Abstract
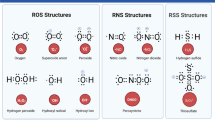
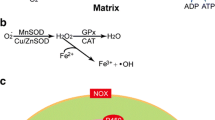
Substantial evidence implies that redox imbalance attributable to an overproduction of reactive oxygen species or reactive nitrogen species that overwhelm the protective defense mechanism of cells contributes to all forms of Parkinson’s disease. Factors such as dopamine, neuromelanin, and transition metals may, under certain circumstances, contribute to the formation of oxygen species such as H2O2, superoxide radicals, and hydroxyl radicals and react with reactive nitrogen species such as nitric oxide or peroxinitrite. Mitochodrial dysfunction and excitotoxicity may be a cause and a result of oxidative stress. Consequences of this redox imbalance are lipid peroxidation, oxidation of proteins, DNA damage, and interference of reactive oxygen species with signal transduction pathways. These consequences become even more harmful when genetic variations impair the normal degradation of altered proteins. Therefore, therapeutic strategies must aim at reducing free-radical formation and scavenging free-radicals.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alam ZI, Jenner A, Daniel SE, Lees AJ, Cairns N, Marsden CD, Jenner P, Halliwell B (1997) Oxidative DNA damage in the parkinsonian brain: a selective increase in 8-hydroxyguanine in substantia nigra? J Neurochem 69:1196–1203
Ambani LM, Van Woert MH, Murphy S (1975) Brain peroxidase and catalase in Parkinson’s disease. Arch Neurol 32:114–118
Antunes F, Han D, Rettori D, Cadenas E (2002) Mitochondrial damage by nitric oxide potentiated by dopmaine in PC12 cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1556:233–238
Barbeau A, Roy M, Cloutier T, Plasse L, Paris S (1987) Environmental and genetic factors in the etiology of Parkinson’s disease. Adv Neurol 45:299–306
Beal MF (2003) Bioenergetic approaches for neuroprotection in Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 53:S39–S47
Beck KD, Knusel B, Hefti F (1993) The nature of the trophic action of brain-derived neurotrophic factor, des(T-3)-insulin-like growth factor, and basic fibroblast growth factor on mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons developing in culture. Neuroscience 52:855–866
Becker G, Seufert J, Bogdahn U, Reichmann H, Reiners K (1995) Degeneration of substantia nigra in chronic Parkinson’s disease visualized by transcranial color-coded real-time sonography. Neurology 45:182–184
Beckmann JS (1996) Oxidative damage and tyrosine nitration from peroxynitrite. Chem Res Toxicol 9:836–844
Ben-Shachar D, Eshel G, Finberg JP, Youdim MB (1991a) The iron chelator desferrioxamine (Desferal) retards 6-hydroxydopamine-induced degeneration of nigrostriatal dopamine neurons. J Neurochem 56:1441–1444
Ben-Shachar, D, Riederer, P, Youdim, MB (1991b) Iron-melanin interaction and lipid peroxidation: implications for Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 57:1609–1614
Berg D, Grote C, Rausch W-D, Mäurer M, Wesemann W, Riederer P, Becker G (1999a) Iron accumulation of the substantia nigra in rats visualized by ultrasound. Ultrasound Med Biol 25:901–904
Berg D, Roggendorf W, Schröder U, Klein R, Tatschner T, Benz P, Tucha O, Preier M, Lange KW, Reiners K, Gerlach M, Becker G (2002) Echogenicity of the substantia nigra—association with increased iron content and marker for susceptibility to nigrostriatal injury. Arch Neurol 59:999–1005
Bharat S, Hsu M, Kaur D, Rajagopalan S, Andersen JK (2002) Glutathione, iron and Parkinson’s disease. Biochem Pharmacol 64:1037–1048
Borie C, Gasparini F, Verpillat P, Bonnet AM, Agid Y, Hetet G, Brice A, Durr A, Grandchamp B (2002) French Parkinson’s disease genetic study group. Association study between iron-related genes polymorphisms and Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol 249:801–804
Braak H, Del Tredici K, Vos RA de, Jansen Steur EN, Braak E (2003) Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 24:197–211
