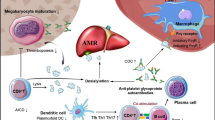
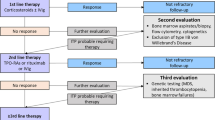
Summary
Immune Thrombocytopenia (ITP) is a rare and – in most patients – mild disease, but might be associated with severe or even life-threatening bleeding complications. The treatment of ITP has partly changed in recent years, due to new therapeutic options. International guidelines changed accordingly. This consensus statement by the Austrian Society of Hematology and Oncology (OEGHO) is not a new evaluation of the current evidence, but rather tries to discuss the available international guidelines and adapt them to the situation in Austria. The subject is primary ITP in adults only. Classification, epidemiology, clinical presentation and diagnostics of ITP, and especially the management of this disease, are discussed in detail. This includes current aspects of first, second, and third line therapies, splenectomy with its indications and contraindications, and the use of new therapeutic options like thrombopoetin receptor agonists (TRA).
Zusammenfassung
Die Immunthrombozytopenie (ITP) ist eine seltene und bei den meisten Patienten nicht schwerwiegende Erkrankung, die jedoch auch zu schwerwiegenden oder sogar lebensbedrohlichen Blutungskomplikationen führen kann. Die Behandlung der ITP hat sich in den letzten Jahren durch neue therapeutische Optionen zum Teil verändert. Dem haben auch neue internationale Leitlinien Rechnung getragen. Das vorliegende Konsensusstatement der Österreichischen Gesellschaft für Hämatologie und Onkologie (ÖGHO) hat nicht das Ziel, vorhandenes Wissen neu zu bewerten, sondern vielmehr die bereits publizierten internationalen Leitlinien für die Situation in Österreich zu diskutieren und zu adaptieren. Behandelt wird dabei nur die primäre ITP des Erwachsenen. Neben Klassifikation, Epidemiologie, Klinik und Diagnostik der primären ITP wird das Management der Erkrankung ausführlich diskutiert. Dabei wird auf aktuelle Aspekte von Therapien erster, zweiter und dritter Wahl, sowie die Splenektomie, deren Indikationen und mögliche Kontraindikationen und die Anwendung neuer Therapiemöglichkeiten, wie z.B. die Thrombopoetinrezeptor-Agonisten (TRA), eingegangen.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Matzdorff A, Giagounidis A, Greinacher A, Hiller E, Kiefel V, Muller-Beissenhirtz H, et al. Diagnosis and therapy of autoimmune thrombocytopenia. Recommendations of a joint Expert Group of DGHO, DGTI, DTH. Onkologie 2010;33(Suppl. 3):2–20
Provan D, Stasi R, Newland AC, Blanchette VS, Bolton-Maggs P, Bussel JB, et al. International consensus report on the investigation and management of primary immune thrombocytopenia. Blood 2010;115:168–86
Rodeghiero F, Stasi R, Gernsheimer T, Michel M, Provan D, Arnold DM, et al. Standardization of terminology, definitions and outcome criteria in immune thrombocytopenic purpura of adults and children: report from an international working group. Blood 2009;113:2386–93
Neunert C, Lim W, Crowther M, Cohen A, Solberg L Jr, Crowther MA. The American Society of Hematology 2011 evidence-based practice guideline for immune thrombocytopenia. Blood 2011;117:4190–207
George JN. Diagnosis, clinical course, and management of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Curr Opin Hematol 1996;3:335–40
Kelton JG, Gibbons S. Autoimmune platelet destruction: idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Semin Thromb Hemost 1982;8:83–104
Stasi R, Stipa E, Masi M, Cecconi M, Scimo MT, Oliva F, et al. Long-term observation of 208 adults with chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Am J Med 1995;98:436–42
Sailer T, Lechner K, Panzer S, Kyrle PA, Pabinger I. The course of severe autoimmune thrombocytopenia in patients not undergoing splenectomy. Haematologica 2006;91:1041–5
Simanek R, Panzer S, Lechner K, Pabinger I. Late spontaneous remissions in severe adult autoimmune thrombocytopenia. Ann Hematol 2007;86:705–10
Abrahamson PE, Hall SA, Feudjo-Tepie M, Mitrani-Gold FS, Logie J. The incidence of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura among adults: a population-based study and literature review. Eur J Haematol 2009;83:83–9
