Abstract
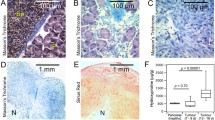
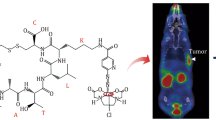
Fibrosis, closely related to chronic various diseases, is a pathological process characterised by the accumulation of collagen (largely collagen type I). Non-invasive methods are necessary for the diagnosis and follow-up of fibrosis. This study aimed to develop a collagen-targeted probe for the molecular imaging of fibrosis. We identified CPKESCNLFVLKD (CBP1495) as an original collagen-binding peptide using isothermal titration calorimetry and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. CBP1495 effectively bound to collagen type I (K d = 861 nM) and (GPO)9 (K d = 633 nM), a collagen mimetic peptide. Western blot and histochemistry validated CBP1495 targeting collagen in vitro and ex vivo. (Gly-(D)-Ala-Gly-Gly) was introduced to CBP1495 for coupling 99mTc. Labelling efficiency of 99mTc-CBP1495 was 95.06 ± 1.08 %. The physico-chemical properties, tracer kinetics and biodistribution of 99mTc-CBP1495 were carried out, and showed that the peptide stably chelated 99mTc in vitro and in vivo. SPECT/CT imaging with 99mTc-CBP1495 was performed in rat fibrosis models, and revealed that 99mTc-CBP1495 significantly accumulated in fibrotic lungs or livers of rats. Finally, 99mTc-CBP1495 uptake and hydroxyproline (Hyp), a specific amino acid of collagen, were quantitatively analysed. The results demonstrated that 99mTc-CBP1495 uptake was positvely correlated with Hyp content in lungs (P < 0.0001, r 2 = 0.8266) or livers (P < 0.0001, r 2 = 0.7581). Therefore, CBP1495 is a novel collagen-binding peptide, and 99mTc-labelled CBP1495 may be a promising radiotracer for the molecular imaging of fibrosis.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
An B, Lin YS, Brodsky B (2016) Collagen interactions: drug design and delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 97:69–84. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2015.11.013
Bala G, Cosyns B (2014) Recent advances in visualizing vulnerable plaque: focus on noninvasive molecular imaging. Curr Cardiol Rep 16:520. doi:10.1007/s11886-014-0520-5
Birbrair A, Zhang T, Wang ZM, Messi ML, Mintz A, Delbono O (2013) Type-1 pericytes participate in fibrous tissue deposition in aged skeletal muscle. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 305:C1098–C1113. doi:10.1152/ajpcell.00171.2013
Bjurlin MA, Rosenkrantz AB, Beltran LS, Raad RA, Taneja SS (2015) Imaging and evaluation of patients with high-risk prostate cancer. Nat Rev Urol 12:617–628. doi:10.1038/nrurol.2015.242
Bondue B et al (2015) PET/CT with 18F-FDG- and 18F-FBEM-labeled leukocytes for metabolic activity and leukocyte recruitment monitoring in a mouse model of pulmonary fibrosis. J Nucl Med 56:127–132. doi:10.2967/jnumed.114.147421
Caravan P et al (2007) Collagen-targeted MRI contrast agent for molecular imaging of fibrosis. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 46:8171–8173. doi:10.1002/anie.200700700
Caravan P et al (2013) Molecular magnetic resonance imaging of pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 49:1120–1126. doi:10.1165/rcmb.2013-0039OC
Carmona-Ribeiro AM, de Melo Carrasco LD (2014) Novel formulations for antimicrobial peptides. Int J Mol Sci 15:18040–18083. doi:10.3390/ijms151018040
Chopra A (2004) [99mTc]Vasoactive intestinal peptide-aminobutyric acid-Gly-Gly-(D)-Ala-Gly. Molecular Imaging and Contrast Agent Database
Depraetere H, Viaene A, Deroo S, Vauterin S, Deckmyn H (1998) Identification of peptides, selected by phage display technology, that inhibit von Willebrand factor binding to collagen. Blood 92:4207–4211
Fallowfield JA et al (2014) Relaxin modulates human and rat hepatic myofibroblast function and ameliorates portal hypertension in vivo. Hepatology 59:1492–1504. doi:10.1002/hep.26627