Bredt DS (1999) Endogenous nitric oxide synthesis: biological functions and pathophysiology. Free Radic Res 31:577–596
Butterfield DA, Castegna A, Lauderback CM, Drake J (2002) Evidence that amyloid beta-peptide-induced lipid peroxidation and its sequelae in Alzheimer’s disease brain contribute to neuronal death. Neurobiol Aging 23:655–664
Calabrese V, Scapagnini G, Colombrita C, Ravagna A, Pennisi G, Giuffrida Stella AM, Galli F, Butterfield DA (2003) Redox regulation of heat shock protein expression in aging and neurodegenerative disorders associated with oxidative stress: a nutritional approach. Amino Acids 25:437–444
Carreras MC, Franco MC, Peralta JG, Poderoso JJ (2004) Nitric oxide, complex I, and the modulation of mitochondrial reactive species in biology and disease. Mol Aspects Med 25:125–139
Castellani RJ, Siedlak SL, Perry S, Smith MA (2000) Sequestration of iron by Lewy bodies in Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathol 100:111–114
Chan TS, Teng S, Wilson JX, Galati G, Khan S, O’Brien PJ (2002) Coenzyme Q cytoprotective mechanisms for mitochondrial complex I cytopathies involves NAD(P)H: quinone oxidoreductase 1(NQO1). Free Radic Res 36:421–427
Choi HJ, Kim SW, Lee SY, Hwang O (2003) Dopamine-dependent cytotoxicity of tetrahydrobiopterin: a possible mechanism for selective neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 86:143–152
Cuajungco MP, Lees GJ (1997) Zinc metabolism in the brain: relevance to human neurodegenerative disorders. Neurobiol Dis 4:137–169
D’Amato RJ, Lipman ZP, Snyder SH (1986) Selectivity of the Parkinson neurotoxin MPTP: toxic metabolite MPP+ binds to neuromelanin. Science 231 987–989
Damier P, Hirsch EC, Zhang P, Agid Y, Javoy-Agid F (1993) Glutathione peroxidase, glial cells and Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience 52:1–6
David GC, Williams AC, Markey SP, Ebert MH, Caine ED, Reichert CM, Kopin IJ (1979) Chronic Parkinsonism secondary to intravenous injection of meperidine analogues. Psychiat Res 1:249–PF Sz
Dawson TM, Dawson VL (2003) Molecular pathways of neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease. Science 302:819–822
Deplazes J, Schobel K, Hochstrasser H, Bauer P, Walter U, Behnke S, Spiegel J, Becker G, Riess O, Berg D (2004) Screening for mutations of the IRP2 gene in Parkinson’s disease patients with hyperechogenicity of the substantia nigra. J Neural Transm 111:515–521
Desagher S, Glowinski J, Premont J (1997) Pyruvate protects neurons against hydrogen peroxide-induced toxicity. J Neurosci 17:9060–9067
Dexter DT, Carter CJ, Wells FR, Javoy-Agid F, Agid Y, Lees A, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1989) Basal lipid peroxidation in substantia nigra is increased in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 52:381–389
Dexter DT, Sian J, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1993) Implications of alterations in trace element levels in brain in Parkinson’s disease and other neurological disorders affecting the basal ganglia. Adv Neurol 60:273–281
Double KL, Riederer P, Gerlach M (1999) Significance of neuromelanin for neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease. Drug News Perspect 12:333–340
Double KL, Gerlach M, Youdim MBH, Riederer P (2000) Impaired iron homeostasis in Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm 60:37–58
Double KL, Gerlach M, Schunemann V, Trautwein AX, Zecca L, Gallorini M, Youdim MB, Riederer P, Ben-Shachar D (2003a) Iron-binding characteristics of neuromelanin of the human substantia nigra. Biochem Pharmacol 66:489–494
Double KL, Halliday GM, Henderson J, Griffiths FM, Heinemann T, Riederer P, Gerlach M (2003b) The dopamine receptor agonist lisuride attenuates iron-mediated dopaminergic neurodegeneration. Exp Neurol 184:530–535