Feudjo-Tepie MA, Robinson NJ, Bennett D. Prevalence of diagnosed chronic immune thrombocytopenic purpura in the US: analysis of a large US claim database: a rebuttal. J Thromb Haemost 2008;6:711–2; author reply 713
Frederiksen H, Schmidt K. The incidence of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura in adults increases with age. Blood 1999;94:909–13
Neylon AJ, Saunders PW, Howard MR, Proctor SJ, Taylor PR. Clinically significant newly presenting autoimmune thrombocytopenic purpura in adults: a prospective study of a population-based cohort of 245 patients. Br J Haematol 2003;122:966–74
Segal JB, Powe NR. Prevalence of immune thrombocytopenia: analyses of administrative data. J Thromb Haemost 2006;4:2377–83
Schoonen WM, Kucera G, Coalson J, Li L, Rutstein M, Mowat F, et al. Epidemiology of immune thrombocytopenic purpura in the general practice research database. Br J Haematol 2009;145:235–44
Cines DB, Blanchette VS. Immune thrombocytopenic purpura. N Engl J Med 2002;346:995–1008
Olsson B, Andersson PO, Jernas M, Jacobsson S, Carlsson B, Carlsson LM, et al. T-cell-mediated cytotoxicity toward platelets in chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Nat Med 2003;9:1123–4
Olsson B, Ridell B, Carlsson L, Jacobsson S, Wadenvik H. Recruitment of T cells into bone marrow of ITP patients possibly due to elevated expression of VLA-4 and CX3CR1. Blood 2008;112:1078–84
Stasi R, Cooper N, Del Poeta G, Stipa E, Laura Evangelista M, Abruzzese E, et al. Analysis of regulatory T-cell changes in patients with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura receiving B cell-depleting therapy with rituximab. Blood 2008;112:1147–50
Yu J, Heck S, Patel V, Levan J, Yu Y, Bussel JB, et al. Defective circulating CD25 regulatory T cells in patients with chronic immune thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood 2008;112:1325–8
Luley KB, Wagner T. Idiopathische thrombozytopenische Purpura (Morbus Werlhof) und ihre Abgrenzung von anderen thrombozytopenischen hämorrhagischen Diathesen. Med Klin 2009;104:372–85
McMillan R, Luiken GA, Levy R, Yelenosky R, Longmire RL. Antibody against megakaryocytes in idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. JAMA 1978;239:2460–2
Alimardani G, Guichard J, Fichelson S, Cramer EM. Pathogenic effects of anti-glycoprotein Ib antibodies on megakaryocytes and platelets. Thromb Haemost 2002;88:1039–46
Chang M, Nakagawa PA, Williams SA, Schwartz MR, Imfeld KL, Buzby JS, et al. Immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) plasma and purified ITP monoclonal autoantibodies inhibit megakaryocytopoiesis in vitro. Blood 2003;102:887–95
Houwerzijl EJ, Blom NR, van der Want JJ, Esselink MT, Koornstra JJ, Smit JW, et al. Ultrastructural study shows morphologic features of apoptosis and para-apoptosis in megakaryocytes from patients with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood 2004;103:500–6
McMillan R, Wang L, Tomer A, Nichol J, Pistillo J. Suppression of in vitro megakaryocyte production by antiplatelet autoantibodies from adult patients with chronic ITP. Blood 2004;103:1364–9
Ballem PJ, Segal GM, Stratton JR, Gernsheimer T, Adamson JW, Slichter SJ. Mechanisms of thrombocytopenia in chronic autoimmune thrombocytopenic purpura. Evidence of both impaired platelet production and increased platelet clearance. J Clin Invest 1987;80:33–40
Louwes H, Zeinali Lathori OA, Vellenga E, de Wolf JT. Platelet kinetic studies in patients with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Am J Med 1999;106:430–4
Siegel RS, Rae JL, Barth S, Coleman RE, Reba RC, Kurlander R, et al. Platelet survival and turnover: important factors in predicting response to splenectomy in immune thrombocytopenic purpura. Am J Hematol 1989;30:206–12
Keine Autoren angegeben. Guidelines for the investigation and management of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura in adults, children and in pregnancy. Br J Haematol 2003;120:574–96
