Abstract
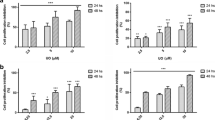
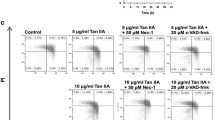
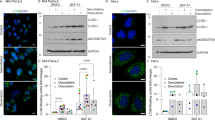
Pancreatic cancer (PaCa) is one of the most aggressive, apoptosis-resistant and currently incurable cancers with a poor survival rate. Eukaryotic elongation factor-2 kinase (eEF-2K) is an atypical kinase, whose role in PaCa survival is not yet known. Here, we show that eEF-2K is overexpressed in PaCa cells and its down-regulation induces apoptotic cell death. Rottlerin (ROT), a polyphenolic compound initially identified as a PKC-δ inhibitor, induces apoptosis and autophagy in a variety of cancer cells including PaCa cells. We demonstrated that ROT induces intrinsic apoptosis, with dissipation of mitochondrial membrane potential (ΔΨm), and stimulates extrinsic apoptosis with concomitant induction of TNF-related apoptosis inducing ligand (TRAIL) receptors, DR4 and DR5, with caspase-8 activation, in PANC-1 and MIAPaCa-2 cells. Notably, while none of these effects were dependent on PKC-δ inhibition, ROT down-regulates eEF-2K at mRNA level, and induce eEF-2K protein degradation through ubiquitin–proteasome pathway. Down-regulation of eEF-2K recapitulates the events observed after ROT treatment, while its over-expression suppressed the ROT-induced apoptosis. Furthermore, eEF-2K regulates the expression of tissue transglutaminase (TG2), an enzyme previously implicated in proliferation, drug resistance and survival of cancer cells. Inhibition of eEF-2K/TG2 axis leads to caspase-independent apoptosis which is associated with induction of apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF). Collectively, these results indicate, for the first time, that the down-regulation of eEF-2K leads to induction of intrinsic, extrinsic as well as AIF-dependent apoptosis in PaCa cells, suggesting that eEF-2K may represent an attractive therapeutic target for the future anticancer agents in PaCa.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Crane CH, Ben-Josef E, Small W Jr (2004) Chemotherapy for pancreatic cancer. N Engl J Med 350:2713–2715 (author reply 2713–2715)
He X, Zheng Z, Li J, Ben Q, Liu J et al (2012) DJ-1 promotes invasion and metastasis of pancreatic cancer cells by activating SRC/ERK/uPA. Carcinogenesis 33:555–562
Ottenhof NA, de Wilde RF, Maitra A, Hruban RH, Offerhaus GJ (2011) Molecular characteristics of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Pathol Res Int 2011:620601
Brown JM, Attardi LD (2005) The role of apoptosis in cancer development and treatment response. Nat Rev Cancer 5:231–237
Maioli E, Torricelli C, Valacchi G (2012) Rottlerin and cancer: novel evidence and mechanisms. ScientificWorldJournal 2012:350826
Kaufmann T, Tai L, Ekert PG, Huang DC, Norris F et al (2007) The BH3-only protein bid is dispensable for DNA damage- and replicative stress-induced apoptosis or cell-cycle arrest. Cell 129:423–433
Ohno I, Eibl G, Odinokova I, Edderkaoui M, Damoiseaux RD et al (2010) Rottlerin stimulates apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells through interactions with proteins of the Bcl-2 family. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 298:G63–G73
Green DR, Reed JC (1998) Mitochondria and apoptosis. Science 281:1309–1312
Lakhani SA, Masud A, Kuida K, Porter GA Jr, Booth CJ et al (2006) Caspases 3 and 7: key mediators of mitochondrial events of apoptosis. Science 311:847–851
Li P, Nijhawan D, Budihardjo I, Srinivasula SM, Ahmad M et al (1997) Cytochrome c and dATP-dependent formation of Apaf-1/caspase-9 complex initiates an apoptotic protease cascade. Cell 91:479–489
Susin SA, Lorenzo HK, Zamzami N, Marzo I, Snow BE et al (1999) Molecular characterization of mitochondrial apoptosis-inducing factor. Nature 397:441–446
Zimmermann KC, Bonzon C, Green DR (2001) The machinery of programmed cell death. Pharmacol Ther 92:57–70
Kroemer G, Reed JC (2000) Mitochondrial control of cell death. Nat Med 6:513–519
Martinou JC, Youle RJ (2011) Mitochondria in apoptosis: Bcl-2 family members and mitochondrial dynamics. Dev Cell 21:92–101
Joza N, Susin SA, Daugas E, Stanford WL, Cho SK et al (2001) Essential role of the mitochondrial apoptosis-inducing factor in programmed cell death. Nature 410:549–554
Akar U, Ozpolat B, Mehta K, Fok J, Kondo Y et al (2007) Tissue transglutaminase inhibits autophagy in pancreatic cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res 5:241–249