Faucheux BA, Martin ME, Beaumont C, Hauw JJ, Agid Y, Hirsch EC (2003) Neuromelanin associated redox-active iron is increased in the substantia nigra of patients with Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 86:1142–1148
Felletschin B, Bauer P, Walter U, Behnke S, Spiegel J, Csoti I, Sommer U, Zeiler B, Becker G, Riess O, Berg D (2003) Screening for mutations of the ferritin light and heavy genes in Parkinson’s disease patients with hyperechogenicity of the substantia nigra. Neurosci Lett 352:53–56
Fiskum G, Starkov A, Polster BM, Chinopoulos C (2003) Mitochondrial mechanisms of neural cell death and neuroprotective interventions in Parkinson’s disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 991:111–119
Forsleff L, Schauss AG, Bier ID, Stuart S (1999) Evidence of functional zinc deficiency in Parkinson’s disease. J Altern Complement Med 5:57–64
Gao HM, Jiang J, Wilson B, Zhang W, Hong JS, Liu B (2002) Microglia activation-mediated delayed and progressive degeneration of rat nigral dopaminergic neurons: relevance to Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 81:1285–1297
Gash DM, Zhang Z, Ovadia A, Cass WA, Yi A, Simmerman L, Russell D, Martin D, Lapchak PA, Collins F, Hoffer BJ, Gerhardt GA (1996) Functional recovery in parkinsonian monkeys treated with GDNF. Nature 380:252–255
Gasser T (2003) Molecular genetics of Parkinon’s disease. In: Calne D, Calne S (eds) Parksinon’s disease. Advances in neurology, vol 86. Lippincott, Philadelphia, pp 23–32
Gerber GB, Leonard A, Hantson P (2002) Carcinogenicity, mutagenicity and teratogenicity of manganese compounds. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 42:25–34
Gerlach M, Ben-Shachar D, Riederer P, Youdim MB (1994) Altered brain metabolism of iron as a cause of neurodegenerative diseases. J Neurochem 63:793–807
Gerlach M, Riederer P, Youdim MBH (1996) Molecular mechanisms for neurodegeneration: synergism between reactive oxygen species, calcium and exitotoxic amino acids. In: Battistin L, Scarlato G, Caraceni T, Ruggieri S (eds) Parkinson’s disease. Advances in neurology, vol 69. Lippincott, Philadelphia, pp 177–194
Gerlach M, Reichmann H, Riederer P (2001) Die Parkinsonkrankheit, Grundlagen, Klinik, Therapie. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Giasson BI, Duda JE, Murray ChenQ IV, Souza JM, Hurtig HI, Ischiropoulos H, Trojanowski JQ, Lee VM (2000) Oxidative damage linked to neurodegeneration by selective alpha-synuclein nitration in synucleinopathy lesions. Science 3:985–989
Goetz ME, Gerlach M (2004) Formation of radicals. In: Herdegen T, Delgado-Garcia J (eds) Brain damage and repair. Kluwer, London, pp 135–164
Golbe LI, Mouradian MM (2004) Alpha-synuclein in Parkinson’s disease: light from two new angles. Ann Neurol 55:153–156
Golts N, Snyder H, Frasier M, Theisler C, Choi P, Wolozin B (2002) Magnesium inhibits spontaneous and iron-induced aggregation of alpha-synuclein. J Biol Chem 277:16116–16123
Good P, Olanow C, Perl D (1992) Neuromelanin-containing neurons of the substantia nigra accumulate iron and aluminium in Parkinson’s disease: a LAMMA study. Brain 593:343–346
Götz ME, Künig G, Riederer P, Youdim MBH (1994) Oxidative stress. Free radical production in neural degeneration. Pharmacol Ther 63:37–122
Gorell JM, Johnson CC, Rybicki BA, Peterson EL, Kortsha GX, Brown GG, Richardson RJ (1999) Occupational exposure to manganese, copper, lead, iron, mercury and zinc and the risk of Parkinson’s disease. Neurotoxicology 20:239–247
Graumann R, Paris I, Martinez-Alvarado P, Rumanque P, Perez-Pastene C, Cardenas SP, Marin P, Diaz-Grez F, Caviedes R, Caviedes P, Segura-Aguilar J (2002) Oxidation of dopamine to aminochrome as a mechanism for neurodegeneration of dopaminergic systems in Parkinson’s disease. Possible neuroprotective role of DT-diaphorase. Pol J Pharmacol 54:573–579
Grisham MB, Jourd’Heul D, Wink DA (1999) Nitric oxide. I. Physiological chemistry of nitric oxide and its metabolites: implications in inflammation. Am J Physiol 276:315–321
