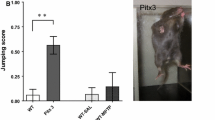
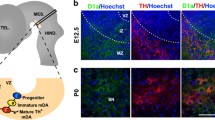
Abstract
The homeobox gene Pitx3 plays an important part in the development and function of vertebrate midbrain dopaminergic neurons. Re-localization of the genetic defect in the mouse mutant aphakia to the Pitx3 locus, together with the subsequent identification of two deletions causing the gene to be silent, has been the hallmark of several studies into the role of Pitx3. In this review, we summarize the data and reflect on the role of Pitx3 in the development of dopamine neurons in the midbrain. The data indicate that Pitx3 is essential for the survival of dopamine neurons located in the substantia nigra compacta during development. Molecular analysis of the underlying mechanisms might provide new insights for understanding the selective degeneration observed in Parkinson patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barzilai A, Melamed E (2003) Molecular mechanisms of selective dopaminergic neuronal death in Parkinson’s disease. Trends Mol Med 9:126–132
Burbach JP, Smits S, Smidt MP (2003) Transcription factors in the development of midbrain dopamine neurons. Ann N Y Acad Sci 991:61–68
Cazorla P, Smidt MP, O’Malley KL, Burbach JP (2000) A response element for the homeodomain transcription factor ptx3 in the tyrosine hydroxylase gene promoter. J Neurochem 74:1829–1837
Chen H, Ovchinnikov D, Pressman CL, Aulehla A, Lun Y, Johnson RL (1998) Multiple calvarial defects in lmx1b mutant mice. Dev Genet 22:314–320
Costall B, Naylor RJ, Nohria V (1978) Climbing behaviour induced by apomorphine in mice: a potential model for the detection of neuroleptic activity. Eur J Pharmacol 50:39–50
Davidson C, Ellinwood EH, Douglas SB, Lee TH (2000) Effect of cocaine, nomifensine, gbr 12909 and win 35428 on carbon fiber microelectrode sensitivity for voltammetric recording of dopamine. J Neurosci Methods 101:75–83
Dreyer SD, Zhou G, Baldini A, Winterpacht A, Zabel B, Cole W, Johnson RL, Lee B (1998) Mutations in lmx1b cause abnormal skeletal patterning and renal dysplasia in nail patella syndrome. Nat Genet 19:47–50
Gage PJ, Camper SA (1997) Pituitary homeobox 2, a novel member of the bicoid-related family of homeobox genes, is a potential regulator of anterior structure formation. Hum Mol Genet 6:457–464
Graw J (1999a) Mouse models of congenital cataract. Eye 13:438–444
Graw J (1999b) Cataract mutations and lens development. Prog Retin Eye Res 18:235–267
Graw J, Loster J (2003) Developmental genetics in ophthalmology. Ophthalmic Genet 24:1–33
Grimm C, Chatterjee B, Favor J, Immervoll T, Loster J, Klopp N, Sandulache R, Graw J (1998) Aphakia (ak), a mouse mutation affecting early eye development: fine mapping, consideration of candidate genes and altered pax6 and six3 gene expression pattern. Dev Genet 23:299–316
Hall AC, Mira H, Wagner J, Arenas E (2003) Region-specific effects of glia on neuronal induction and differentiation with a focus on dopaminergic neurons. Glia 43:47–51
Hanaway J, McConnell JA, Netsky MG (1971) Histogenesis of the substantia nigra, ventral tegmental area of tsai and interpeduncular nucleus: an autoradiographic study of the mesencephalon in the rat. J Comp Neurol 142:59–73
Hwang DY, Ardayfio P, Kang UJ, Semina EV, Kim KS (2003) Selective loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra of pitx3-deficient aphakia mice. Brain Res Mol Brain Res 114:123–131
Hynes M, Rosenthal A (1999) Specification of dopaminergic and serotonergic neurons in the vertebrate CNS. Curr Opin Neurobiol 9:26–36
Hynes M, Poulsen K, Tessier-Lavigne M, Rosenthal A (1995a) Control of neuronal diversity by the floor plate: contact-mediated induction of midbrain dopaminergic neurons. Cell 80:95–101
Hynes M, Porter JA, Chiang C, Chang D, Tessier-Lavigne M, Beachy PA, Rosenthal A (1995b) Induction of midbrain dopaminergic neurons by sonic hedgehog. Neuron 15:35–44
