Abstract
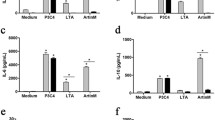
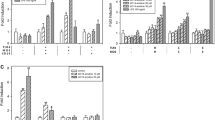
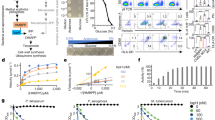
The signaling pathways of mammalian Toll-like receptors (TLR) are well characterized, but the initial molecular mechanisms activated following ligand interactions with the receptors remain poorly defined. Here, we show a membrane controlling mechanism that is initiated by ligand binding to TLR-2, -3 and-4 to induce Neu1 sialidase activity within minutes in live primary bone marrow (BM) macrophage cells and macrophage and dendritic cell lines. Central to this process is that Neu1 and not Neu2,-3 and-4 forms a complex with TLR-2,-3 and-4 on the cell surface of naïve macrophage cells. Neuraminidase inhibitors BCX1827, 2-deoxy-2,3-dehydro-N-acetylneuraminic acid (DANA), zanamivir and oseltamivir carboxylate have a limited significant inhibition of the LPS-induced sialidase activity in live BMC-2 macrophage cells but Tamiflu (oseltamivir phosphate) completely blocks this activity. Tamiflu inhibits LPS-induced sialidase activity in live BMC-2 cells with an IC50 of 1.2 μM compared to an IC50 of 1015 μM for its hydrolytic metabolite oseltamivir carboxylate. Tamiflu blockage of LPS-induced Neu1 sialidase activity is not affected in BMC-2 cells pretreated with anticarboxylesterase agent clopidogrel. Endotoxin LPS binding to TLR4 induces Neu1 with subsequent activation of NFκB and the production of nitric oxide and pro-inflammatory IL-6 and TNFα cytokines in primary and macrophage cell lines. Hypomorphic cathepsin A mice with a secondary Neu1 deficiency respond poorly to LPS-induced pro-inflammatory cytokines compared to the wild-type or hypomorphic cathepsin A with normal Neu1 mice. Our findings establish an unprecedented mechanism for pathogen molecule-induced TLR activation and cell function, which is critically dependent on Neu1 sialidase activity associated with TLR ligand treated live primary macrophage cells and macrophage and dendritic cell lines.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- (TLR):
-
Toll-like receptors
- (PAMPS):
-
pathogen-associated molecular patterns
- (oseltamivir phosphate):
-
Tamiflu
- (DANA):
-
2-deoxy-2,3-dehydro-N-acetylneuraminic acid
- (IL-6):
-
interleukin-6
- (TNFα):
-
tumor necrosis factor
- (LPS):
-
lipopolysaccride
- (IC50):
-
50% inhibition concentration
- (ECD):
-
ectodomain
- (poly:IC):
-
polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid
- (TS):
-
T. cruzi trans-sialidase
- (BM):
-
bone marrow
- (M-CSF):
-
monocyte colony-stimulating factor
- (4-MUNANA (4-MU)):
-
[2′-(4-methylumbelliferyl)-α-N-acetylneuraminic acid]
- (PVDF):
-
polyvinylidene fluoride
- (NO):
-
nitric oxide
- (Neu1-CathA KD):
-
hypomorphic cathepsin A mice with the secondary ~90% reduction of the Neu1 activity
- (CathA KI):
-
normal Neu1 sialidase bound to inactive cathepsin A Ser190Ala mutant
- (Neu4 KO):
-
Neu4 knockout
References
Choe, J., Kelker, M.S., Wilson, I.A.: Crystal structure of human toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) ectodomain. Science 309, 581–585 (2005). doi:10.1126/science.1115253
Bell, J.K., Botos, I., Hall, P.R., Askins, J., Shiloach, J., Segal, D.M., Davies, D.R.: The molecular structure of the Toll-like receptor 3 ligand-binding domain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102, 10976–10980 (2005). doi:10.1073/pnas.0505077102
Miggin, S.M., O’Neill, L.A.: New insights into the regulation of TLR signaling. J. Leukoc. Biol 80, 220–226 (2006). doi:10.1189/jlb.1105672
Sun, J., Duffy, K.E., Ranjith-Kumar, C.T., Xiong, J., Lamb, R.J., Santos, J., Masarapu, H., Cunningham, M., Holzenburg, A., Sarisky, R.T., Mbow, M.L., Kao, C.: Structural and functional analyses of the human Toll-like receptor 3. Role of glycosylation. J. Biol. Chem 281, 11144–11151 (2006). doi:10.1074/jbc.M510442200