Gu M, Cooper JM, Taanman JW, Schapira AHV (1998) Mitochondrial DNA transmission of the mitochondrial defect in Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 44:177–186
Gu G, Reyes PE, Golden GT, Woltjer RL, Hulette C, Montine TJ, Zhang J (2002) Mitochondrial DNA deletions/rearrangements in Parkinson disease and related neurodegenerative disorders. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 61:634–639
Hallgren B, Sourander P (1958) The effect of age on non-haem iron in the human brain. J Neurochem 3:41–51
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JM (2003) Free radicals in biology and medicine. Oxford University, New York
HaMai D, Bondy SC (2004) Oxidative basis of manganese neurotoxicity. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1012:129–141
Hashimoto M, Hsu LJ, Sisk A, Xia Y, Takeda A, Sundsmo M, Masliah E (1998) Human recombinant NACP/alpha-synuclein is aggregated and fibrillated in vitro: relevance for Lewy body disease. Brain Res 799:301–306
He Y, Thong PS, Lee T, Leong SK, Shi CY, Wong PT, Yuan SY, Watt F (1996) Increased iron in the substantia nigra of 6-OHDA induced parkinsonian rats: a nuclear microscopy study. Brain Res 735:149–153
Hirsch EC, Graybiel AM, Agid YA (1988) Melanized dopaminergic neurons are differentially susceptible to degeneration in Parkinson’s disease. Nature 334:345–348
Hochstrasser H, Bauer P, Walter U, Behnke S, Spiegel J, Csoti I, Zeiler B, Bornemann A, Pahnke J, Becker G, Riess O, Berg D (2004) Ceruloplasmin gene variations are associated with substantia nigra hyperechogenicity in Parkinson’s disease. Neurology (in press)
Hoglinger GU, Carrard G, Michel PP, Medja F, Lombes A, Ruberg M, Friguet B, Hirsch EC (2003) Dysfunction of mitochondrial complex I and the proteasome: interactions between two biochemical deficits in a cellular model of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 86:1297–1307
Hunot S, Dugas N, Hartmann A, Tardieu M, Debre P, Agid Y, Dugas B, Hirsch EC (1999) Fcepsilon-RII/CD23 is expressed in Parkinson’s disease and induces, in vitro, production of nitric oxide and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in glial cells. J Neurosci 19:3440–3447
Iravani MM, Kashefi K, Mander P, Rose S, Jenner P (2002) Involvement of inducible nitric oxide synthase in inflammation-induced dopaminergic neurodegeneration. Neuroscience 110:49–58
Jahngen-Hodge J, Obin MS, Gong X, Shang F, Nowell TR Jr, Gong J, Abasi H, Blumberg J, Taylor A (1997) Regulation of ubiquitin-conjugating enzymes by glutathione following oxidative stress. J Biol Chem 272:28218–28226
Jellinger K, Kienzl E, Rumpelmair G, Riederer P, Stachellberger H, Ben-Shachar D, Youdim MB (1992) Iron-melanin complex in substantia nigra of parkinsonian brains: an X-ray microanalysis. J Neurochem 59:1168–1171
Jenner P (1993) Altered mitochondrial function, iron metabolism and glutathione levels in Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl 146:6–13
Jenner P (2003) Oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 53:S26–S38
Jenner P, Olanow CW (1998) Understanding cell death in Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 44:S72–S84
Jimenez-Jimenez FJ, Molina JA, Aguilar MV, Meseguer I, Mateos-Vega CJ, Gonzalez-Munoz MJ, Bustos F de, Martinez-Salio A, Orti-Pareja M, Zurdo M, Martinez-Para MC (1998) Cerebrospinal fluid levels of transition metals in patients with Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm 105:497–505
Junn E, Mouradian MM (2002) Human alpha-synuclein over-expression increases intracellular reactive oxygen species and suceptibility to dopamine. Neurosci Lett 320:146–150
Kanthasamy AG, Kitazawa M, Kaul S, Yang Y, Lahiri DK, Anantharam V, Kanthasamy A (2003) Proteolytic activation of proapoptotic kinase PKCdelta is regulated by overexpression of Bcl-2: implications for oxidative stress and environmental factors in Parkinson’s disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1010:683–686
