Abstract
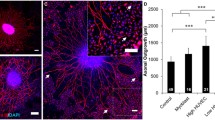
Several mitogens such as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) have been implicated in mammalian vascular proliferation and repair. However, the molecular mediators of human blood-nerve barrier (BNB) development and specialization are unknown. Primary human endoneurial endothelial cells (pHEndECs) were expanded in vitro and specific mitogen receptors detected by western blot. pHEndECs were cultured with basal medium containing different mitogen concentrations with or without heparin. Non-radioactive cell proliferation, Matrigel™-induced angiogenesis and sterile micropipette injury wound healing assays were performed. Proliferation rates, number and total length of induced microvessels, and rate of endothelial cell monolayer wound healing were determined and compared to basal conditions. VEGF-A165 in the presence of heparin, was the most potent inducer of pHEndEC proliferation, angiogenesis, and wound healing in vitro. 1.31 nM VEGF-A165 induced ~110 % increase in cell proliferation relative to basal conditions (∼51 % without heparin). 2.62 pM VEGF-A165 induced a three-fold increase in mean number of microvessels and 3.9-fold increase in total capillary length/field relative to basal conditions. In addition, 0.26 nM VEGF-A165 induced ∼1.3-fold increased average rate of endothelial wound healing 4–18 h after endothelial monolayer injury, mediated by increased cell migration. VEGF-A165 was the only mitogen capable of complete wound closure, occurring within 30 h following injury via increased cell proliferation. This study demonstrates that VEGF-A165, in the presence of heparin, is a potent inducer of pHEndEC proliferation, angiogenesis, and wound healing in vitro. VEGF-A165 may be an important mitogen necessary for human BNB development and recovery in response to peripheral nerve injury.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe M, Sano Y, Maeda T, Shimizu F, Kashiwamura Y, Haruki H, Saito K, Tasaki A, Kawai M, Terasaki T, Kanda T (2012) Establishment and characterization of human peripheral nerve microvascular endothelial cell lines: a new in vitro blood-nerve barrier (BNB) model. Cell Struct Funct 37(2):89–100
Aird W (2007a) Phenotypic heterogeneity of the endothelium: I. structure, function, and mechanisms. Circ Res 100(2):158–173
Aird W (2007b) Phenotypic heterogeneity of the endothelium: II. Representative vascular beds. Circ Res 100(2):174–190
Al Ahmad A, Gassmann M, Ogunshola O (2009) Maintaining blood-brain barrier integrity: pericytes perform better than astrocytes during prolonged oxygen deprivation. J Cell Physiol 218(3):612–622. doi:10.1002/jcp.21638
Allt G, Lawrenson J (2000) The blood-nerve barrier: enzymes, transporters and receptors–a comparison with the blood-brain barrier. Brain Res Bull 52(1):1–12
Arai K, Jin G, Navaratna D, Lo E (2009) Brain angiogenesis in developmental and pathological processes: neurovascular injury and angiogenic recovery after stroke. FEBS J 276(17):4644–4652. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07176.x
Ashikari-Hada S, Habuchi H, Kariya Y, Kimata K (2005) Heparin regulates vascular endothelial growth factor165-dependent mitogenic activity, tube formation, and its receptor phosphorylation of human endothelial cells. Comparison of the effects of heparin and modified heparins. J Biol Chem 280(36):31508–31515. doi:10.1074/jbc.M414581200
Bell M, Weddell A (1984a) A descriptive study of the blood vessels of the sciatic nerve in the rat, man and other mammals. Brain 107(Pt 3):871–898
Bell M, Weddell A (1984b) A morphometric study of intrafascicular vessels of mammalian sciatic nerve. Muscle Nerve 7(7):524–534
Bendfeldt K, Radojevic V, Kapfhammer J, Nitsch C (2007) Basic fibroblast growth factor modulates density of blood vessels and preserves tight junctions in organotypic cortical cultures of mice: a new in vitro model of the blood-brain barrier. J Neurosci 27(12):3260–3267. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4033-06.2007
Engelhardt B, Ransohoff R (2005) The ins and outs of T-lymphocyte trafficking to the CNS: anatomical sites and molecular mechanisms. Trends Immunol 26(9):485–495
Förster C, Silwedel C, Golenhofen N, Burek M, Kietz S, Mankertz J, Drenckhahn D (2005) Occludin as direct target for glucocorticoid-induced improvement of blood-brain barrier properties in a murine in vitro system. J Physiol 565(Pt 2):475–486. doi:10.1113/jphysiol.2005.084038
Galvan V, Greenberg D, Jin K (2006) The role of vascular endothelial growth factor in neurogenesis in adult brain. Mini Rev Med Chem 6(6):667–669
Garcia C, Darland D, Massingham L, D’Amore P (2004) Endothelial cell-astrocyte interactions and TGF beta are required for induction of blood-neural barrier properties. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 152(1):25–38. doi:10.1016/j.devbrainres.2004.05.008
Guo S, Lo E (2009) Dysfunctional cell–cell signaling in the neurovascular unit as a paradigm for central nervous system disease. Stroke 40(3 Suppl):S4–S7. doi:10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.534388
Hirakawa H, Okajima S, Nagaoka T, Takamatsu T, Oyamada M (2003) Loss and recovery of the blood-nerve barrier in the rat sciatic nerve after crush injury are associated with expression of intercellular junctional proteins. Exp Cell Res 284(2):196–210
Kanda T, Numata Y, Mizusawa H (2004) Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy: decreased claudin-5 and relocated ZO-1. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 75(5):765–769
Kashiwamura Y, Sano Y, Abe M, Shimizu F, Haruki H, Maeda T, Kawai M, Kanda T (2011) Hydrocortisone enhances the function of the blood-nerve barrier through the up-regulation of claudin-5. Neurochem Res 36(5):849–855. doi:10.1007/s11064-011-0413-6
Krizanac-Bengez L, Mayberg M, Janigro D (2004) The cerebral vasculature as a therapeutic target for neurological disorders and the role of shear stress in vascular homeostatis and pathophysiology. Neurol Res 26(8):846–853
Latker C, Shinowara N, Miller J, Rapoport S (1987) Differential localization of alkaline phosphatase in barrier tissues of the frog and rat nervous systems: a cytochemical and biochemical study. J Comp Neurol 264(3):291–302
Lee J, Kay E (2006) FGF-2-induced wound healing in corneal endothelial cells requires Cdc42 activation and Rho inactivation through the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 47(4):1376–1386. doi:10.1167/iovs.05-1223
Lee JH, Lee H, Joung YK, Jung KH, Choi JH, Lee DH, Park KD, Hong SS (2011) The use of low molecular weight heparin–pluronic nanogels to impede liver fibrosis by inhibition the TGF-beta/Smad signaling pathway. Biomaterials 32(5):1438–1445. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2010.10.023
Malmgren L, Olsson Y (1980) Differences between the peripheral and the central nervous system in permeability to sodium fluorescein. J Comp Neurol 191(1):103–107. doi:10.1002/cne.901910106
Man S, Ubogu E, Ransohoff R (2007) Inflammatory cell migration into the central nervous system: a few new twists on an old tale. Brain Pathol 17(2):243–250
Man S, Ubogu E, Williams K, Tucky B, Callahan M, Ransohoff R (2008) Human brain microvascular endothelial cells and umbilical vein endothelial cells differentially facilitate leukocyte recruitment and utilize chemokines for T cell migration. Clin Dev Immunol 2008:384982
Marchi N, Teng Q, Ghosh C, Fan Q, Nguyen M, Desai N, Bawa H, Rasmussen P, Masaryk T, Janigro D (2010) Blood-brain barrier damage, but not parenchymal white blood cells, is a hallmark of seizure activity. Brain Res 1353:176–186. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2010.06.051
McCaffrey TA, Falcone DJ, Brayton CF, Agarwal LA, Welt FG, Weksler BB (1989) Transforming growth factor-beta activity is potentiated by heparin via dissociation of the transforming growth factor-beta/alpha 2-macroglobulin inactive complex. J Cell Biol 109(1):441–448
McCaffrey TA, Falcone DJ, Du B (1992) Transforming growth factor-beta 1 is a heparin-binding protein: identification of putative heparin-binding regions and isolation of heparins with varying affinity for TGF-beta 1. J Cell Physiol 152(2):430–440. doi:10.1002/jcp.1041520226
Mu E, Ding R, An X, Li X, Chen S, Ma X (2012) Heparin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by inhibiting nitric oxide synthase and TGF-beta/Smad signaling pathway. Thromb Res 129(4):479–485. doi:10.1016/j.thromres.2011.10.003
Murphy H, Bakopoulos N, Dame M, Varani J, Ward P (1998) Heterogeneity of vascular endothelial cells: differences in susceptibility to neutrophil-mediated injury. Microvasc Res 56(3):203–211. doi:10.1006/mvre.1998.2110
Olsson Y (1971) Studies on vascular permeability in peripheral nerves. IV. Distribution of intravenously injected protein tracers in the peripheral nervous system of various species. Acta Neuropathol 17(2):114–126
