Abstract
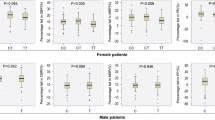
To evaluate the interaction between the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) gene insertion/deletion (I/D) polymorphism and gender with individual blood pressure response to hydrochlorothiazide (HCTZ) in hypertensives, we enrolled 829 mild-moderate hypertensive patients. All subjects were given HCTZ (12.5 mg) orally each day for 6 weeks. A total of 776 patients completed the study. There was statistically significant interaction between the effects of genotype and gender on systolic (P = 0.002) and diastolic (P = 0.048) response after adjusting for covariables. Moreover, in each gender, the genotype that was associated with the greatest blood pressure response to HCTZ (DD homozygotes in men and II homozygotes in women) was also associated with the greatest increase in serum ACE activity in response to HCTZ. The results suggest that the I/D polymorphism of the ACE gene is associated with interindividual differences in the blood pressure response to a low dose of a diuretic in a gender-specific manner in the Han Chinese population with hypertension.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnett DK, Claas SA, Lynch AI (2009) Has pharmacogenetics brought us closer to personalized medicine for initial drug treatment of hypertension? Curr Opin Cardiol 24(4):333–339
Bandelow B, Saleh K, Pauls J, Domschke K, Wedekind D, Falkai P (2007) Insertion/deletion polymorphism in the gene for angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) in panic disorder: A gender-specific effect? World J Biol Psychiatry 11: 66–70
Caprioli J, Mele C, Mossali C, Gallizioli L, Giacchetti G, Noris M, Remuzzi G, Benigni A (2008) Polymorphisms of EDNRB, ATG, and ACE genes in salt-sensitive hypertension. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 86(8):505–510
Chobanian AV, Bakris GL, Black HR, Cushman WC, Green LA, Izzo JL Jr, Jones DW, Materson BJ, Oparil S, Wright JT Jr, Roccella EJ (2003) Seventh report of the Joint National Committee on prevention, detection, evaluation, and treatment of high blood pressure. Hypertension 42(6):1206–1252
Danser AH, Derkx FH, Hense HW, Jeunemaitre X, Riegger GA, Schunkert H (1998) Angiotensinogen (M235T) and angiotensin-converting enzyme (I/D) polymorphisms in association with plasma renin and prorenin levels. J Hypertens 16(12 Pt 2):1879–1883
Franson KL, Kuk JM, Lam NP, Lau AH (1996) Gender effect on diuretic response to hydrochlorothiazide and furosemide. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 34(3):101–105
Frazier L, Turner ST, Schwartz GL, Chapman AB, Boerwinkle E (2004) Multilocus effects of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system genes on blood pressure response to a thiazide diuretic. Pharmacogenomics J 4(1):17–23
Helbecque N, Codron V, Cottel D, Amouyel P (2009) An age effect on the association of common variants of ACE with Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Lett 461(2):181–184
Huang M, Gai X, Yang X, Hou J, Lan X, Zheng W, Chen F, He J (2009) Functional polymorphisms in ACE and CYP11B2 genes and atrial fibrillation in patients with hypertensive heart disease. Clin Chem Lab Med 47(1):32–37
Hughes AD (2004) How do thiazide and thiazide-like diuretics lower blood pressure? J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst 5(4):155–160
Jiang X, Sheng HH, Lin G, Li J, Lu XZ, Cheng YL, Huang J, Xiao HS, Zhan YY (2007) Effect of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system gene polymorphisms on blood pressure response to antihypertensive treatment. Chin Med J (Engl) 120(9):782–786
Johnson JA, Boerwinkle E, Zineh I, Chapman AB, Bailey K, Cooper-DeHoff RM, Gums J, Curry RW, Gong Y, Beitelshees AL, Schwartz G, Turner ST (2009) Pharmacogenomics of antihypertensive drugs: rationale and design of the Pharmacogenomic Evaluation of Antihypertensive Responses (PEAR) study. Am Heart J 157(3):442–449
Kumar R, Nejatizadeh A, Arif E, Akhtar S, Gupta M, Tyagi S, Goyal AK, Jain SK, Qadar Pasha MA (2009) Multi-locus interactions of vascular homeostasis genes in essential hypertension: a gender-based study. Clin Chim Acta 405(1–2):87–93
Niu W, Qi Y, Hou S, Zhai X, Zhou W, Qiu C (2009) Haplotype-based association of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system genes polymorphisms with essential hypertension among Han Chinese: the Fangshan study. J Hypertens 27(7):1384–1391
Orlowska-Baranowska E, Placha G, Gaciong Z, Baranowski R, Zakrzewski D, Michalek P, Hoffman P, Rawczynska-Englert I (2004) Influence of ACE I/D genotypes on left ventricular hypertrophy in aortic stenosis: gender-related differences. J Heart Valve Dis 13(4):574–581
Perloff D, Grim C, Flack J, Frohlich ED, Hill M, McDonald M, Morgenstern BZ (1993) Human blood pressure determination by sphygmomanometry. Circulation 88(5 Pt 1):2460–2470
Rigat B, Hubert C, Alhenc-Gelas F, Cambien F, Corvol P, Soubrier F (1990) An insertion/deletion polymorphism in the angiotensin I-converting enzyme gene accounting for half the variance of serum enzyme levels. J Clin Investig 86(4):1343–1346
Schwartz GL, Turner ST, Chapman AB, Boerwinkle E (2002) Interacting effects of gender and genotype on blood pressure response to hydrochlorothiazide. Kidney Int 62(5):1718–1723
Sciarrone MT, Stella P, Barlassina C, Manunta P, Lanzani C, Bianchi G, Cusi D (2003) ACE and alpha-adducin polymorphism as markers of individual response to diuretic therapy. Hypertension 41(3):398–403
Tien KJ, Hsiao JY, Hsu SC, Liang HT, Lin SR, Chen HC, Hsieh MC (2009) Gender-dependent effect of ACE I/D and AGT M235T polymorphisms on the progression of urinary albumin excretion in Taiwanese with type 2 diabetes. Am J Nephrol 29(4):299–308
Tiret L, Rigat B, Visvikis S, Breda C, Corvol P, Cambien F, Soubrier F (1992) Evidence, from combined segregation and linkage analysis, that a variant of the angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) gene controls plasma ACE levels. Am J Hum Genet 51(1):197–205
Turner ST, Schwartz GL, Chapman AB, Beitelshees AL, Gums JG, Cooper-DeHoff RM, Boerwinkle E, Johnson JA, Bailey KR (2010) Plasma renin activity predicts blood pressure responses to beta-blocker and thiazide diuretic as monotherapy and add-on therapy for hypertension. Am J Hypertens 23(9):1014–1022
Zapater P, Novalbos J, Gallego-Sandin S, Hernandez FT, Abad-Santos F (2004) Gender differences in angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) activity and inhibition by enalaprilat in healthy volunteers. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 43(5):737–744
Zhou Y, Wu SL, Liu JQ, Liang WN, Liu GF (2007) Possible association of ACE gene I/D polymorphism with blood pressure-lowering response to hydrochlorothiazide. Biomed Environ Sci 20(5):351–356
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Yang, P., Wu, S. et al. Gender-Specific Association Between ACE Gene I/D Polymorphism and Blood Pressure Response to Hydrochlorothiazide in Han Chinese Hypertensive Patients. Biochem Genet 49, 704–714 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-011-9444-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10528-011-9444-6