Abstract
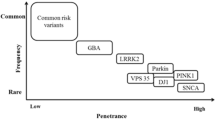
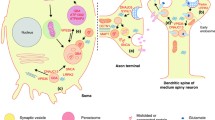
Research into Parkinson’s disease (PD), once considered the archetypical non-genetic neurodegenerative disorder, has been revolutionized by the identification of a number of genes, mutations of which underlie various familial forms of the disease. Whereas such mutations appear to exist in a relatively small number of individuals from a few families, the study of the function of these genes promises to reveal the fundamental disease pathogenesis, not only of familial forms of the disease, but also of the much more common sporadic PD. The observation that mutations in the second identified PD locus (parkin) are common in juvenile- and early-onset PD and increasing evidence supporting a direct role for parkin in late-onset disease make this gene a particularly compelling candidate for intensified investigation. The determination of the frequency and effect of parkin mutations in various subsets of PD will be crucial for understanding the way in which parkin is related to neurodegenerative mechanisms, and whether these subsets might be effectively identified and treated. In addition, many aspects of parkin-linked disease, originally thought to be well defined, have now been obscured both by genetic studies that preclude a simple model of disease transmission and by clinical and pathological studies that demonstrate broad variability in cases with parkin mutations. Future studies that address the issues in question should have a far-reaching impact in downstream biochemical studies and our understanding of parkin’s role in PD.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbas N, Lucking CB, Ricard S, Durr A, Bonifati V, De Michele G, Bouley S, Vaughan JR, Gasser T, Marconi R, Broussolle E, Brefel-Courbon C, Harhangi BS, Oostra BA, Fabrizio E, Bohme GA, Pradier L, Wood NW, Filla A, Meco G, Denefle P, Agid Y, Brice A (1999) A wide variety of mutations in the parkin gene are responsible for autosomal recessive parkinsonism in Europe. French Parkinson’s Disease Genetics Study Group and the European Consortium on Genetic Susceptibility in Parkinson’s Disease. Hum Mol Genet 8:567–574
Bernheimer H, Birkmayer W, Hornykiewicz O, Jellinger K, Seitelberger F (1973) Brain dopamine and the syndromes of Parkinson and Huntington. Clinical, morphological and neurochemical correlations. J Neurol Sci 20:415–455
Braak H, Del Tredici K, Rub U, Vos RA de, Jansen Steur EN, Braak E (2003) Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 24:197–211
Broussolle E, Lucking CB, Ginovart N, Pollak P, Remy P, Durr A (2000) [18 F]-dopa PET study in patients with juvenile-onset PD and parkin gene mutations. Neurology 55:877–879
Cesari R, Martin ES, Calin GA, Pentimalli F, Bichi R, McAdams H, Trapasso F, Drusco A, Shimizu M, Masciullo V, D’Andrilli G, Scambia G, Picchio MC, Alder H, Godwin AK, Croce CM (2003) Parkin, a gene implicated in autosomal recessive juvenile parkinsonism, is a candidate tumor suppressor gene on chromosome 6q25-q27. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:5956–5961
Chen R, Gosavi NS, Langston JW, Chan P (2003) Parkin mutations are rare in patients with young-onset parkinsonism in a US population. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 9:309–312
Cookson MR (2003) Neurodegeneration: how does parkin prevent Parkinson’s disease? Curr Biol 13:R522–R524
Darios F, Corti O, Lucking CB, Hampe C, Muriel MP, Abbas N, Gu WJ, Hirsch EC, Rooney T, Ruberg M, Brice A (2003) Parkin prevents mitochondrial swelling and cytochrome c release in mitochondria-dependent cell death. Hum Mol Genet 12:517–526
Denison SR, Callahan G, Becker NA, Phillips LA, Smith DI (2003) Characterization of FRA6E and its potential role in autosomal recessive juvenile parkinsonism and ovarian cancer. Genes Chromosom Cancer 38:40–52
Farrer M, Chan P, Chen R, Tan L, Lincoln S, Hernandez D, Forno L, Gwinn-Hardy K, Petrucelli L, Hussey J, Singleton A, Tanner C, Hardy J, Langston JW (2001) Lewy bodies and parkinsonism in families with parkin mutations. Ann Neurol 50:293–300
Feany MB, Pallanck LJ (2003) Parkin: a multipurpose neuroprotective agent? Neuron 38:13–16
Foroud T, Uniacke SK, Liu L, Pankratz N, Rudolph A, Halter C, Shults C, Marder K, Conneally PM, Nichols WC (2003) Heterozygosity for a mutation in the parkin gene leads to later onset Parkinson disease. Neurology 60:796–801
Goldberg MS, Fleming SM, Palacino JJ, Cepeda C, Lam HA, Bhatnagar A, Meloni EG, Wu N, Ackerson LC, Klapstein GJ, Gajendiran M, Roth BL, Chesselet MF, Maidment NT, Levine MS, Shen J (2003) Parkin-deficient mice exhibit nigrostriatal deficits but not loss of dopaminergic neurons. J Biol Chem 44:43628–43635
Greene JC, Whitworth AJ, Kuo I, Andrews LA, Feany MB, Pallanck LJ (2003) Mitochondrial pathology and apoptotic muscle degeneration in Drosophila parkin mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:4078–4083
Hardy J, Cookson MR, Singleton A (2003) Genes and parkinsonism. Lancet Neurol 2:221–228
Hattori N, Kitada T, Matsumine H, Asakawa S, Yamamura Y, Yoshino H, Kobayashi T, Yokochi M, Wang M, Yoritaka A, Kondo T, Kuzuhara S, Nakamura S, Shimizu N, Mizuno Y (1998) Molecular genetic analysis of a novel parkin gene in Japanese families with autosomal recessive juvenile parkinsonism: evidence for variable homozygous deletions in the parkin gene in affected individuals. Ann Neurol 44:935–941
Hayashi S, Wakabayashi K, Ishikawa A, Nagai H, Saito M, Maruyama M, Takahashi T, Ozawa T, Tsuji S, Takahashi H (2000) An autopsy case of autosomal-recessive juvenile parkinsonism with a homozygous exon 4 deletion in the parkin gene. Mov Disord 15:884–888
Hedrich K, Marder K, Harris J, Kann M, Lynch T, Meija-Santana H, Pramstaller PP, Schwinger E, Bressman SB, Fahn S, Klein C (2002) Evaluation of 50 probands with early-onset Parkinson’s disease for parkin mutations. Neurology 58:1239–1246
Hilker R, Klein C, Ghaemi M, Kis B, Strotmann T, Ozelius LJ, Lenz O, Vieregge P, Herholz K, Heiss WD, Pramstaller PP (2001) Positron emission tomographic analysis of the nigrostriatal dopaminergic system in familial parkinsonism associated with mutations in the parkin gene. Ann Neurol 49:367–376
Hilker R, