Abstract
Autologous endothelial progenitor cell (EPC) transplantation has been suggested as a potential therapeutic approach in diabetic neuropathy (DN). However, such treatment might be limited by safety concerns regarding possible unwanted proliferation or differentiation of the transplanted stem cells. An alternative approach is the stimulation of endogenous bone-marrow-derived EPC (BM-EPC) recruitment into ischemic lesions by the administration of stem cell mobilization agents or chemokines. We first tested the EPC mobilization effect of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and AMD3100 in a mouse model of diabetes and found that AMD3100 was effective as an EPC mobilization agent, whereas VEGF did not increase circulating EPCs in these animals. Because recent studies have suggested that deceased local expression of stromal-cell-derived factor (SDF)-1α in diabetes is the main cause of defective EPC migration, AMD3100 was administrated systemically to stimulate EPC mobilization and SDF-1α was injected locally to enhance its migration into the streptozotocin-induced DN mice model. This combined therapy increased local expression levels of vasculogenesis-associated factors and newly formed endothelial cells in the sciatic nerve, resulting in the restoration of the sciatic vasa nervorum. The treatment also improved the impaired conduction velocity of the sciatic nerve in DN mice. Thus, AMD3100 might be an effective EPC mobilization agent in diabetes, with local SDF-1α injection synergistically increasing vascularity in diabetic nerves. This represents a novel potential therapeutic option for DN patients.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aicher A, Heeschen C, Mildner-Rihm C, Urbich C, Ihling C, Technau-Ihling K, Zeiher AM, Dimmeler S (2003) Essential role of endothelial nitric oxide synthase for mobilization of stem and progenitor cells. Nat Med 9:1370–1376
Asahara T, Murohara T, Sullivan A, Silver M, van der Zee R, Li T, Witzenbichler B, Schatteman G, Isner JM (1997) Isolation of putative progenitor endothelial cells for angiogenesis. Science 275:964–967
Byrd N, Grabel L (2004) Hedgehog signaling in murine vasculogenesis and angiogenesis. Trends Cardiovasc Med 14:308–313
Calcutt NA, Allendoerfer KL, Mizisin AP, Middlemas A, Freshwater JD, Burgers M, Ranciato R, Delcroix JD, Taylor FR, Shapiro R, Strauch K, Dudek H, Engber TM, Galdes A, Rubin LL, Tomlinson DR (2003) Therapeutic efficacy of sonic hedgehog protein in experimental diabetic neuropathy. J Clin Invest 111:507–514
Cameron NE, Cotter MA, Low PA (1991) Nerve blood flow in early experimental diabetes in rats: relation to conduction deficits. Am J Physiol 261:E1–E8
Capoccia BJ, Shepherd RM, Link DC (2006) G-CSF and AMD3100 mobilize monocytes into the blood that stimulate angiogenesis in vivo through a paracrine mechanism. Blood 108:2438–2445
Ceradini DJ, Kulkarni AR, Callaghan MJ, Tepper OM, Bastidas N, Kleinman ME, Capla JM, Galiano RD, Levine JP, Gurtner GC (2004) Progenitor cell trafficking is regulated by hypoxic gradients through HIF-1 induction of SDF-1. Nat Med 10:858–864
Duda DG, Fukumura D, Jain RK (2004) Role of eNOS in neovascularization: NO for endothelial progenitor cells. Trends Mol Med 10:143–145
Fadini GP, Sartore S, Agostini C, Avogaro A (2007) Significance of endothelial progenitor cells in subjects with diabetes. Diabetes Care 30:1305–1313
Fernyhough P, Diemel LT, Hardy J, Brewster WJ, Mohiuddin L, Tomlinson DR (1995) Human recombinant nerve growth factor replaces deficient neurotrophic support in the diabetic rat. Eur J Neurosci 7:1107–1110
Fernyhough P, Diemel LT, Tomlinson DR (1998) Target tissue production and axonal transport of neurotrophin-3 are reduced in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Diabetologia 41:300–306
Gallagher KA, Liu ZJ, Xiao M, Chen H, Goldstein LJ, Buerk DG, Nedeau A, Thom SR, Velazquez OC (2007) Diabetic impairments in NO-mediated endothelial progenitor cell mobilization and homing are reversed by hyperoxia and SDF-1 alpha. J Clin Invest 117:1249–1259
Goldstein LJ, Gallagher KA, Bauer SM, Bauer RJ, Baireddy V, Liu ZJ, Buerk DG, Thom SR, Velazquez OC (2006) Endothelial progenitor cell release into circulation is triggered by hyperoxia-induced increases in bone marrow nitric oxide. Stem Cells 24:2309–2318
Hasegawa T, Kosaki A, Shimizu K, Matsubara H, Mori Y, Masaki H, Toyoda N, Inoue-Shibata M, Nishikawa M, Iwasaka T (2006) Amelioration of diabetic peripheral neuropathy by implantation of hematopoietic mononuclear cells in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Exp Neurol 199:274–280
Jarajapu YP, Grant MB (2010) The promise of cell-based therapies for diabetic complications: challenges and solutions. Circ Res 106:854–869
Jeong JO, Kim MO, Kim H, Lee MY, Kim SW, Ii M, Lee JU, Lee J, Choi YJ, Cho HJ, Lee N, Silver M, Wecker A, Kim DW, Yoon YS (2009) Dual angiogenic and neurotrophic effects of bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells on diabetic neuropathy. Circulation 119:699–708
Jiao C, Fricker S, Schatteman GC (2006) The chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 4 inhibitor AMD3100 accelerates blood flow restoration in diabetic mice. Diabetologia 49:2786–2789
Kalka C, Masuda H, Takahashi T, Kalka-Moll WM, Silver M, Kearney M, Li T, Isner JM, Asahara T (2000) Transplantation of ex vivo expanded endothelial progenitor cells for therapeutic neovascularization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:3422–3427
Kawamoto A, Tkebuchava T, Yamaguchi J, Nishimura H, Yoon YS, Milliken C, Uchida S, Masuo O, Iwaguro H, Ma H, Hanley A, Silver M, Kearney M, Losordo DW, Isner JM, Asahara T (2003) Intramyocardial transplantation of autologous endothelial progenitor cells for therapeutic neovascularization of myocardial ischemia. Circulation 107:461–468
Kazemi S, Wenzel D, Kolossov E, Lenka N, Raible A, Sasse P, Hescheler J, Addicks K, Fleischmann BK, Bloch W (2002) Differential role of bFGF and VEGF for vasculogenesis. Cell Physiol Biochem 12:55–62
Kim H, Park JS, Choi YJ, Kim MO, Huh YH, Kim SW, Han JW, Lee J, Kim S, Houge MA, Ii M, Yoon YS (2009) Bone marrow mononuclear cells have neurovascular tropism and improve diabetic neuropathy. Stem Cells 27:1686–1696
Kusano KF, Allendoerfer KL, Munger W, Pola R, Bosch-Marce M, Kirchmair R, Yoon YS, Curry C, Silver M, Kearney M, Asahara T, Losordo DW (2004) Sonic hedgehog induces arteriogenesis in diabetic vasa nervorum and restores function in diabetic neuropathy. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 24:2102–2107
Leng Q, Nie Y, Zou Y, Chen J (2008) Elevated CXCL12 expression in the bone marrow of NOD mice is associated with altered T cell and stem cell trafficking and diabetes development. BMC Immunol 9:51
Loomans CJ, de Koning EJ, Staal FJ, Rookmaaker MB, Verseyden C, de Boer HC, Verhaar MC, Braam B, Rabelink TJ, van Zonneveld AJ (2004) Endothelial progenitor cell dysfunction: a novel concept in the pathogenesis of vascular complications of type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 53:195–199
Massberg S, Konrad I, Schürzinger K, Lorenz M, Schneider S, Zohlnhoefer D, Hoppe K, Schiemann M, Kennerknecht E, Sauer S, Schulz C, Kerstan S, Rudelius M, Seidl S, Sorge F, Langer H, Peluso M, Goyal P, Vestweber D, Emambokus NR, Busch DH, Frampton J, Gawaz M (2006) Platelets secrete stromal cell-derived factor 1alpha and recruit bone marrow-derived progenitor cells to arterial thrombi in vivo. J Exp Med 203:1221–1233
Mochizuki Y, Ojima K, Uezumi A, Masuda S, Yoshimura K, Takeda S (2005) Participation of bone marrow-derived cells in fibrotic changes in denervated skeletal muscle. Am J Pathol 166:1721–1732
Nakae M, Kamiya H, Naruse K, Horio N, Ito Y, Mizubayashi R, Hamada Y, Nakashima E, Akiyama N, Kobayashi Y, Watarai A, Kimura N, Horiguchi M, Tabata Y, Oiso Y, Nakamura J (2006) Effects of basic fibroblast growth factor on experimental diabetic neuropathy in rats. Diabetes 55:1470–1477
Naruse K, Hamada Y, Nakashima E, Kato K, Mizubayashi R, Kamiya H, Yuzawa Y, Matsuo S, Murohara T, Matsubara T, Oiso Y, Nakamura J (2005) Therapeutic neovascularization using cord blood-derived endothelial progenitor cells for diabetic neuropathy. Diabetes 54:1823–1828
Nishimura Y, Ii M, Qin G, Hamada H, Asai J, Takenaka H, Sekiguchi H, Renault MA, Jujo K, Katoh N, Kishimoto S, Ito A, Kamide C, Kenny J, Millay M, Misener S, Thorne T, Losordo DW (2012) CXCR4 antagonist AMD3100 accelerates impaired wound healing in diabetic mice. J Invest Dermatol 132:711–720
Park L, Raman KG, Lee KJ, Lu Y, Ferran LJ Jr, Chow WS, Stern D, Schmidt AM (1998) Suppression of accelerated diabetic atherosclerosis by the soluble receptor for advanced glycation endproducts. Nat Med 4:1025–1031
Petit I, Jin D, Rafii S (2007) The SDF-1-CXCR4 signaling pathway: a molecular hub modulating neo-angiogenesis. Trends Imunol 28:299–307
