generation of placental lipid signals and fetal obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 91(1):248–255
Weinberg RA (1991) Tumor suppressor genes. Science 254(5035):1138–1146
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Research Foundation of Akdeniz University, Antalya, Turkey (project number: 2008.02.0122.008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Unek, G., Ozmen, A., Mendilcioglu, I. et al. Immunohistochemical distribution of cell cycle proteins p27, p57, cyclin D3, PCNA and Ki67 in normal and diabetic human placentas. J Mol Hist 45, 21–34 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-013-9534-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-013-9534-3