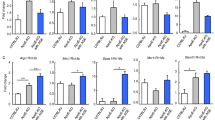
Abstract
Baicalin, a herb-derived flavonoid compound, has beneficial activities, including the modulation of oxidative stress and inflammation. Nuclear receptor peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ (PPARγ) is a ligand-activated transcription factor that plays an important role in regulating nuclear factor-κB (NF-κB)-induced age-related inflammation. We investigated the anti-inflammatory action of baicalin, which depends on its ability to activate PPARγ, and subsequently to suppress NF-κB. We examined baicalin-treated kidney tissue from 24-month-old Fischer 344 aged rats (10 or 20 mg/kg/day for 10 days) and baicalin-fed mice (10 mg/kg/day for 3 days) for in vivo investigations, and used endothelial YPEN-1 cells for in vitro studies. In the baicalin-fed aged rats, there was a marked enhancement of both nuclear protein levels and DNA binding activity of PPARγ, and a decreased expression of NF-κB target genes (VCAM-1, IL-1β, and IL-6) compared with non-baicalin-fed aged rats. Furthermore, to confirm the anti-inflammatory action of PPARγ activated by baicalin, we used lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-treated cells and mice. The results showed that baicalin induced PPARγ-selective activation in YPEN-1 cells, and that the effects of baicalin were blocked by the PPARγ receptor antagonist, GW9662. In addition, baicalin treatment prevented RS generation, NF-κB activation and the expression of pro-inflammatory genes, whereas it increased PPARγ expression in LPS-treated cells and mouse kidney. Our data suggest that baicalin-induced PPARγ expression reduced age-related inflammation through blocking pro-inflammatory NF-κB activation. These results indicate that baicalin is a novel PPARγ activator and that this agent may have the potential to minimize inflammation.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- EMSA:
-
Electrophoretic mobility shift assay
- H2DCF-DA:
-
2′,7′-Dichlorofluorescin diacetate
- IL-1β:
-
Interukin-1β
- iNOS:
-
Inducible nitric oxide synthase
- I.P.:
-
Intraperitoneal
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor-κB
- PPARγ:
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ
- PPRE:
-
Peroxisome proliferator response element
- RS:
-
Reactive species
- RXR:
-
Retinoid X receptor
- SPF:
-
Specific pathogen free
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-α
- TZD:
-
Thiazolidinedione
- VCAM-1:
-
Vascular cell adhesion protein-1
References
Amoruso A, Gunella G, Rondano E, Bardelli C, Fresu LG, Ferrero V, Ribichini F, Vassanelli C, Brunelleschi S (2009) Tobacco smoke affects expression of peroxisome proliferator activated receptor γ in monocyte/macrophages of patients with coronary heart disease. Br J Pharmacol 158:1276–1284
Bailey ST, Ghosh S (2005) PPAR’ting ways with inflammation. Nat Immunol 6:966–967
Bassaganya-Riera J, Reynolds K, Martino-Catt S, Cui Y, Hennighausen L, Gonzalez F, Rohrer J, Benninghoff AU, Hontecillas R (2004) Activation of PPAR [gamma] and [delta] by conjugated linoleic acid mediates protection from experimental inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 127:777–791
Blanquart C, Barbier O, Fruchart J, Staels B, Glineur C (2003) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors: regulation of transcriptional activities and roles in inflammation. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 85:267–273
Blanquicett C, Kang BY, Ritzenthaler JD, Jones DP, Hart CM (2010) Oxidative stress modulates PPAR [gamma] in vascular endothelial cells. Free Radic Biol Med 48:1618–1625
Chan ED, Riches D, White CW (2001) Redox paradox: effect of N-acetylcysteine and serum on oxidation reduction-sensitive mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 24:627–632
Chung JH, Seo A, Chung SW, Kim MK, Leeuwenburgh C, Yu BP, Chung HY (2008) Molecular mechanism of PPAR in the regulation of age-related inflammation. Ageing Res Rev 7:126–136