Joyce JN, Frohna PA, Neal-Beliveau BS (1996) Functional and molecular differentiation of the dopamine system induced by neonatal denervation. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 20:45–86
Kawano H, Ohyama K, Kawamura K, Nagatsu I (1995) Migration of dopaminergic neurons in the embryonic mesencephalon of mice. Brain Res Dev Brain Res 86:101–113
Knusel B, Michel PP, Schwaber JS, Hefti F (1990) Selective and nonselective stimulation of central cholinergic and dopaminergic development in vitro by nerve growth factor, basic fibroblast growth factor, epidermal growth factor, insulin and the insulin-like growth factors I and II. J Neurosci 10:558–570
Krieglstein K, Suter-Crazzolara C, Unsicker K (1995) Development of mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons and the transforming growth factor-beta superfamily. J Neural Transm Suppl 46:209–216
Lamonerie T, Tremblay JJ, Lanctot C, Therrien M, Gauthier Y, Drouin J (1996) Ptx1, a bicoid-related homeo box transcription factor involved in transcription of the pro-opiomelanocortin gene. Genes Dev 10:1284–1295
Law SW, Conneely OM, DeMayo FJ, O’Malley BW (1992) Identification of a new brainspecific transcription factor, Nurr1. Mol Endocrinol 6:2129–2135
Lebel M, Gauthier Y, Moreau A, Drouin J (2001) Pitx3 activates mouse tyrosine hydroxylase promoter via a high-affinity binding site. J Neurochem 77:558–567
Lin JC, Rosenthal A (2003) Molecular mechanisms controlling the development of dopaminergic neurons. Semin Cell Dev Biol 14:175–180
Marchand R, Poirier LJ (1983) Isthmic origin of neurons of the rat substantia nigra. Neuroscience 9:373–381
Marcos C, Pachnis V (1996) The effect of the ret-mutation on the normal development of the central and parasympathetic nervous systems. Int J Dev Biol Suppl 1:137S–138S
Medina L, Reiner A (1995) Neurotransmitter organization and connectivity of the basal ganglia in vertebrates: implications for the evolution of basal ganglia. Brain Behav Evol 46:235–258
Munckhof P van den , Luk KC, Ste-Marie L, Montgomery J, Blanchet PJ, Sadikot AF, Drouin J (2003) Pitx3 is required for motor activity and for survival of a subset of midbrain dopaminergic neurons. Development 130:2535–2542
Nunes I, Tovmasian LT, Silva RM, Burke RE, Goff SP (2003) Pitx3 is required for development of substantia nigra dopaminergic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:4245–4250
Rieger DK, Reichenberger E, McLean W, Sidow A, Olsen BR (2001) A double-deletion mutation in the pitx3 gene causes arrested lens development in aphakia mice. Genomics 72:61–72
Saucedo-Cardenas O, Quintana-Hau JD, Le WD, Smidt MP, Cox JJ, De Mayo F, Burbach JP, Conneely OM (1998) Nurr1 is essential for the induction of the dopaminergic phenotype and the survival of ventral mesencephalic late dopaminergic precursor neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:4013–4018
Semina EV, Reiter R, Leysens NJ, Alward WL, Small KW, Datson NA, Siegel-Bartelt J, Bierke-Nelson D, Bitoun P, Zabel BU, Carey JC, Murray JC (1996) Cloning and characterization of a novel bicoid-related homeobox transcription factor gene, rieg, involved in Rieger syndrome. Nat Genet 14:392–399
Semina EV, Reiter RS, Murray JC (1997) Isolation of a new homeobox gene belonging to the pitx/rieg family: expression during lens development and mapping to the aphakia region on mouse chromosome 19. Hum Mol Genet 6:2109–2116
Semina EV, Ferrell RE, Mintz-Hittner HA, Bitoun P, Alward WL, Reiter RS, Funkhauser C, Daack-Hirsch S, Murray JC (1998) A novel homeobox gene Pitx3 is mutated in families with autosomal-dominant cataracts and ASMD. Nat Genet 19:167–170
Semina EV, Murray JC, Reiter R, Hrstka RF, Graw J (2000) Deletion in the promoter region and altered expression of pitx3 homeobox gene in aphakia mice. Hum Mol Genet 9:1575–1585
Shults CW, Hashimoto R, Brady RM, Gage FH (1990) Dopaminergic cells align along radial glia in the developing mesencephalon of the rat. Neuroscience 38:427–436