George JN, Woolf SH, Raskob GE, Wasser JS, Aledort LM, Ballem PJ, et al. Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura: A practice guideline developed by explicit methods for the American Society of Hematology. Blood 1996;88:3–40
Stasi R, Amadori S, Osborn J, Newland AC, Provan D. Long-term outcome of otherwise healthy individuals with incidentally discovered borderline thrombocytopenia. PLoS Med 2006;3:e24
Aledort LM, Hayward CP, Chen MG, Nichol JL, Bussel J. Prospective screening of 205 patients with ITP, including diagnosis, serological markers, and the relationship between platelet counts, endogenous thrombopoietin, and circulating antithrombopoietin antibodies. Am J Hematol 2004;76:205–13
Raife TJ, Olson JD, Lentz SR. Platelet antibody testing in idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood 1997;89:1112–4
Stasi R, Stipa E, Masi M, Oliva F, Sciarra A, Perrotti A, et al. Prevalence and clinical significance of elevated antiphospholipid antibodies in patients with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood 1994;84:4203–8
Anderson MJ, Peebles CL, McMillan R, Curd JG. Fluorescent antinuclear antibodies and anti-SS-A/Ro in patients with immune thrombocytopenia subsequently developing systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Intern Med 1985;103:548–50
Kurata Y, Miyagawa S, Kosugi S, Kashiwagi H, Honda S, Mizutani H, et al. High-titer antinuclear antibodies, anti-SSA/Ro antibodies and anti-nuclear RNP antibodies in patients with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Thromb Haemost 1994;71:184–7
Khellaf M, Quittet P, Viallard J-F, Alexis M, Cheze S, Durand J-M, et al. Safety and Efficacy of Romiplostim in Immune Thrombocytopenia (ITP) in the "real-life": Result of the french experience in 72 adults. ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts, Blood 2009;114; Abstract #3519
Soupir CP, Vergilio JA, Kelly E, Dal Cin P, Kuter D, Hasserjian RP. Identification of del(20q) in a subset of patients diagnosed with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Br J Haematol 2009;144:800–2
Heddle NM, Cook RJ, Tinmouth A, Kouroukis CT, Hervig T, Klapper E, et al. A randomized controlled trial comparing standard- and low-dose strategies for transfusion of platelets (SToP) to patients with thrombocytopenia. Blood 2009;113:1564–73
Miller AB, Hoogstraten B, Staquet M, Winkler A. Reporting results of cancer treatment. Cancer 1981;47:207–14
National Cancer Institute. NCI Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events: CTCAE, version MedDRA v9.0. [cited Jänner 2010]; Erhältlich unter: www.cancer.gov
Portielje JE, Westendorp RG, Kluin-Nelemans HC, Brand A. Morbidity and mortality in adults with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood 2001;97:2549–54
Cohen YC, Djulbegovic B, Shamai-Lubovitz O, Mozes B. The bleeding risk and natural history of idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura in patients with persistent low platelet counts. Arch Intern Med 2000;160:1630–8
Bellucci S, Charpak Y, Chastang C, Tobelem G. Low doses v conventional doses of corticoids in immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) results of a randomized clinical trial in 160 children, 223 adults. Blood 1988;71:1165–9
George JN, el-Harake MA, Raskob GE. Chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. N Engl J Med 1994;331:1207–11
Pizzuto J, Ambriz R. Therapeutic experience on 934 adults with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura: Multicentric trial of the cooperative latin American group on hemostasis and thrombosis. Blood 1984;64:1179–83
Stasi R, Provan D. Management of immune thrombocytopenic purpura in adults. Mayo Clin Proc 2004;79:504–22
Cheng Y, Wong RS, Soo YO, Chui CH, Lau FY, Chan NP, et al. Initial treatment of immune thrombocytopenic purpura with high-dose dexamethasone. N Engl J Med 2003;349:831–6
Zaja F, Baccarani M, Mazza P, Bocchia M, Gugliotta L, Zaccaria A, et al. Dexamethasone plus rituximab yields higher sustained response rates than dexamethasone monotherapy in adults with primary immune thrombocytopenia. Blood 2010;115:2755–62