Kim Y, Kim JM, Kim JW, Yoo CI, Lee CR, Lee JH, Kim HK, Yang SO, Chung HK, Lee DS, Jeon B (2002) Dopamine transporter density is decreased in parkinsonian patients with a history of manganese exposure: what does it mean? Mov Disord 17:568–575
Kish SJ, Morito CH, Hornykiewics (1985) Glutathione peroxidase activity in Parkinson’s disease brain. Neruosci Lett 58:343–346
Kotake Y, Ohta S (2003) MPP+ analogs acting on mitochondria and inducing neuro-degeneration. Curr Med Chem 10:2507–2516
Koutsilieri E, Scheller C, Tribl F, Riederer P (2002) Degeneration of neuronal cells due to oxidative stress—microglial contribution. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 8:401–406
Kramer BC, Yabut JA, Cheong J, JnoBaptiste R, Robakis T, Olanow CW, Mytilineou C (2002) Lipopolysaccharide prevents cell death caused by glutathione depletion: possible mechanism of protection. Neuroscience 114:361–372
Krishnan S, Chi EY, Wood SJ, Kendrick BS, Li C, Garzon-Rodriguez W, Wypych J, Randolph TW, Narhi LO, Biere AL, Citron M, Carpenter JF (2003) Oxidative dimer formation is the critical rate-limiting step for Parkinson’s disease α-synuclein fibrillogenesis. Biochemistry 42:829–837
Lan J, Jiang DH (1997) Excessive iron accumulation in the brain: a possible potential risk of neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease. J Neural Transm 104:649–660
Langston JW, Ballard P, Tetrud JW, Irwin I (1983) Chronic parkinsonism in humans due to a product of meperidine-analog synthesis. Science 219:989–990
Lee EN, Lee SY, Lee D, Kim J, Paik SR (2003) Lipid interaction of alpha-synuclein during the metal-catalyzed oxidation in the presence of Cu2+ and H2O2. J Neurochem 84:1128–1142
Lin LF, Doherty DH, Lile JD, Bektesh S, Collins F (1993) GDNF: a glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor for midbrain dopaminergic neurons. Science 260:1130–1132
Liu B, Gao H, Wang J, Jeohn G, Cooper C, Hong J (2002a) Role of nitric oxide in inflammation-mediated neurodegeneration. Ann N Y Acad Sci 962:318–331
Liu Y, Fiskum G, Schubert D (2002b) Generation of reactive oxygen species by the mitochondrial electron transport chain. J Neurochem 80:780–787
Lopiano L, Chiesa M, Digilio G, Giraudo S, Bergamasco B, Torre E, Fasano M (2000) Q-band EPR investigations of neuromelanin in control and Parkinson’s disease patients. Biochim Biophys 17:306–312
Maharaj DS, Saravanan KS, Maharaj H, Mohanakumar KP, Daya S (2004) Acetaminophen and aspirin inhibit superoxide anion generation and lipid peroxidation, and protect against 1-methyl-4-phenyl pyridinium-induced dopaminergic neurotoxicity in rats. Neurochem Int 44:355–360
Mandel S, Weinreb O, Amit T, Youdim MB (2004) Cell signaling pathways in the neuroprotective actions of the green tea polyphenol (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate: implications for neurodegenerative diseases. J Neurochem 88:1555–1569
Marnett LJ (2000) Oxyradicals and DNA damage. Carcinogenesis 21:361–370
Martilla RJ, Lorentz H, Rinne UK (1988) Oxygen toxicity protecting enzymes in Parkinson’s disease: increase of superoxide-dismutase-like activity in the substantia nigra and basal nucleus. J Neurol Sci 86:321–331
Masliah E, Rockenstein E, Veinbergs I, Mallory M, Hashimoto M, Takeda A, Sagara Y, Sisk A, Mucke L (2000) Dopaminergic loss and inclusion body formation in alpha-synuclein mice: implications for neurodegenerative disorders. Science 287:1265–1269
Mattson MP (2004) Metal-catalyzed disruption of membrane protein and lipid signaling in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative disorders. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1012:37–50
McNaught KSP, Jenner P (2000) Extracellular accumulation of nitric oxide, hydrogen peroxide and glutamate in astrocytic cultures following glutathione depletion, complex I inhibition and/or lipopolysaccharide-induced activation. Biochem Pharmacol 60:979–988