Olsson Y (1990) Microenvironment of the peripheral nervous system under normal and pathological conditions. Crit Rev Neurobiol 5(3):265–311
Orte C, Lawrenson J, Finn T, Reid A, Allt G (1999) A comparison of blood-brain barrier and blood-nerve barrier endothelial cell markers. Anat Embryol (Berl) 199(6):509–517
Poduslo J, Curran G, Dyck P (1988) Increase in albumin, IgG, and IgM blood-nerve barrier indices in human diabetic neuropathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85(13):4879–4883
Poduslo J, Curran G, Berg C (1994) Macromolecular permeability across the blood-nerve and blood-brain barriers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91(12):5705–5709
Pola R, Aprahamian TR, Bosch-Marce M, Curry C, Gaetani E, Flex A, Smith RC, Isner JM, Losordo DW (2004) Age-dependent VEGF expression and intraneural neovascularization during regeneration of peripheral nerves. Neurobiol Aging 25(10):1361–1368. doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2004.02.028
Pummi K, Heape A, Grénman R, Peltonen J, Peltonen S (2004) Tight junction proteins ZO-1, occludin, and claudins in developing and adult human perineurium. J Histochem Cytochem 52(8):1037–1046
Reina M, López A, Villanueva M, de Andrés J, León G (2000) Morphology of peripheral nerves, their sheaths, and their vascularization. Rev Esp Anestesiol Reanim 47(10):464–475
Reina M, López A, Villanueva M, De Andrés J, Machés F (2003) The blood-nerve barrier in peripheral nerves. Rev Esp Anestesiol Reanim 50(2):80–86
Rider CC (2006) Heparin/heparan sulphate binding in the TGF-beta cytokine superfamily. Biochem Soc Trans 34(Pt 3):458–460. doi:10.1042/BST0340458
Ropper AH, Gorson KC, Gooch CL, Weinberg DH, Pieczek A, Ware JH, Kershen J, Rogers A, Simovic D, Schratzberger P, Kirchmair R, Losordo D (2009) Vascular endothelial growth factor gene transfer for diabetic polyneuropathy: a randomized, double-blinded trial. Ann Neurol 65(4):386–393. doi:10.1002/ana.21675
Roskoski R Jr (2007) Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling in tumor progression. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 62(3):179–213. doi:10.1016/j.critrevonc.2007.01.006
Sadowska G, Malaeb S, Stonestreet B (2010) Maternal glucocorticoid exposure alters tight junction protein expression in the brain of fetal sheep. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 298(1):H179–H188. doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00828.2009
Sano Y, Shimizu F, Nakayama H, Abe M, Maeda T, Ohtsuki S, Terasaki T, Obinata M, Ueda M, Takahashi R, Kanda T (2007) Endothelial cells constituting blood-nerve barrier have highly specialized characteristics as barrier-forming cells. Cell Struct Funct 32(2):139–147
Schlessinger J (2004) Common and distinct elements in cellular signaling via EGF and FGF receptors. Science 306(5701):1506–1507. doi:10.1126/science.1105396
Schratzberger P, Walter DH, Rittig K, Bahlmann FH, Pola R, Curry C, Silver M, Krainin JG, Weinberg DH, Ropper AH, Isner JM (2001) Reversal of experimental diabetic neuropathy by VEGF gene transfer. J Clin Invest 107(9):1083–1092. doi:10.1172/JCI12188
Shabb J (2001) Physiological substrates of cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Chem Rev 101(8):2381–2411
Shibuya M (2008) Vascular endothelial growth factor-dependent and -independent regulation of angiogenesis. BMB Rep 41(4):278–286
Shibuya M (2009) Brain angiogenesis in developmental and pathological processes: therapeutic aspects of vascular endothelial growth factor. FEBS J 276(17):4636–4643. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2009.07175.x
Shimizu F, Sano Y, Abe MA, Maeda T, Ohtsuki S, Terasaki T, Kanda T (2011a) Peripheral nerve pericytes modify the blood-nerve barrier function and tight junctional molecules through the secretion of various soluble factors. J Cell Physiol 226(1):255–266. doi:10.1002/jcp.22337
Shimizu F, Sano Y, Haruki H, Kanda T (2011b) Advanced glycation end-products induce basement membrane hypertrophy in endoneurial microvessels and disrupt the blood-nerve barrier by stimulating the release of TGF-beta and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) by pericytes. Diabetologia 54(6):1517–1526. doi:10.1007/s00125-011-2107-7