Feng S et al (2014) Modulation, bioinformatic screening, and assessment of small molecular peptides targeting the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor. Cell Biochem Biophys 70:1913–1921. doi:10.1007/s12013-014-0151-x
Fields GB (2010) Synthesis and biological applications of collagen-model triple-helical peptides. Org Biomol Chem 8:1237–1258. doi:10.1039/b920670a
Fuchs BC et al (2013) Molecular MRI of collagen to diagnose and stage liver fibrosis. J Hepatol 59:992–998. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2013.06.026
Helm PA et al (2008) Postinfarction myocardial scarring in mice: molecular MR imaging with use of a collagen-targeting contrast agent. Radiology 247:788–796. doi:10.1148/radiol.2473070975
Helms BA, Reulen SW, Nijhuis S, de Graaf-Heuvelmans PT, Merkx M, Meijer EW (2009) High-affinity peptide-based collagen targeting using synthetic phage mimics: from phage display to dendrimer display. J Am Chem Soc 131:11683–11685. doi:10.1021/ja902285m
Ho YY, Lagares D, Tager AM, Kapoor M (2014) Fibrosis–a lethal component of systemic sclerosis. Nat Rev Rheumatol 10:390–402. doi:10.1038/nrrheum.2014.53
Kilic T et al (2014) Protective and therapeutic effect of molsidomine on bleomycin-induced lung fibrosis in rats. Inflammation 37:1167–1178. doi:10.1007/s10753-014-9841-1
Lee ER, Lamplugh L, Kluczyk B, Leblond CP, Mort JS (2009) Neoepitopes reveal the features of type II collagen cleavage and the identity of a collagenase involved in the transformation of the epiphyses anlagen in development. Dev Dyn 238:1547–1563. doi:10.1002/dvdy.21960
Lee SH, Moroz E, Castagner B, Leroux JC (2014) Activatable cell penetrating peptide-peptide nucleic acid conjugate via reduction of azobenzene PEG chains. J Am Chem Soc 136:12868–12871. doi:10.1021/ja507547w
Li Y et al (2012) Targeting collagen strands by photo-triggered triple-helix hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109:14767–14772. doi:10.1073/pnas.1209721109
Liu Z, Li Z (2014) Molecular imaging in tracking tumor-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes (CTLs). Theranostics 4:990–1001. doi:10.7150/thno.9268
Long KB, Artlett CM, Blankenhorn EP (2014) Tight skin 2 mice exhibit a novel time line of events leading to increased extracellular matrix deposition and dermal fibrosis. Matrix Biol 38:91–100. doi:10.1016/j.matbio.2014.05.002
Lu S et al (2013) Quantitative FRET imaging to visualize the invasiveness of live breast cancer cells. PLoS One 8:e58569. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0058569
Mandal SM, Mahata D, Migliolo L, Parekh A, Addy PS, Mandal M, Basak A (2014) Glucose directly promotes antifungal resistance in the fungal pathogen, Candida spp. J Biol Chem 289:25468–25473. doi:10.1074/jbc.C114.571778
Moore BB, Hogaboam CM (2008) Murine models of pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 294:L152–L160. doi:10.1152/ajplung.00313.2007
Moroni G et al (2012) The value of (18)F-FDG PET/CT in the assessment of active idiopathic retroperitoneal fibrosis. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 39:1635–1642. doi:10.1007/s00259-012-2144-6
Muzard J et al (2009) Non-invasive molecular imaging of fibrosis using a collagen-targeted peptidomimetic of the platelet collagen receptor glycoprotein VI. PLoS One 4:e5585. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0005585
Neeb M, Czodrowski P, Heine A, Barandun LJ, Hohn C, Diederich F, Klebe G (2014) Chasing protons: how isothermal titration calorimetry, mutagenesis, and pKa calculations trace the locus of charge in ligand binding to a tRNA-binding enzyme. J Med Chem 57:5554–5565. doi:10.1021/jm500401x
Pallela VR, Thakur ML, Chakder S, Rattan S (1999) 99 mTc-labeled vasoactive intestinal peptide receptor agonist: functional studies. J Nucl Med 40:352–360