Mendez-Alvarez E, Soto-Otero R, Hermida-Ameijeiras A, Lopez-Real AM, Labandeira-Garcia JL (2002) Effects of aluminum and zinc on the oxidative stress caused by 6-hydroxydopamine autoxidation: relevance for the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1586:155–168
Minghetti L, Levi G (1998) Microglia as effector cells in brain damage and repair: focus on prostanoids and nitric oxide. Prog Neurobiol 54:99–125
Mizuno Y, Ohta S, Tanaka M, Takamiya S, Suzuki K, Sato T, Oya H, Ozawa T, Kagawa Y (1989) Deficiencies in complex I subunits of the respiratory chain in Parkinson’s disease. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 163:1450–1455
Mochizuki H, Imai H, Endo K, Yokomizo K, Murata Y, Hattori N, Mizuno Y (1994) Iron accumulation in the substantia nigra of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP)-induced hemiparkinsonian monkeys. Neurosci Lett 168:251–253
Mogi M, Harada M, Kondo T, Riederer P, Inagaki H, Minami M, Nagatsu T (1994) Interleukin-1 beta, interleukin-6, epidermal growth factor and transforming growth factor-alpha are elevated in the brain from parkinsonian patients. Neurosci Lett 180:147–150
Münch G, Lüth HJ, Wong A, Arendt T, Hirsch E, Ravid R, Riederer P (2000) Crosslinking of α-synuclein by advanced glycation endproducts—an early pathophysiological step in Lewy body formation. J Clin Neuroanat 20:253–257
Mytilineou C, Kramer BC, Yabut JA (2002) Glutathione depletion and oxidative stress. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 8:385–387
Naoi M, Maruyama W, Akao Y, Zhang J, Parvez H (2000) Apoptosis induced by an endogenous neurotoxin, N-methyl(R)salsolinol, in dopamine neurons. Toxicology 153:123–141
Naoi M, Maruyama W, Akao Y, Yi H (2002) Mitochondria determine the survival and death in apoptosis by an endogenous neurotoxin, N-methyl(R)salsolinol, and neuroprotection by propargylamines. J Neural Transm 109:607–621
Paik, S, Shin, H, Lee, J, Chang, C, Kim, J (1999) Copper(II)-induced self oligomerization of α-synuclein. Biochem J 340:821–828
Paris I, Dagnino-Subiabre A, Marcelain K, Bennett LB, Caviedes P, Caviedes R, Azar CO, Segura-Aguilar J (2001) Copper neurotoxicity is dependent on dopamine-mediated copper uptake and one-electron reduction of aminochrome in a rat substantia nigra neuronal cell line. J Neurochem 77:519–529
Plaitakis A, Shashidharan P (2000) Glutamate transport and metabolism in dopaminergic neurons of substantia nigra: implications for the pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol 247:S25–S35
Power JH, Shannon JM, Blumbergs PC, Gai WP (2002) Nonselenium glutathione peroxidase in human brain: elevated levels in Parkinson’s disease and dementia with lewy bodies. Am J Pathol 161:885–894
Powers KM, Smith-Weller T, Franklin GM, Longstreth WT Jr, Swanson PD, Checkoway H (2003) Parkinson’s disease risks associated with dietary iron, manganese, and other nutrient intakes. Neurology 60:1761–1766
Practico D (2001) In vivo measurement of the redox state. Lipids 36:S45–S49
Rajput AH, Uitti RJ, Stern W, Laverty W (1986) Early onset Parkinson’s disease and childhood environment. Adv Neurol 45:295–297
Rausch WD, Hirata Y, Nagatsu T, Riederer P, Jellinger K (1988) Tyrosine hydroxylase activity in caudate nucleus from Parkinson’s disease: effects of iron and phosphorylating agents. J Neurochem 50:202–208
Reichmann H, Janetzky B (2000) Mitochondrial dysfunction—a pathogenetic factor in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol 247:S63–S67
Reichmann H, Riederer P (1989) Biochemical analyses of respiratory chain enzymes in different brain regions of patients with Parkinson’s disease. BMFT Symposium “Morbus Parkinson und andere Basalganglienerkrankungen”, Bad Kissingen (Abstract S 44)
Reif DW, Simmons RD (1990) Nitric oxide mediates iron release from ferritin. Arch Biochem Biophys 283:537–541
