Abstract
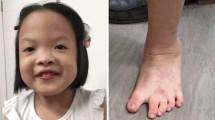
We have applied FISH with fully integrated BACs and BAC subfragments assessed in the human genome sequence to a de novo t(7;10)(q33;q23) translocation in a patient with developmental delay and macrocephaly. The translocation breakpoints disrupt the SEC8L1 gene on chromosome 7 and the PTEN gene on chromosome 10. RT-PCR demonstrated chimeric transcripts containing the first 11 exons of SEC8L1 fused to exon 3 of PTEN. In addition to the balanced translocation, we found a 7-Mb deletion in the translocated part of chromosome 7 at 4-Mb distance of the translocation breakpoint. This microdeletion, which disrupts the PTN and TPK1 genes and deletes 29 bonafide genes and the T-cell receptor beta locus, arose in the paternal germline. The patient’s phenotype may be caused by a dominant-negative effect of the SEC8L1-PTEN fusion protein and/or haploinsufficiency of the disrupted or deleted genes. Our study demonstrates that de novo translocations can be associated with microdeletions outside the breakpoint region(s), rendering the study and risk estimation of such breakpoints more complicated than previously assumed.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arch EM, Goodman BK, van Wesep RA, Liaw D, Clarke K, Parsons R, McKusick VA, Geraghty MT (1997) Deletion of PTEN in a patient with Bannayan–Riley–Ruvalcaba syndrome suggests allelism with Cowden disease. Am J Med Genet 71:489–493
Bugge M, Bruun-Petersen G, Brøndum-Nielsen K, Friedrich U, Hansen J, Jensen G, Jensen PK, Kristoffersson U, Lundsteen C, Niebuhr E, Rasmussen KR, Rasmussen K, Tommerup N (2000) Disease associated balanced chromosome rearrangements: a resource for large scale genotype-phenotype delineation in man. J Med Genet 37:858–865
Di Cristofano A, Pesce B, Cordon-Cardo C, Pandolfi PP (1998) Pten is essential for embryonic development and tumor suppression. Nat Genet 19:348–355
Fantes J, Ragge NK, Lynch SA, McGill NI, Collin JRO, Howard-Peebles PN, Hayward C, Vivian AJ, Williamson K, van Heyningen V, FitzPatrick DR (2003) Mutations in SOX2 cause anophthalmia. Nat Genet 33:461–463
Gribble SM, Prigmore E, Burford DC, Porter KM, Ng BL, Douglas EJ, Fiegler H, Carr P, Kalaitzopoulos D, Clegg S, Sandstrom R, Temple I, Youings SA, Thomas N, Dennis N, Jacobs PA, Crolla JA, Carter NP (2005) The complex nature of constitutional de novo apparently balanced translocations in patients with abnormal phenotypes. J Med Genet 42:8–16
Gu J, Tamura M, Yamada KM (1998) Tumor suppressor PTEN inhibits integrin- and growth factor-mediated mitogen activated protein (MAP) kinase signaling pathway. J Cell Biol 143:1375–1383
Haaf T (2000) Fluorescence in situ hybridization. In: Meyers RA (ed) Encyclopedia of analytical chemistry, vol 1. Nucleic acids structure and mapping. Wiley, Chichester, pp 4984–5006
Inoue M, Chang L, Hwang J, Chiang SH, Saltiel AR (2003) The exocyst complex is required for targeting of Glut4 to the plasma membrane by insulin. Nature 422:629–633
Knobbe CB, Merlo A, Reifenberger G (2002) Pten signaling in gliomas. Neuro-oncol 4:196–211
Kumar A, Becker LA, Depinet TW, Haren JM, Kurtz CL, Robin NH, Cassidy SB, Wolff DJ, Schwartz S (1998) Molecular characterization and delineation of subtle deletions in de novo “balanced” chromosomal rearrangements. Hum Genet 103:173–178
Li YS, Milner PG, Chauhan AK, Watson MA, Hoffman RM, Kodner CM, Mibrandt J, Deuel TF (1990) Cloning and expression of a developmentally regulated protein that induces mitogenic and neurite outgrowth activity. Science 250:1690–1694
Marsh DJ, Dahia PLM, Coulon V (1998) Allelic imbalance, including deletion of PTEN/MMAC1, at the Cowden disease locus on 10q22-23, in hamartomas from patients with Cowden syndrome and germline PTEN mutation. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 21:61–69