Leonard, J.N., Ghirlando, R., Askins, J., Bell, J.K., Margulies, D.H., Davies, D.R., Segal, D.M.: The TLR3 signaling complex forms by cooperative receptor dimerization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105, 258–263 (2008). doi:10.1073/pnas.0710779105
Weber, A.N., Morse, M.A., Gay, N.J.: Four N-linked glycosylation sites in human toll-like receptor 2 cooperate to direct efficient biosynthesis and secretion. J. Biol. Chem 279, 34589–34594 (2004). doi:10.1074/jbc.M403830200
da Silva, C.J., Ulevitch, R.J.: MD-2 and TLR4 N-linked glycosylations are important for a functional lipopolysaccharide receptor. J. Biol. Chem 277, 1845–1854 (2002). doi:10.1074/jbc.M109910200
Watson, F.L., Porcionatto, M.A., Bhattacharyya, A., Stiles, C.D., Segal, R.A.: TrkA glycosylation regulates receptor localization and activity. J. Neurobiol 39, 323–336 (1999). doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4695(199905)39:2<323::AID-NEU15>3.0.CO;2-4
Woronowicz, A., Amith, S.R., De Vusser, K., Laroy, W., Contreras, R., Basta, S., Szewczuk, M.R.: Dependence of Neurotrophic Factor Activation of Trk Tyrosine Kinase Receptors on Cellular Sialidase. Glycobiology 17, 10–24 (2007). doi:10.1093/glycob/cwl049
Woronowicz, A., Amith, S.R., Davis, V.W., Jayanth, P., De Vusser, K., Laroy, W., Contreras, R., Meakin, S.O., Szewczuk, M.R.: Trypanosome trans-sialidase mediates neuroprotection against oxidative stress, serum/glucose deprivation, and hypoxia-induced neurite retraction in Trk-expressing PC12 cells. Glycobiology 17, 725–734 (2007). doi:10.1093/glycob/cwm034
Woronowicz, A., De Vusser, K., Laroy, W., Contreras, R., Meakin, S.O., Ross, G.M., Szewczuk, M.R.: Trypanosome trans-sialidase targets TrkA tyrosine kinase receptor and induces receptor internalization and activation. Glycobiology 14, 987–998 (2004). doi:10.1093/glycob/cwh123
Kovacsovics-Bankowski, M., Rock, K.L.: Presentation of exogenous antigens by macrophages: analysis of major histocompatibility complex class I and II presentation and regulation by cytokines. Eur. J. Immunol 24, 2421–2428 (1994). doi:10.1002/eji.1830241024
Shen, Z., Reznikoff, G., Dranoff, G., Rock, K.L.: Cloned dendritic cells can present exogenous antigens on both MHC class I and class II molecules. J. Immunol 158, 2723–2730 (1997)
Alatery, A., Basta, S.: An efficient culture method for generating large quantities of mature mouse splenic macrophages. J. Immunol. Methods 338, 47–57 (2008). doi:10.1016/j.jim.2008.07.009
Werling, D., Hope, J.C., Howard, C.J., Jungi, T.W.: Differential production of cytokines, reactive oxygen and nitrogen by bovine macrophages and dendritic cells stimulated with Toll-like receptor agonists. Immunology 111, 41–52 (2004). doi:10.1111/j.1365-2567.2004.01781.x
Lundberg, A.M., Drexler, S.K., Monaco, C., Williams, L.M., Sacre, S.M., Feldmann, M., Foxwell, B.M.: Key differences in TLR3/poly I:C signaling and cytokine induction by human primary cells: a phenomenon absent from murine cell systems. Blood 110, 3245–3252 (2007). doi:10.1182/blood-2007-02-072934
Hata, K., Koseki, K., Yamaguchi, K., Moriya, S., Suzuki, Y., Yingsakmongkon, S., Hirai, G., Sodeoka, M., von Itzstein, M., Miyagi, T.: Limited inhibitory effects of oseltamivir and zanamivir on human sialidases. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother 52, 3484–3491 (2008). doi:10.1128/AAC.00344-08
Nan, X., Carubelli, I., Stamatos, N.M.: Sialidase expression in activated human T lymphocytes influences production of IFN-gamma. J. Leukoc. Biol 81, 284–296 (2007). doi:10.1189/jlb.1105692
Mendel, D.B., Tai, C.Y., Escarpe, P.A., Li, W., Sidwell, R.W., Huffman, J.H., Sweet, C., Jakeman, K.J., Merson, J., Lacy, S.A., Lew, W., Williams, M.A., Zhang, L., Chen, M.S., Bischofberger, N., Kim, C.U.: Oral administration of a prodrug of the influenza virus neuraminidase inhibitor GS 4071 protects mice and ferrets against influenza infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother 42, 640–646 (1998)