Riederer P, Youdim MBH (eds) (1993) Iron in central nervous system disorders. Springer, Vienna
Riederer P, Rausch WD, Schmidt B, Kruzik P, Konradi C, Sofic E, Danielczyk W, Fischer M, Ogris E (1988) Biochemical fundamentals of Parkinson’s disease. M Sinai J Med 55:21–28
Riederer P, Sofic E, Rausch WD, Schmidt B, Reynolds GP, Jellinger K, Youdim MB (1989) Transition metals, ferritin, glutathione and ascorbic acid in Parkinsonian brains. J Neurochem 52:515–520
Rossi L, Lombardo MF, Ciriolo MR, Rotilio G (2004) Mitochondrial dysfunction in neurodegenerative diseases associated with copper imbalance. Neurochem Res 29:493–504
Sanchez-Ramos JR, Hefti F, Weiner WJ (1987) Paraquat and Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 37:728b
Sanchez-Ramos JR, Övervik E, Ames BN (1994) A marker of oxyradical-mediated DNA damage (8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine) is increased in nigro-striatum of Parkinson’s disease brain. Neurodegeneration 3:197–204
Scherman D, Desnos C, Darchen F, Javoy-Agid F, Agid Y (1989) Striatal dopamine deficiency in Parkinson’s disease: role of aging. Ann Neurol 26:551–557
Schipper HM, Liberman A, Stopa EG (1998) Neural heme oxygenase-1 expression in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Exp Neurol 150:60–68
Shachar DB, Kahana N, Kampel V, Warshawsky A, Youdim MB (2004) Neuroprotection by a novel brain permeable iron chelator, VK-28, against 6-hydroxydopamine lesion in rats. Neuropharmacology 46:254–263
Shamoto-Nagai M, Maruyama W, Kato Y, Isobe K, Tanaka M, Naoi M, Osawa T (2003) An inhibitor of mitochondrial complex I, rotenone, inactivates proteasome by oxidative modification and induces aggregation of oxidized proteins in SH-SY5Y cells. J Neurosci Res 74:589–597
Shaw CA, Bains JS (2002) Synergistic versus antagonistic actions of glutamate and glutathione: the role of excitotoxicity and oxidative stress in neuronal disease. Cell Mol Biol 48:127–136
Sherer TB, Betarbet R, Stout AK, Lund S, Baptista M (2002a) An in vitro model of Parkinson’s disease: Linking mitochondrial impairment to altered α-synuclein metabolism and oxidative damage. J Neurosci 22:7006–7015
Sherer TB, Betarbet R, Greenamyre JT (2002b) Environment, mitochondria, and Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscientist 8:192–197
Shima T, Sarna T, Swartz H, Stroppolo A, Gerbasi R, Zecca L (1997) Binding of iron to neuromelanin of human substantia nigra and synthetic neuromelanin: an electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy study. Free Radic Biol Med 23:110–119
Shoham S, Youdim MB (2002) The effects of iron deficiency and iron and zinc supplementation on rat hippocampus ferritin. J Neural Transm 109:1241–1256
Shoulson I (1998) DATATOP: a decade of neuroprotective inquiry. Parkinson Study Group. Deprenyl and tocopherol antioxidative therapy of Parkinsonism. Ann Neurol 44:S160–S166
Sian J, Dexter DT, Lees AJ, Daniel S, Jenner P, Marsden CD (1994) Glutathione-related enzymes in brain in Parkinson’ s disease. Ann Neurol 36:356–361
Sofic E, Riederer P, Heinsen H, Beckmann H, Reynolds GP, Hebenstreit G, Youdim MB (1988) Increased iron (III) and total iron content in post mortem substantia nigra of parkinsonian brain. J Neural Transm 74:199–205
Sofic E, Lange KW, Jellinger K, Riederer P (1992) Reduced and oxidized glutathione in the substantia nigra of patients with Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Lett 142:128–130
Souza JM, Giasson BI, Chen Q, Lee VM, Ischiropoulos H (2000) Dityrosine cross-linking promotes formation of stable α-synuclein polymers. Implication of nitrative and oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative synucleinopathies. J Biol Chem 275:18344–18349
Spencer PS, Nunn PB, Hugon J, Ludolph AC, Ross SM, Roy DN, Robertson RC (1987) Guam amyotrophic lateral sclerosis-parkinsonism-dementia linked to a plant excitant neurotoxin. Science 237:517–522