Shimizu F, Sano Y, Saito K, Abe MA, Maeda T, Haruki H, Kanda T (2012) Pericyte-derived glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor increase the expression of claudin-5 in the blood-brain barrier and the blood-nerve barrier. Neurochem Res 37(2):401–409. doi:10.1007/s11064-011-0626-8
Smith C, Atchabahian A, Mackinnon S, Hunter D (2001) Development of the blood-nerve barrier in neonatal rats. Microsurgery 21(7):290–297
Sobue K, Yamamoto N, Yoneda K, Hodgson M, Yamashiro K, Tsuruoka N, Tsuda T, Katsuya H, Miura Y, Asai K, Kato T (1999) Induction of blood-brain barrier properties in immortalized bovine brain endothelial cells by astrocytic factors. Neurosci Res 35(2):155–164
Stonestreet B, Sadowska G, McKnight A, Patlak C, Petersson K (2000) Exogenous and endogenous corticosteroids modulate blood-brain barrier development in the ovine fetus. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 279(2):R468–R477
Sun Y, Jin K, Xie L, Childs J, Mao X, Logvinova A, Greenberg D (2003) VEGF-induced neuroprotection, neurogenesis, and angiogenesis after focal cerebral ischemia. J Clin Invest 111(12):1843–1851. doi:10.1172/JCI17977
Takahashi M (2001) The GDNF/RET signaling pathway and human diseases. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 12(4):361–373
Tang J, Wang J, Kong X, Yang J, Guo L, Zheng F, Zhang L, Huang Y, Wan Y (2009) Vascular endothelial growth factor promotes cardiac stem cell migration via the PI3 K/Akt pathway. Exp Cell Res 315(20):3521–3531. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2009.09.026
Utsumi H, Chiba H, Kamimura Y, Osanai M, Igarashi Y, Tobioka H, Mori M, Sawada N (2000) Expression of GFRalpha-1, receptor for GDNF, in rat brain capillary during postnatal development of the BBB. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 279(2):C361–C368
Wakefield L, Roberts A (2002) TGF-beta signaling: positive and negative effects on tumorigenesis. Curr Opin Genet Dev 12(1):22–29
Wang Y, Jin K, Mao X, Xie L, Banwait S, Marti H, Greenberg D (2007) VEGF-overexpressing transgenic mice show enhanced post-ischemic neurogenesis and neuromigration. J Neurosci Res 85(4):740–747. doi:10.1002/jnr.21169
Weidenfeller C, Schrot S, Zozulya A, Galla H (2005) Murine brain capillary endothelial cells exhibit improved barrier properties under the influence of hydrocortisone. Brain Res 1053(1–2):162–174
Yano K, Gale D, Massberg S, Cheruvu P, Monahan-Earley R, Morgan E, Haig D, von Andrian U, Dvorak A, Aird W (2007) Phenotypic heterogeneity is an evolutionarily conserved feature of the endothelium. Blood 109(2):613–615
Yosef N, Ubogu EE (2012) GDNF restores human blood-nerve barrier function via RET tyrosine kinase-mediated cytoskeletal reorganization. Microvasc Res 83(3):298–310. doi:10.1016/j.mvr.2012.01.005
Yosef N, Ubogu EE (2013) An immortalized human blood-nerve barrier endothelial cell line for in vitro permeability studies. Cell Mol Neurobiol 33(2):175–186. doi:10.1007/s10571-012-9882-7
Yosef N, Xia R, Ubogu E (2010) Development and characterization of a novel human in vitro blood-nerve barrier model using primary endoneurial endothelial cells. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 69(1):82–97
Zheng Z, Yenari M (2004) Post-ischemic inflammation: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Neurol Res 26(8):884–892
Acknowledgments
Special thanks to Dr. Monique Stins for providing THBMECs. Aspects of this study were presented in part in abstract form at the 2011 American Academy of Neurology meeting, Honolulu, Hawaii, USA and the 2011 Peripheral Nerve Society meeting, Potomac, Maryland, USA. This study was supported by a Baylor College of Medicine New Investigator Start-Up Award (2007–2011). The Neuromuscular Immunopathology Research Laboratory is currently supported by the National Institutes of Health Grants R21 NS073702, R21 NS078226, and R01 NS075212, and a subaward P30 AI27767 to E.E.U. The funding sources had no involvement in the conduct of the research, manuscript preparation, data collection/analyses or decision to submit this work for publication. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the NIH.
Conflict of interest
There are no financial conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Reddy, C.L., Yosef, N. & Ubogu, E.E. VEGF-A165 Potently Induces Human Blood–Nerve Barrier Endothelial Cell Proliferation, Angiogenesis, and Wound Healing In Vitro. Cell Mol Neurobiol 33, 789–801 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-013-9946-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-013-9946-3