Shi, D., Yang, J., Yang, D., LeCluyse, E.L., Black, C., You, L., Akhlaghi, F., Yan, B.: Anti-influenza prodrug oseltamivir is activated by carboxylesterase human carboxylesterase 1, and the activation is inhibited by antiplatelet agent clopidogrel. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther 319, 1477–1484 (2006). doi:10.1124/jpet.106.111807
Morimoto, K., Nakakariya, M., Shirasaka, Y., Kakinuma, C., Fujita, T., Tamai, I., Ogihara, T.: Oseltamivir (Tamiflu) efflux transport at the blood-brain barrier via P-glycoprotein. Drug Metab. Dispos 36, 6–9 (2008). doi:10.1124/dmd.107.017699
Miyagi, T., Sagawa, J., Konno, K., Tsuiki, S.: Immunological discrimination of intralysosomal, cytosolic, and two membrane sialidases present in rat tissues. J. Biochem 107, 794–798 (1990)
Lukong, K.E., Elsliger, M.A., Chang, Y., Richard, C., Thomas, G., Carey, W., Tylki-Szymanska, A., Czartoryska, B., Buchholz, T., Criado, G.R., Palmeri, S., Pshezhetsky, A.V.: Characterization of the sialidase molecular defects in sialidosis patients suggests the structural organization of the lysosomal multienzyme complex. Hum. Mol. Genet 9, 1075–1085 (2000). doi:10.1093/hmg/9.7.1075
Feng, L., Seyrantepe, V., Landry, K., Ahmad, R., Ahmad, A., Stamatos, N.M., Pshezhetsky, A.V.: Monocyte differentiation upregulates the expression of the lysosomal sialidase, neu1 and triggers its targeting to the plasma membrane via MHC class II-positive compartments. J. Biol. Chem 281, 27526–27538 (2006). doi:10.1074/jbc.M605633200
Yogalingam, G., Bonten, E.J., van de Vlekkert, D., Hu, H., Moshiach, S., Connell, S.A., d’Azzo, A.: Neuraminidase 1 is a negative regulator of lysosomal exocytosis. Dev. Cell 15, 74–86 (2008). doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2008.05.005
Hinek, A., Pshezhetsky, A.V., Von, I.M., Starcher, B.: Lysosomal sialidase (neuraminidase-1) is targeted to the cell surface in a multiprotein complex that facilitates elastic fiber assembly. J. Biol. Chem 281, 3698–3710 (2006). doi:10.1074/jbc.M508736200
Duca, L., Blanchevoye, C., Cantarelli, B., Ghoneim, C., Dedieu, S., Delacoux, F., Hornebeck, W., Hinek, A., Martiny, L., Debelle, L.: The elastin receptor complex transduces signals through the catalytic activity of its Neu-1 subunit. J. Biol. Chem 282, 12484–12491 (2007). doi:10.1074/jbc.M609505200
Starcher, B., d’Azzo, A., Keller, P. W., Rao, G. K., Nadarajah, D., and Hinek, A.: Neuraminidase-1 is Required for the Normal Assembly of Elastic Fibers. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol (2008)
Rodriguez, J.A., Piddini, E., Hasegawa, T., Miyagi, T., Dotti, C.G.: Plasma membrane ganglioside sialidase regulates axonal growth and regeneration in hippocampal neurons in culture. J. Neurosci 21, 8387–8395 (2001)
Sasaki, A., Hata, K., Suzuki, S., Sawada, M., Wada, T., Yamaguchi, K., Obinata, M., Tateno, H., Suzuki, H., Miyagi, T.: Overexpression of plasma membrane-associated sialidase attenuates insulin signaling in transgenic mice. J. Biol. Chem 278, 27896–27902 (2003). doi:10.1074/jbc.M212200200
Papini, N., Anastasia, L., Tringali, C., Croci, G., Bresciani, R., Yamaguchi, K., Miyagi, T., Preti, A., Prinetti, A., Prioni, S., Sonnino, S., Tettamanti, G., Venerando, B., Monti, E.: The plasma membrane-associated sialidase MmNEU3 modifies the ganglioside pattern of adjacent cells supporting its involvement in cell-to-cell interactions. J. Biol. Chem 279, 16989–16995 (2004). doi:10.1074/jbc.M400881200
Yamaguchi, K., Hata, K., Koseki, K., Shiozaki, K., Akita, H., Wada, T., Moriya, S., Miyagi, T.: Evidence for mitochondrial localization of a novel human sialidase (NEU4). Biochem. J 390, 85–93 (2005). doi:10.1042/BJ20050017
Seyrantepe, V., Poupetova, H., Froissart, R., Zabot, M.T., Maire, I., Pshezhetsky, A.V.: Molecular pathology of NEU1 gene in sialidosis. Hum. Mutat 22, 343–352 (2003). doi:10.1002/humu.10268
Seyrantepe, V., Hinek, A., Peng, J., Fedjaev, M., Ernest, S., Kadota, Y., Canuel, M., Itoh, K., Morales, C.R., Lavoie, J., Tremblay, J., Pshezhetsky, A.V.: Enzymatic activity of lysosomal carboxypeptidase (cathepsin) A is required for proper elastic fiber formation and inactivation of endothelin-1. Circulation 117, 1973–1981 (2008). doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.733212