Dasu MR, Park S, Devaraj S, Jialal I (2009) Pioglitazone inhibits toll-like receptor expression and activity in human monocytes and db/db mice. Endocrinology 150:3457–3464
Dubuquoy L, Rousseaux C, Thuru X, Peyrin-Biroulet L, Romano O, Chavatte P, Chamaillard M, Desreumaux P (2006) PPARgamma as a new therapeutic target in inflammatory bowel diseases. Gut 55:1341–1349
Francis GA, Annicotte JS, Auwerx J (2003) PPAR agonists in the treatment of atherosclerosis. Curr Opin Pharmacol 3:186–191
Graham TL, Mookherjee C, Suckling KE (2005) The PPAR [delta] agonist GW0742X reduces atherosclerosis in LDLR-/-mice. Atherosclerosis 181:29–37
Gumieniczek A (2003) Effect of the new thiazolidinedione-pioglitazone on the development of oxidative stress in liver and kidney of diabetic rabbits. Life Sci 74:553–562
Izzedine H, Launay-Vacher V, Buhaescu I, Heurtier A, Baumelou A, Deray G (2005) PPAR-gamma-agonists’ renal effects. Minerva Urol Nefrol 57:247–260
Jaramillo M, Olivier M (2002) Hydrogen peroxide induces murine macrophage chemokine gene transcription via extracellular signal-regulated kinase-and cyclic adenosine 5′-monophosphate (cAMP)-dependent pathways: involvement of NF-{kappa}B, activator protein 1, and cAMP response element binding protein. J Immunol 169:7026–7038
Jung SH, Kang KD, Ji D, Fawcett RJ, Safa R, Kamalden TA, Osborne NN (2008) The flavonoid baicalin counteracts ischemic and oxidative insults to retinal cells and lipid peroxidation to brain membranes. Neurochem Int 53:325–337
Kelly D, Campbell JI, King TP, Grant G, Jansson EA, Coutts AG, Pettersson S, Conway S (2003) Commensal anaerobic gut bacteria attenuate inflammation by regulating nuclear-cytoplasmic shuttling of PPAR-γ and RelA. Nat Immunol 5:104–112
Kielian T, Drew PD (2003) Effects of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ agonists on central nervous system inflammation. J Neurosci Res 71:315–325
Kim DH, Kim HK, Park S, Kim JY, Zou Y, Cho KH, Kim YS, Yu BP, Choi JS, Chung HY (2006) Short-term feeding of baicalin inhibits age-associated NF-[kappa]B activation. Mech Ageing Dev 127:719–725
Kim MK, Chung SW, Kim DH, Kim JY, Lee EK, Kim JM, Ha YM, Kim YS, No JK, Chung HY (2010) Modulation of age-related NF-[kappa]B activation by dietary zingerone via MAPK pathway. Exp Gerontol 45:419–426
Kota BP, Huang TH, Roufogalis BD (2005) An overview on biological mechanisms of PPARs. Pharmacol Res 51:85–94
Kumazawa Y, Kawaguchi K, Takimoto H (2006) Immunomodulating effects of flavonoids on acute and chronic inflammatory responses caused by tumor necrosis factor. Curr Pharm Des 12:4271–4279
Leesnitzer LM, Parks DJ, Bledsoe RK, Cobb JE, Collins JL, Consler TG, Davis RG, Hull-Ryde EA, Lenhard JM, Patel L, Plunkeet KD, Shenk JL, Stimmel JB, Therapontos C, Willson TM, Blanchard SG (2002) Functional consequences of cysteine modification in the ligand binding sites of peroxisome proliferator activated receptors by GW9662. Biochemistry 41:6640–6650
Li MH, Huang KL, Wu SY, Chen CW, Yan HC, Hsu K, Hsu CW, Tsai SH, Chu SJ (2009) Baicalin attenuates air embolism-induced acute lung injury in rat isolated lungs. Br J Pharmacol 157:244–251
Liang YC, Huang YT, Tsai SH, Lin-Shiau SY, Chen CF, Lin JK (1999) Suppression of inducible cyclooxygenase and inducible nitric oxide synthase by apigenin and related flavonoids in mouse macrophages. Carcinogenesis 20:1945–1952
Liang YC, Tsai SH, Tsai DC, Lin-Shiau SY, Lin JK (2001) Suppression of inducible cyclooxygenase and nitric oxide synthase through activation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-[gamma] by flavonoids in mouse macrophages. FEBS Lett 496:12–18
Li-Weber M (2009) New therapeutic aspects of flavones: the anticancer properties of scutellaria and its main active constituents wogonin, baicalein and baicalin. Cancer Treat Rev 35:57–68
Lixuan Z, Jingcheng D, Wenqin Y, Jianhua H, Baojun L, Xiaotao F (2010) Baicalin attenuates inflammation by inhibiting NF-[kappa]B activation in cigarette smoke induced inflammatory models. Pulm Pharmacol Ther 23:411–419