Bae SH, Ryoo HM, Lee WS, Yoo YD, Lee KH, Lee JH, et al. High Dose Dexamethasone Vs. Conventional Dose Prednisolone for Adults with Immune Thrombocytopenia: A Prospective Multicenter Phase III Trial. ASH Annual Meeting. Orlando. Abstract #3687, 2010
Clynes R. Immune complexes as therapy for autoimmunity. J Clin Invest 2005;115:25–7
Rault R, Piraino B, Johnston JR, Oral A. Pulmonary and renal toxicity of intravenous immunoglobulin. Clin Nephrol 1991;36:83–6
Ruggeri M, Castaman G, De Nardi G, Rodeghiero F. Acute renal failure after high-dose intravenous immune globulin in a patient with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Haematologica 1993;78:338–9
Woodruff RK, Grigg AP, Firkin FC, Smith IL. Fatal thrombotic events during treatment of autoimmune thrombocytopenia with intravenous immunoglobulin in elderly patients. Lancet 1986;2:217–8
Caress JB, Hobson-Webb L, Passmore LV, Finkbiner AP, Cartwright MS. Case-control study of thromboembolic events associated with IV immunoglobulin. J Neurol 2009;256:339–42
Scaradavou A, Woo B, Woloski BM, Cunningham-Rundles S, Ettinger LJ, Aledort LM, et al. Intravenous anti-D treatment of immune thrombocytopenic purpura: experience in 272 patients. Blood 1997;89:2689–700
Lazarus AH, Crow AR. Mechanism of action of IVIG and anti-D in ITP. Transfus Apher Sci 2003;28:249–55
Gaines AR. Disseminated intravascular coagulation associated with acute hemoglobinemia or hemoglobinuria following Rh(0)(D) immune globulin intravenous administration for immune thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood 2005;106:1532–7
Salama A, Kiesewetter H, Kalus U, Movassaghi K, Meyer O. Massive platelet transfusion is a rapidly effective emergency treatment in patients with refractory autoimmune thrombocytopenia. Thromb Haemost 2008;100:762–5
Pamuk GE, Pamuk ON, Baslar Z, Ongoren S, Soysal T, Ferhanoglu B, et al. Overview of 321 patients with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Retrospective analysis of the clinical features and response to therapy. Ann Hematol 2002;81:436–40
Emmons RV, Reid DM, Cohen RL, Meng G, Young NS, Dunbar CE, et al. Human thrombopoietin levels are high when thrombocytopenia is due to megakaryocyte deficiency and low when due to increased platelet destruction. Blood 1996;87:4068–71
Nichol JL. Endogenous TPO (eTPO) levels in health and disease: possible clues for therapeutic intervention. Stem Cells 1998;16(Suppl. 2):165–75
Bussel JB, Provan D, Shamsi T, Cheng G, Psaila B, Kovaleva L, et al. Effect of eltrombopag on platelet counts and bleeding during treatment of chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura: a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2009;373:641–8
Cheng G, Saleh MN, Marcher C, Vasey S, Mayer B, Aivado M, et al. Eltrombopag for management of chronic immune thrombocytopenia (RAISE) a 6-month, randomised, phase 3 study. Lancet 2011;377:393–402
Kuter DJ, Bussel JB, Lyons RM, Pullarkat V, Gernsheimer TB, Senecal FM, et al. Efficacy of romiplostim in patients with chronic immune thrombocytopenic purpura: A double-blind randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2008;371:395–403
Kuter DJ, Rummel M, Boccia R, Macik BG, Pabinger I, Selleslag D, et al. Romiplostim or standard of care in patients with immune thrombocytopenia. N Engl J Med 2010;363:1889–99
Bussel JB, Kuter DJ, Pullarkat V, Lyons RM, Guo M, Nichol JL. Safety and efficacy of long-term treatment with romiplostim in thrombocytopenic patients with chronic ITP. Blood 2009;113:2161–71
Stasi R, Pagano A, Stipa E, Amadori S. Rituximab chimeric anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody treatment for adults with chronic idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Blood 2001;98:952–7
Giagounidis AA, Anhuf J, Schneider P, Germing U, Sohngen D, Quabeck K, et al. Treatment of relapsed idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura with the anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody rituximab: A pilot study. Eur J Haematol 2002;69:95–100