Seyrantepe, V., Canuel, M., Carpentier, S., Landry, K., Durand, S., Liang, F., Zeng, J., Caqueret, A., Gravel, R.A., Marchesini, S., Zwingmann, C., Michaud, J., Morales, C.R., Levade, T., Pshezhetsky, A.V.: Mice deficient in Neu4 sialidase exhibit abnormal ganglioside catabolism and lysosomal storage. Hum. Mol. Genet 17, 1556–1568 (2008). doi:10.1093/hmg/ddn043
Kacergius, T., Ambrozaitis, A., Deng, Y., Gravenstein, S.: Neuraminidase inhibitors reduce nitric oxide production in influenza virus-infected and gamma interferon-activated RAW 264.7 macrophages. Pharmacol. Rep 58, 924–930 (2006)
Latz, E., Verma, A., Visintin, A., Gong, M., Sirois, C.M., Klein, D.C., Monks, B.G., McKnight, C.J., Lamphier, M.S., Duprex, W.P., Espevik, T., Golenbock, D.T.: Ligand-induced conformational changes allosterically activate Toll-like receptor 9. Nat. Immunol 8, 772–779 (2007). doi:10.1038/ni1479
Haas, T., Metzger, J., Schmitz, F., Heit, A., Muller, T., Latz, E., Wagner, H.: The DNA sugar backbone 2' deoxyribose determines toll-like receptor 9 activation. Immunity 28, 315–323 (2008). doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2008.01.013
Ewald, S.E., Lee, B.L., Lau, L., Wickliffe, K.E., Shi, G.P., Chapman, H.A., Barton, G.M.: The ectodomain of Toll-like receptor 9 is cleaved to generate a functional receptor. Nature 456, 658–662 (2008). doi:10.1038/nature07405
Chen, X.P., Enioutina, E.Y., Daynes, R.A.: The control of IL-4 gene expression in activated murine T lymphocytes: a novel role for neu-1 sialidase. J. Immunol 158, 3070–3080 (1997)
Ohnishi, T., Muroi, M., Tanamoto, K.: N-linked glycosylations at Asn(26) and Asn(114) of human MD-2 are required for toll-like receptor 4-mediated activation of NF-kappaB by lipopolysaccharide. J. Immunol 167, 3354–3359 (2001)
Qiu, X.T., Li, Y.H., Li, H., Yu, Y., Zhang, Q.: Molecular cloning, mapping, and tissue expression of the porcine cluster of differentiation 14 (CD14) gene. Biochem. Genet 45, 459–468 (2007). doi:10.1007/s10528-007-9088-8
Acknowledgements
These studies are partially supported by grants to MRS from Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC), the Harry Botterell Foundation for Neuroscience Research, ARC, and the Garfield Kelly Cardiovascular Research and Development Fund. S.R.A. is a recipient of the Queen’s University Research Award, the Robert J. Wilson Fellowship and the Ontario Graduate Scholarship. P.J. is a recipient of the Queen’s Graduate Award and the Robert J. Wilson Fellowship. SF is a recipient of the Ontario Graduate Scholarship in Science and Technology (OGSST). Work on KD mice is supported by grant to A.V.P. from Canadian Institutes of Health (CIHR). Research work on the TLR transfected cell lines is supported by grants to R.B. from the ‘Interuniversitaire Attractiepolen’ (IAP6/18), the ‘Fonds voor Wetenschappelijk Onderzoek-Vlaanderen’ (FWO; grant 3G010505), and the ‘Geconcerteerde Onderzoeksacties’ of the Ghent University (GOA; grant 01G06B6).
Author Contributions M.R.S. and S.R.A. wrote the paper, designed and performed experiments; P.J. performed the WB and EMSA blots; S.F. did the neuraminidase inhibitor studies; S.S. performed the NO experiments; V.S. generated Neu1-deficient, Neu1-CathA, Neu4 KO mice; K.G., S.B., R.B. and A.V.P. helped with experiments and writing the paper; M.R.S. supervised the research design and the writing of the paper. All authors read and commented on the manuscript, and declare no competing financial interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Amith, S., Jayanth, P., Franchuk, S. et al. Dependence of pathogen molecule-induced Toll-like receptor activation and cell function on Neu1 sialidase. Glycoconj J 26, 1197–1212 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-009-9239-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-009-9239-8