Marion-Letellier R, Dechelotte P, Iacucci M, Ghosh S (2009) Dietary modulation of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma. Gut 58:586–593
Pascual G, Fong AL, Ogawa S, Gamliel A, Li AC, Perissi V, Rose DW, Willson TM, Rosenfeld MG, Glass CK (2005) A sumoylation-dependent pathway mediates transrepression of inflammatory response genes by PPAR-γ. Nature 437:759–763
Pedersen G, Brynskov J (2010) Topical rosiglitazone treatment improves ulcerative colitis by restoring peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ activity. Am J Gastroenterol 105:1595–1603
Ricote M, Glass CK (2007) PPARs and molecular mechanisms of transrepression. Biochim Biophys Acta 1771:926–935
Sasaki M, Jordan P, Welbourne T, Minagar A, Joh T, Itoh M, Elrod JW, Alexander JS (2005) Troglitazone, a PPAR-γ activator prevents endothelial cell adhesion molecule expression and lymphocyte adhesion mediated by TNF-α. BMC Physiol 5:3
Serafini M, Peluso I, Raguzzini A (2010) Flavonoids as anti-inflammatory agents. Proc Nutr Soc 69:273–278
Sommer M, Wolf G (2000) Rosiglitazone increases PPARγ in renal tubular epithelial cells and protects against damage by hydrogen peroxide. Am J Nephrol 27:425–434
Staels B, Fruchart JC (2005) Therapeutic roles of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor agonists. Diabetes 54:2460–2470
Straus DS, Glass CK (2007) Anti-inflammatory actions of PPAR ligands: new insights on cellular and molecular mechanisms. Trends Immunol 28:551–558
Sung B, Park S, Yu BP, Chung HY (2006) Amelioration of age-related inflammation and oxidative stress by PPAR [gamma] activator: suppression of NF-[kappa]B by 2,4-thiazolidinedione. Exp Gerontol 41:590–599
Takano H, Hasegawa H, Nagai T, Komuro I (2003) The role of PPARgamma-dependent pathway in the development of cardiac hypertrophy. Timely Top Med Cardiovasc Dis 39:347–357
Tu XK, Yang WZ, Shi SS, Chen Y, Wang CH, Chen CM, Chen Z (2010) Baicalin inhibits TLR2/4 signaling pathway in rat brain following permanent cerebral ischemia. Inflammation 1–8 [Epub ahead of print]
Uwe S (2008) Anti-inflammatory interventions of NF-[kappa] B signaling: potential applications and risks. Biochem Pharmacol 75:1567–1579
van Beekum O, Fleskens V, Kalkhoven E (2009) Posttranslational modifications of PPAR-γ: fine-tuning the metabolic master regulator. Obesity 17:213–219
Videla LA (2010) Liver NF-κB and AP-1 activation and PPAR-α expression are negatively correlated in obese patients: pro-inflammatory implications. Clin Nutr 29:687–688
Wang T, Qin L, Liu B, Liu Y, Wilson B, Eling TE, Langenbach R, Taniura S, Hong JS (2004) Role of reactive oxygen species in LPS-induced production of prostaglandin E2 in microglia. J Neurochem 88:939–947
Xiping Z, Guanghua F, Jinxian H, Weihong W, Rujun X, Wei Z, Jing Y, Qijun Y, Meijuan Y, Qing W (2010) Baicalin protects thymus of rats with severe acute pancreatitis. Inflammation 33:157–165
Yang HC, Deleuze S, Zuo Y, Potthoff SA, Ma LJ, Fogo AB (2009) The PPAR agonist pioglitazone ameliorates aging-related progressive renal injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 20:2380–2388
Yeh CC, Kao SJ, Lin CC, Wang SD, Liu CJ, Kao ST (2007) The immunomodulation of endotoxin-induced acute lung injury by hesperidin in vivo and in vitro. Life Sci 80:1821–1831
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MEST) (MRC Program No. 2009-0083538) and a grant (Code # 7-19-42) from Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea. We are grateful to the Aging Tissue Bank for providing aged rat kidney tissue. The authors thank Editage (a division of Cactus Communications Pvt. Ltd.) for valuable editing of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Hyun Ae Lim and Eun Kyeong Lee contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lim, H.A., Lee, E.K., Kim, J.M. et al. PPARγ activation by baicalin suppresses NF-κB-mediated inflammation in aged rat kidney. Biogerontology 13, 133–145 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-011-9361-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10522-011-9361-4