McCracken MA, Miraglia LJ, McKay RA, Strobl JS (2003) Protein kinase C delta is a prosurvival factor in human breast tumor cell lines. Mol Cancer Ther 2:273–281
Tillman DM, Izeradjene K, Szucs KS, Douglas L, Houghton JA (2003) Rottlerin sensitizes colon carcinoma cells to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand-induced apoptosis via uncoupling of the mitochondria independent of protein kinase C. Cancer Res 63:5118–5125
Clark AS, West KA, Blumberg PM, Dennis PA (2003) Altered protein kinase C (PKC) isoforms in non-small cell lung cancer cells: PKCdelta promotes cellular survival and chemotherapeutic resistance. Cancer Res 63:780–786
Ni H, Ergin M, Tibudan SS, Denning MF, Izban KF et al (2003) Protein kinase C-delta is commonly expressed in multiple myeloma cells and its downregulation by rottlerin causes apoptosis. Br J Haematol 121:849–856
Gschwendt M, Muller HJ, Kielbassa K, Zang R, Kittstein W et al (1994) Rottlerin, a novel protein kinase inhibitor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 199:93–98
Soltoff SP (2001) Rottlerin is a mitochondrial uncoupler that decreases cellular ATP levels and indirectly blocks protein kinase Cdelta tyrosine phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 276:37986–37992
Davies SP, Reddy H, Caivano M, Cohen P (2000) Specificity and mechanism of action of some commonly used protein kinase inhibitors. Biochem J 351:95–105
Bain J, Plater L, Elliott M, Shpiro N, Hastie CJ et al (2007) The selectivity of protein kinase inhibitors: a further update. Biochem J 408:297–315
Duchen MR (2004) Roles of mitochondria in health and disease. Diabetes 53(Suppl 1):S96–102
Hait WN, Wu H, Jin S, Yang JM (2006) Elongation factor-2 kinase: its role in protein synthesis and autophagy. Autophagy 2:294–296
Tekedereli I, Alpay SN, Tavares CD, Cobanoglu ZE, Kaoud TS et al (2012) Targeted silencing of elongation factor 2 kinase suppresses growth and sensitizes tumors to doxorubicin in an orthotopic model of breast cancer. PLoS ONE 7:e41171
Jorgensen R, Merrill AR, Andersen GR (2006) The life and death of translation elongation factor 2. Biochem Soc Trans 34:1–6
Bagaglio DM, Hait WN (1994) Role of calmodulin-dependent phosphorylation of elongation factor 2 in the proliferation of rat glial cells. Cell Growth Differ 5:1403–1408
Nilsson A, Nygard O (1995) Phosphorylation of eukaryotic elongation factor 2 in differentiating and proliferating HL-60 cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1268:263–268
Parmer TG, Ward MD, Yurkow EJ, Vyas VH, Kearney TJ et al (1999) Activity and regulation by growth factors of calmodulin-dependent protein kinase III (elongation factor 2-kinase) in human breast cancer. Br J Cancer 79:59–64
Knebel A, Haydon CE, Morrice N, Cohen P (2002) Stress-induced regulation of eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase by SB 203580-sensitive and -insensitive pathways. Biochem J 367:525–532
Devkota AK, Tavares CD, Warthaka M, Abramczyk O, Marshall KD et al (2012) Investigating the kinetic mechanism of inhibition of elongation factor 2 kinase by NH125: evidence of a common in vitro artifact. Biochemistry 51:2100–2112
Mehta K, Fok J, Miller FR, Koul D, Sahin AA (2004) Prognostic significance of tissue transglutaminase in drug resistant and metastatic breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res 10:8068–8076
Akar U, Chaves-Reyez A, Barria M, Tari A, Sanguino A et al (2008) Silencing of Bcl-2 expression by small interfering RNA induces autophagic cell death in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Autophagy 4:669–679
Vermes I, Haanen C, Steffens-Nakken H, Reutelingsperger C (1995) A novel assay for apoptosis. Flow cytometric detection of phosphatidylserine expression on early apoptotic cells using fluorescein labelled Annexin V. J Immunol Methods 184:39–51
Espina V, Mehta AI, Winters ME, Calvert V, Wulfkuhle J et al (2003) Protein microarrays: molecular profiling technologies for clinical specimens. Proteomics 3:2091–2100
Soltoff SP (2007) Rottlerin: an inappropriate and ineffective inhibitor of PKCdelta. Trends Pharmacol Sci 28:453–458
Tibes R, Qiu Y, Lu Y, Hennessy B, Andreeff M et al (2006) Reverse phase protein array: validation of a novel proteomic technology and utility for analysis of primary leukemia specimens and hematopoietic stem cells. Mol Cancer Ther 5:2512–2521