Braendstrup P, Bjerrum OW, Nielsen OJ, Jensen BA, Clausen NT, Hansen PB, et al. Rituximab chimeric anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody treatment for adult refractory idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Am J Hematol 2005;78:275–80
Penalver FJ, Jimenez-Yuste V, Almagro M, Alvarez-Larran A, Rodriguez L, Casado M, et al. Rituximab in the management of chronic immune thrombocytopenic purpura: an effective and safe therapeutic alternative in refractory patients. Ann Hematol 2006;85:400–6
Godeau B, Porcher R, Fain O, Lefrere F, Fenaux P, Cheze S, et al. Rituximab efficacy and safety in adult splenectomy candidates with chronic immune thrombocytopenic purpura: results of a prospective multicenter phase 2 study. Blood 2008;112:999–1004
Arnold DM, Dentali F, Crowther MA, Meyer RM, Cook RJ, Sigouin C, et al. Systematic review: efficacy and safety of rituximab for adults with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura. Ann Intern Med 2007;146:25–33
Provan D, Butler T, Evangelista ML, Amadori S, Newland AC, Stasi R. Activity and safety profile of low-dose rituximab for the treatment of autoimmune cytopenias in adults. Haematologica 2007;92:1695–8
Stasi R, Evangelista ML, Stipa E, Buccisano F, Venditti A, Amadori S. Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura: current concepts in pathophysiology and management. Thromb Haemost 2008;99:4–13
Kaznelson P. Verschwinden der hämorrhagischen Diathese bei einem Falle von "essentieller Thrombopenie" (Frank) nach Milzexstirpation. Splenogene thrombolytische Purpura. Wien Klin Wochenschr 1916;29:1451–4
Kojouri K, Vesely SK, Terrell DR, George JN. Splenectomy for adult patients with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura: a systematic review to assess long-term platelet count responses, prediction of response, and surgical complications. Blood 2004;104:2623–34
Stasi R, Newland A, Thornton P, Pabinger I. Should medical treatment options be exhausted before splenectomy is performed in adult ITP patients? A debate. Ann Hematol 2010;89:1185–95
Winslow ER, Brunt LM. Perioperative outcomes of laparoscopic versus open splenectomy: A meta-analysis with an emphasis on complications. Surgery 2003;134:647–653; discussion 654–645
Schilling RF. Estimating the risk for sepsis after splenectomy in hereditary spherocytosis. Ann Intern Med 1995;122:187–8
Singer DB. Postsplenectomy sepsis. Perspect Pediatr Pathol 1973;1:285–311
O'Neal BJ, McDonald JC. The risk of sepsis in the asplenic adult. Ann Surg 1981;194:775–8
Schwartz PE, Sterioff S, Mucha P, Melton LJ, 3rd, Offord KP. Postsplenectomy sepsis and mortality in adults. JAMA 1982;248:2279–83
Waghorn DJ. Overwhelming infection in asplenic patients: current best practice preventive measures are not being followed. J Clin Pathol 2001;54:214–8
Thomsen RW, Schoonen WM, Farkas DK, Riis A, Jacobsen J, Fryzek JP, et al. Risk for hospital contact with infection in patients with splenectomy: A population-based cohort study. Ann Intern Med 2009;151:546–55
Crary SE, Buchanan GR. Vascular complications after splenectomy for hematologic disorders. Blood 2009;114:2861–8
Newland A, Provan D, Myint S. Preventing severe infection after splenectomy. BMJ 2005;331:417–8
Dolan JP, Sheppard BC, DeLoughery TG. Splenectomy for immune thrombocytopenic purpura: surgery for the 21st century. Am J Hematol 2008;83:93–6.
Wolters U, Wolf T, Stutzer H, Schroder T. ASA classification and perioperative variables as predictors of postoperative outcome. Br J Anaesth 1996;77:217–22
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pabinger, I., Gastl, G., Steurer, M. et al. Primäre Immunthrombozytopenie des Erwachsenen – Diagnostik und Therapie, Konsensus-Statement der Österreichischen Gesellschaft für Hämatologie und Onkologie (ÖGHO). Wien Klin Wochenschr 124, 111–123 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00508-012-0123-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00508-012-0123-3