Simon HH, Saueressig H, Wurst W, Goulding MD, O’Leary DD (2001) Fate of midbrain dopaminergic neurons controlled by the engrailed genes. J Neurosci 21:3126–3134
Simon HH, Bhatt L, Gherbassi D, Sgado P, Alberi L (2003) Midbrain dopaminergic neurons: determination of their developmental fate by transcription factors. Ann N Y Acad Sci 991:36–47
Smidt MP, Schaick HS van, Lanctot C, Tremblay JJ, Cox JJ, Kleij AA van der, Wolterink G, Drouin J, Burbach JP (1997) A homeodomain gene Ptx3 has highly restricted brain expression in mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:13305–13310
Smidt MP, Asbreuk CH, Cox JJ, Chen H, Johnson RL, Burbach JP (2000a) A second independent pathway for development of mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons requires lmx1b. Nat Neurosci 3:337–341
Smidt MP, Cox JJ, Schaick HS van, Coolen M, Schepers J, Kleij AM van der, Burbach JP (2000b) Analysis of three Ptx2 splice variants on transcriptional activity and differential expression pattern in the brain. J Neurochem 75:1818–1825
Smidt MP, Smits SM, Burbach JP (2003) Molecular mechanisms underlying midbrain dopamine neuron development and function. Eur J Pharmacol 480:75–88
Smidt MP, Smits SM, Bouwmeester H, Hamers FP, Linden AJ van der, Hellemons AJ, Graw J, Burbach JP (2004) Early developmental failure of substantia nigra dopamine neurons in mice lacking the homeodomain gene pitx3. Development 131:1145–1155
Smits SM, Ponnio T, Conneely OM, Burbach JP, Smidt MP (2003) Involvement of nurr1 in specifying the neurotransmitter identity of ventral midbrain dopaminergic neurons. Eur J Neurosci 18:1731–1738
Teitelman G, Jaeger CB, Albert V, Joh TH, Reis DJ (1983) Expression of amino acid decarboxylase in proliferating cells of the neural tube and notochord of developing rat embryo. J Neurosci 3:1379–1388
Thuret S, Bhatt L, O’Leary DD, Simon HH (2004) Identification and developmental analysis of genes expressed by dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra pars compacta. Mol Cell Neurosci 25:394–405
Tzschentke TM, Schmidt WJ (2000) Functional relationship among medial prefrontal cortex, nucleus accumbens, and ventral tegmental area in locomotion and reward. Crit Rev Neurobiol 14:131–142
Varnum DS, Stevens LC (1968) Aphakia, a new mutation in the mouse. J Hered 59:147–150
Wallen A, Zetterstrom RH, Solomin L, Arvidsson M, Olson L, Perlmann T (1999) Fate of mesencephalic ahd2-expressing dopamine progenitor cells in nurr1 mutant mice. Exp Cell Res 253:737–746
Wallen AA, Castro DS, Zetterstrom RH, Karlen M, Olson L, Ericson J, Perlmann T (2001) Orphan nuclear receptor Nurr1 is essential for ret expression in midbrain dopamine neurons and in the brain stem. Mol Cell Neurosci 18:649–663
Zetterstrom RH, Solomin L, Jansson L, Hoffer BJ, Olson L, Perlmann T (1997) Dopamine neuron agenesis in nurr1-deficient mice. Science 276:248–250
Zhao S, Maxwell S, Jimenez-Beristain A, Vives J, Kuehner E, Zhao J, O’Brien C, Felipe C de , Semina E, Li M (2004) Generation of embryonic stem cells and transgenic mice expressing green fluorescence protein in midbrain dopaminergic neurons. Eur J Neurosci 19:1133–1140
Zhuang X, Oosting RS, Jones SR, Gainetdinov RR, Miller GW, Caron MG, Hen R (2001) Hyperactivity and impaired response habituation in hyperdopaminergic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:1982–1987
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work was supported by the Korczak Foundation for Autism and Related Disorders (The Netherlands) to S.M.S., and by the Netherlands Organization of Scientific Research NWO (fellowship 903-42-075 to M.P.S.)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smidt, M.P., Smits, S.M. & Burbach, J.P.H. Homeobox gene Pitx3 and its role in the development of dopamine neurons of the substantia nigra. Cell Tissue Res 318, 35–43 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-004-0943-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-004-0943-1