Polasek M et al (2012) Molecular MR imaging of liver fibrosis: a feasibility study using rat and mouse models. J Hepatol 57:549–555. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2012.04.035
Rockey DC, Bell PD, Hill JA (2015) Fibrosis—a common pathway to organ injury and failure. N Engl J Med 372:1138–1149. doi:10.1056/NEJMra1300575
Rosado E, Rodriguez-Vilarrupla A, Gracia-Sancho J, Tripathi D, Garcia-Caldero H, Bosch J, Garcia-Pagan JC (2013) Terutroban, a TP-receptor antagonist, reduces portal pressure in cirrhotic rats. Hepatology 58:1424–1435. doi:10.1002/hep.26520
Tye CE, Hunter GK, Goldberg HA (2005) Identification of the type I collagen-binding domain of bone sialoprotein and characterization of the mechanism of interaction. J Biol Chem 280:13487–13492. doi:10.1074/jbc.M408923200
Wahyudi H, Reynolds AA, Li Y, Owen SC, Yu SM (2016) Targeting collagen for diagnostic imaging and therapeutic delivery. J Control Release. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2016.01.007
Win T et al (2012) Novel positron emission tomography/computed tomography of diffuse parenchymal lung disease combining a labeled somatostatin receptor analogue and 2-deoxy-2[18F]fluoro-d-glucose. Mol Imaging 11:91–98
Withana NP et al (2016) Non-invasive imaging of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis using cathepsin protease probes. Sci Rep 6:19755. doi:10.1038/srep19755
Zhang X et al (2013) Visualising liver fibrosis by phase-contrast X-ray imaging in common bile duct ligated mice. Eur Radiol 23:417–423. doi:10.1007/s00330-012-2630-z
Zhang JM, Zhao XM, Wang SJ, Ren XC, Wang N, Han JY, Jia LZ (2014) Evaluation of 99mTc-peptide-ZHER2:342 Affibody(R) molecule for in vivo molecular imaging. Br J Radiol 87:20130484. doi:10.1259/bjr.20130484
Zhao X et al (2014) Preparation and evaluation of (99m)Tc-epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-peptide nucleic acid for visualization of EGFR messenger RNA expression in malignant tumors. J Nucl Med 55:1008–1016. doi:10.2967/jnumed.113.136101
Zheng L, Xie G, Duan G, Yan X, Li Q (2011) High expression of testes-specific protease 50 is associated with poor prognosis in colorectal carcinoma. PLoS One 6:e22203. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0022203
Zhuge Y, Xu J (2001) Rac1 mediates type I collagen-dependent MMP-2 activation. Role in cell invasion across collagen barrier. J Biol Chem 276:16248–16256
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81201119). We would like to thank Hongmin Li and Laiping Xie for their technical advice. We also thank the editors at American Journal Experts for revising the manuscript (certificate verification key: B309-95BB-0D64-4EDD-A057).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This study has been approved by the Ethical Committee of Southwest Hospital of Third Military Medical University and has been performed in accordance with the ethical standards as laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Research involving human participants and/or animals
Statement of human rights: This study has been approved by the Ethical Committee of Southwest Hospital of Third Military Medical University and has been performed in accordance with the ethical standards as laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Statement on the welfare of animals: All applicable international, national and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed.
Informed consent
None.
Additional information
Handling Editor: S. Dai.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, L., Ding, X., Liu, K. et al. Molecular imaging of fibrosis using a novel collagen-binding peptide labelled with 99mTc on SPECT/CT. Amino Acids 49, 89–101 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-016-2328-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-016-2328-7