Pitchford SC, Furze RC, Jones CP, Wengner AM, Rankin SM (2009) Differential mobilization of subsets of progenitor cells from the bone marrow. Cell Stem Cell 4:62–72
Romagnani P, Annunziato F, Liotta F, Lazzeri E, Mazzinghi B, Frosali F, Cosmi L, Maggi L, Lasagni L, Scheffold A, Kruger M, Dimmeler S, Marra F, Gensini G, Maggi E, Romagnani S (2005) CD14+CD34low cells with stem cell phenotypic and functional features are the major source of circulating endothelial progenitors. Circ Res 97:314–322
Schratzberger P, Walter DH, Rittig K, Bahlmann FH, Pola R, Curry C, Silver M, Krainin JG, Weinberg DH, Ropper AH, Isner JM (2001) Reversal of experimental diabetic neuropathy by VEGF gene transfer. J Clin Invest 107:1083–1092
Shepherd RM, Capoccia BJ, Devine SM, Dipersio J, Trinkaus KM, Ingram D, Link DC (2006) Angiogenic cells can be rapidly mobilized and efficiently harvested from the blood following treatment with AMD3100. Blood 108:3662–3667
Shibata T, Naruse K, Kamiya H, Kozakae M, Kondo M, Yasuda Y, Nakamura N, Ota K, Tosaki T, Matsuki T, Nakashima E, Hamada Y, Oiso Y, Nakamura J (2008) Transplantation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells improves diabetic polyneuropathy in rats. Diabetes 57:3099–3107
Shyu WC, Lin SZ, Chiang MF, Su CY, Li H (2006) Intracerebral peripheral blood stem cell (CD34+) implantation induces neuroplasticity by enhancing beta1 integrin-mediated angiogenesis in chronic stroke rats. J Neurosci 26:3444–3453
Tepper OM, Galiano RD, Capla JM, Kalka C, Gagne PJ, Jacobowitz GR, Levine JP, Gurtner GC (2002) Human endothelial progenitor cells from type II diabetics exhibit impaired proliferation, adhesion, and incorporation into vascular structures. Circulation 106:2781–2786
Tepper OM, Capla JM, Galiano RD, Ceradini DJ, Callaghan MJ, Kleinman ME, Gurtner GC (2005) Adult vasculogenesis occurs through in situ recruitment, proliferation, and tubulization of circulating bone marrow-derived cells. Blood 105:1068–1077
Thum T, Fraccarollo D, Schultheiss M, Froese S, Galuppo P, Widder JD, Tsikas D, Ertl G, Bauersachs J (2007) Endothelial nitric oxide synthase uncoupling impairs endothelial progenitor cell mobilization and function in diabetes. Diabetes 56:666–674
Yamaguchi J, Kusano KF, Masuo O, Kawamoto A, Silver M, Murasawa S, Bosch-Marce M, Masuda H, Losordo DW, Isner JM, Asahara T (2003) Stromal cell-derived factor-1 effects on ex vivo expanded endothelial progenitor cell recruitment for ischemic neovascularization. Circulation 107:1322–1328
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
B.J.K. and J.K.L. contributed equally to this work.
This work was supported by a grant of the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program (2012M3A9C6049913, 2010-0020234) and World Class University Program (R32-10064) of the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology, Republic of Korea. It was also supported by the Korea Healthcare Technology R&D Project, Ministry for Health, Welfare & Family Affairs, Republic of Korea (A084065).
The authors declare no potential conflicts of interest.
J.S.B. designed all experiments; B.J.K., J.K.L. and H.K.J. performed the experiments; H.K.J. and J.S.B. supervised the project; B.J.K. and J.K.L. wrote the manuscript; J.S.B. and E.H.S. edited and reviewed the manuscript.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Fig. 1
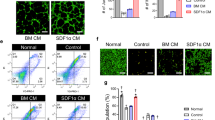
Co-treatment of AMD3100 and SDF-1α induces the restoration of sciatic vasa nervorum but the effects last less than 3 weeks. Sciatic nerve vasa nervorum were stained by in vivo perfusion with FITC-conjugated BS-1 lectin at 21 days after treatment. a Representative fluorescence images of cross-sections of BS-1-lectin-perfused mouse sciatic nerves. Bar 50 μm. b The number of vessels per cross-section was quantified. The number of vessels was not significantly different between all experimental groups (n = 3 per group). Data represent means ± SEM. Tukey’s HSD test. (JPEG 48 kb)
High-resolution Image
(TIFF 430 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, B.J., Lee, J.K., Schuchman, E.H. et al. Synergistic vasculogenic effects of AMD3100 and stromal-cell-derived factor-1α in vasa nervorum of the sciatic nerve of mice with diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Cell Tissue Res 354, 395–407 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-013-1689-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-013-1689-4