Sheehan KM, Calvert VS, Kay EW, Lu Y, Fishman D et al (2005) Use of reverse phase protein microarrays and reference standard development for molecular network analysis of metastatic ovarian carcinoma. Mol Cell Proteomics 4:346–355
Arora S, Yang JM, Hait WN (2005) Identification of the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway in the regulation of the stability of eukaryotic elongation factor-2 kinase. Cancer Res 65:3806–3810
Mitchell BS (2003) The proteasome: an emerging therapeutic target in cancer. N Engl J Med 348:2597–2598
Ozpolat B, Akar U, Mehta K, Lopez-Berestein G (2007) PKC delta and tissue transglutaminase are novel inhibitors of autophagy in pancreatic cancer cells. Autophagy 3:480–483
Riedl SJ, Shi Y (2004) Molecular mechanisms of caspase regulation during apoptosis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5:897–907
Gottlieb E, Armour SM, Harris MH, Thompson CB (2003) Mitochondrial membrane potential regulates matrix configuration and cytochrome c release during apoptosis. Cell Death Differ 10:709–717
Kim CH, Gupta S (2000) Expression of TRAIL (Apo2L), DR4 (TRAIL receptor 1), DR5 (TRAIL receptor 2) and TRID (TRAIL receptor 3) genes in multidrug resistant human acute myeloid leukemia cell lines that overexpress MDR 1 (HL60/Tax) or MRP (HL60/AR). Int J Oncol 16:1137–1139
Masdehors P, Glaisner S, Maciorowski Z, Magdelenat H, Delic J (2000) Ubiquitin-dependent protein processing controls radiation-induced apoptosis through the N-end rule pathway. Exp Cell Res 257:48–57
Singh BN, Kumar D, Shankar S, Srivastava RK (2012) Rottlerin induces autophagy which leads to apoptotic cell death through inhibition of PI3 K/Akt/mTOR pathway in human pancreatic cancer stem cells. Biochem Pharmacol 84:1154–1163
Parmer TG, Ward MD, Hait WN (1997) Effects of rottlerin, an inhibitor of calmodulin-dependent protein kinase III, on cellular proliferation, viability, and cell cycle distribution in malignant glioma cells. Cell Growth Differ 8:327–334
Verma A, Wang H, Manavathi B, Fok JY, Mann AP et al (2006) Increased expression of tissue transglutaminase in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma and its implications in drug resistance and metastasis. Cancer Res 66:10525–10533
Yu SW, Wang H, Poitras MF, Coombs C, Bowers WJ et al (2002) Mediation of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1-dependent cell death by apoptosis-inducing factor. Science 297:259–263
Kang YH, Yi MJ, Kim MJ, Park MT, Bae S et al (2004) Caspase-independent cell death by arsenic trioxide in human cervical cancer cells: reactive oxygen species-mediated poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 activation signals apoptosis-inducing factor release from mitochondria. Cancer Res 64:8960–8967
Virag L, Szabo C (2002) The therapeutic potential of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors. Pharmacol Rev 54:375–429
Wu H, Yang JM, Jin S, Zhang H, Hait WN (2006) Elongation factor-2 kinase regulates autophagy in human glioblastoma cells. Cancer Res 66:3015–3023
Cheng Y, Li H, Ren X, Niu T, Hait WN et al (2010) Cytoprotective effect of the elongation factor-2 kinase-mediated autophagy in breast cancer cells subjected to growth factor inhibition. PLoS ONE 5:e9715
Wu H, Zhu H, Liu DX, Niu TK, Ren X et al (2009) Silencing of elongation factor-2 kinase potentiates the effect of 2-deoxy-d-glucose against human glioma cells through blunting of autophagy. Cancer Res 69:2453–2460
Cheng Y, Ren X, Zhang Y, Patel R, Sharma A et al (2011) eEF-2 kinase dictates cross-talk between autophagy and apoptosis induced by Akt Inhibition, thereby modulating cytotoxicity of novel Akt inhibitor MK-2206. Cancer Res 71:2654–2663
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank Dr. Kevin N. Dalby, and his laboratory members, Division of Medicinal Chemistry, College of Pharmacy, The University of Texas at Austin, for helpful discussions and critically reading the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ashour, A.A., Abdel-Aziz, AA.H., Mansour, A.M. et al. Targeting elongation factor-2 kinase (eEF-2K) induces apoptosis in human pancreatic cancer cells. Apoptosis 19, 241–258 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-013-0927-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-013-0927-2