Abstract
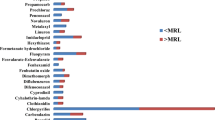
Fruit samples of ber, grapes and guava analysed for pesticide residues employing multiresidue analysis by gas liquid chromatography equipped with ECD and NPD detectors and capillary columns showed contamination with organochlorine, synthetic pyrethroid and organophosphate insecticides. Among organochlorines, HCH, DDT and endosulfan were detected in almost all the samples. Residues of HCH and DDT were maximum in ber followed by grapes and guava where as of endosulfan were maximum in guava followed by grapes and ber. All the fruit samples showed the presence of residues with one or the other group of pesticides. Residues of none of the pesticides exceeded the MRL values in any sample. On the basis of these studies, it is suggested that monitoring studies should be extended to other fruits grown in different agro climatic regions which may serve as basis for future policy in chemical use.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agnihotri, N. P.: 1999, Pesticide Safety Evaluation and Monitoring. Division of Agriculture Chemicals, Indian Agricultural Research Institute, New Delhi p. 14.
Atuma, S. S.: 1985, ‘Residues of organochlorine pesticides in some Nigerian food material’, Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 35, 735–738.
FAO/WHO: 1996, Joint Food Standards Programme, Codex Alimentarius Commission, Codex Committee and Pesticide Residues, Rome'. Vol. 213, 2nd ed.
Frank, R., Braun, H. E. and Ripley, B. D.: 1987, ‘Residues of insecticides, fungicides and herbicides in fruit produced in Ontario, Canada, 1980–1984’, Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 39, 272–279.
Kaphalia, B. S., Takroo, R., Mehrotra, S., Nigamu, and Seth, T. D.: 1990, ‘Organochlorine pesticide residues in different Indian cereals, pulses, vegetables, spices, fruits, milk, butter, desi ghee and edible oil’, JAOAC 73, 509–512.
Kumari, B., Singh, R., Madan, V. K., Kumar, R. and Kathpal, T. S.: 1996, ‘DDT and HCH Compounds in soils, ponds and drinking water of Haryana, India’, Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 57(5), 787–793.
Kumari, B., Kumar. R. and Kathpal, T. S.: 2001, ‘An improved multi-residue procedure for determination of pesticides in vegetables’, Pesticide. Res. J. 13(1), 32–35.
Kumari, B., Madan, V. K., Kumar, R. and Kathpal, T. S.: 2002, ‘Monitoring of seasonal vegetables for pesticide residues’, Environ. Monit. Assess. 74, 263–270.
Kumari, B., Singh, R., Madan, V. K., Kumar, R., Kathpal, T. S. and Singh, J.: 2003, ‘Magnitude of pesticidal contamination in winter vegetables from Hisar, Haryana’, Environ. Monit. Assess. 87, 311–318.
Lal, R., Dhanraj, P. S. and Narayana Rao, V. V. S.: 1989, ‘Residues of organochlorine insecticides in Delhi vegetables’, Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 42, 45–49.
Perez Bendito, D. and Rubio, S.: In: Environmental Analytical Chemistry. (Volume XXXII Comprehensive Analytical Chemistry): Elseveir: Amsterdam.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumari, B., Madan, V.K. & Kathpal, T.S. Monitoring of Pesticide Residues in Fruits. Environ Monit Assess 123, 407–412 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-1493-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-006-1493-7