Stadtman ER (2001) Protein oxidation in aging and age-related diseases. Ann N Y Acad Sci 928:22–38
Starkov AA, Polster BM, Fiskum G (2002) Regulation of hydrogen peroxide production by brain mitochondria by calcium and Bax. J Neurochem 83:220–228
Stewart VC, Heales SJR (2003) Nitric oxide-induced mitochondrial dysfunction: implications for neurodegeneration. Free Radic Biol Med 34:287–303
Strijks E, Kremer HP, Horstink MW (1997) Q10 therapy in patients with idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Mol Aspects Med 18 (Suppl):S237–S240
Tanaka M (2002) Mitochondrial genotypes and cytochrome b variants associated with longevity or Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol 249:III1–III8
Trimmer PA, Swerdlow RH, Parks JK, Keeney P, Bennett JP Jr, Miller SW, Davis RE, Parker WD Jr (2000) Abnormal mitochondrial morphology in sporadic Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease cybrid cell lines. Exp Neurol 162:37–50
Turnbull S, Tabner BJ, El-Agnaf OMA, Moore S, Davies Y, Allsop D (2001) α-Synuclein implicated in Parkinons’s disease catalyses the formation of hydrogen peroxide in vitro. Free Radic Biol Med 30:1163–1170
Uversky VN, Li J, Fink AL (2001) Metal-triggered structural transformations, aggregation, and fibrillation of human alpha-synuclein. A possible molecular NK between Parkinson’s disease and heavy metal exposure. J Biol Chem 276:44284–44296
Wu G, Fang YZ, Yang S, Lupton JR, Turner ND (2004) Glutathione metabolism and its implications for health. J Nutr 134:489–492
Yoshida E, Mokuno K, Aoki SI, Takahashi A, Riku S, Murayama T, Yanagi T, Kato K (1994) Cerebrospinal fluid levels of superoxide dismutase. J Neurol Sci 124:25–31
Youdim MB, Stephenson G, Ben Shachar D (2004) Ironing iron out in Parkinson’s disease and other neurodegenerative diseases with iron chelators: a lesson from 6-hydroxydopamine and iron chelators, desferal and VK-28. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1012:306–325
Zafar KS, Siddiqui A, Sayeed I, Ahmad M, Salim S, Islam F (2003) Dose-dependent protective effect of selenium in rat model of Parkinson’s disease: neurobehavioral and neurochemical evidences. J Neurochem 84:438–446
Zareba M, Bober A, Korytowski W, Zecca L, Sarna T (1995) The effect of a synthetic neuromelanin on yield of free hydroxyl radicals generated in model systems. Biochim Biophys Acta 1271:343–348
Zecca L, Swartz HM (1993) Total and paramagnetic metals in human substantia nigra and its neuromelanin. J Neural Transm 5:203–213
Zecca L, Mecacci O, Seraglia R, Parati E (1992) The chemical characterization of melanin contained in substantia nigra of human brain. Biochim Biophys Acta 1138:6–10
Zecca L, Gallorini M, Schünemann V, Trautwein AX, Gerlach M, Riederer P, Vezzoni P, Tampellini D (2001) Iron, neuromelanin and ferritin in substantia nigra of normal subjects at different ages, consequences for iron storage and neurodegenerative processes. J Neuochem 76:1766–1773
Zecca L, Fariello R, Riederer P, Sulzer D, Gatti A, Tampellini D (2002) The absolute concentration of nigral dopamine, assayed by a new sensitive method, increases throughout the life and is dramatically decreased in Parkisnon’s disease. FEBS Lett 510:216–220
Zhang J, Fitsanakis VA, Gu G, Jing D, Ao M, Amarnath V, Montine TJ (2003) Manganese ethylene-bis-dithiocarbamate and selective dopaminergic neurodegeneration in rat: a link through mitochondrial dysfunction. J Neurochem 84:336–346
Zhu BT (2004) CNS dopamine oxidation and catechol-O-methyltransferase: importance in the etiology, pharmacotherapy, and dietary prevention of Parkinson’s disease. Int J Mol Med 13:343–353
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berg, D., Youdim, M.B.H. & Riederer, P. Redox imbalance. Cell Tissue Res 318, 201–213 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-004-0976-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-004-0976-5