Nakashima N, Sharma PM, Imamura T, Bookstein R, Olefsky JM (2000) The tumor suppressor PTEN negatively regulates insulin signaling in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. J Biol Chem 275:12889–12895
Pilarski R, Eng C (2004) Will the real Cowden syndrome please stand up (again)? Expanding mutational and clinical spectra of the PTEN hamartoma tumor syndrome. J Med Genet 41:323–326
Plasilova M, Risitano A, Maciejewski JP (2003) Application of the molecular analysis of the T-cell receptor repertoire in the study of immune-mediated hematologic diseases. Hematology 8:173–181
Polzin A, Shipitsin M, Goi T, Feig LA, Turner TJ (2002) Ral-GTPase influences the regulation of the readily releasable pool of synaptic vesicles. Mol Cell Biol 22:1714–1722
Reardon W, Zhou XP, Eng C (2001) A novel germline mutation of the PTEN gene in a patient with macrocephaly, ventricular dilatation, and features of VATER association. J Med Genet 38:820–823
Reifenberger J, Rauch L, Beckmann MW, Megahed M, Ruzicka T, Reifenberger G (2003) Cowden’s disease: clinical and molecular genetic findings in a patient with a novel PTEN germline mutation. Br J Dermatol 148:1040-1046
Stambolic V, Tsao MS, MacPherson D, Suzuki A, Chapman WB, Mak TW (2000) High incidence of breast and endometrial neoplasia resembling human Cowden syndrome in pten +/– mice. Cancer Res 60:3605–3611
Stankiewicz P, Lupski JR (2002) Genome architecture, rearrangements and genomic disorders. Trends Genet 18:74–82
Sulis ML, Parsons R (2003) PTEN: from pathology to biology. Trends Cell Biol 13:478–483
Tommerup N (1993) Mendelian cytogenetics. Chromosome rearrangements associated with Mendelian disorders. J Med Genet 30:713–727
Tsuchiya KD, Wiesner G, Cassidy SB, Limwongse C, Boyle JT, Schwartz S (1998) Deletion 10q23.2-q23.33 in a patient with gastrointestinal juvenile polyposis and other features of a Cowden-like syndrome. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 21:113–118
Warburton D (1991) De novo balanced chromosome rearrangements and extra marker chromosomes identified at prenatal diagnosis: clinical significance and distribution of breakpoints. Am J Hum Genet 49:995–101
Weng LP, Smith WM, Brown JL, Eng C (2001) PTEN inhibits insulin-stimulated MEK/MAPK activation and cell growth by blocking IRS-1 phosphorylation and IRS-1/Grb-2/Sos complex formation in a breast cancer model. Hum Mol Genet 10:605–616
Wirth J, Nothwang HG, van der Maarel S, Menzel C, Borck G, Lopez-Pajares I, Brøndum-Nielsen K, Tommerup N, Bugge M, Ropers HH, Haaf T (1999) Systematic characterisation of disease associated balanced chromosome rearrangements by FISH: cytogenetically and genetically anchored YACs identify microdeletions and candidate regions for mental retardation genes. J Med Genet 36:271–278
Zhang N, Yeh H, Zhong R, Li YS, Deuel TF (1999) A dominant-negative pleiotrophin mutant introduced by homologous recombination leads to germ-cell apoptosis in male mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:6734–6738
Zhao R, Gao F, Goldman ID (2001) Molecular cloning of human thiamin pyrophosphokinase. Biochim Biophys Acta 1517:320–322
Zhou XP, Waite KA, Pilarski R, Hampel H, Fernandez MJ, Bos C, Dasouki M, Feldman GL, Greenberg LA, Ivanovich J, Matloff E, Patterson A, Pierpont ME, Russo D, Nassif NT, Eng C (2003) Germline PTEN promoter mutations and deletions in Cowden/Bannayan-Riley-Ruvalcaba syndrome result in aberrant PTEN protein and dysregulation of the phosphoinositol-3-kinase/Akt pathway. Am J Hum Genet 73:404–411
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the German Research Foundation and the Boehringer Ingelheim Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yue, Y., Grossmann, B., Holder, S.E. et al. De novo t(7;10)(q33;q23) translocation and closely juxtaposed microdeletion in a patient with macrocephaly and developmental delay. Hum Genet 117, 1–8 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-005-1273-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-005-1273-4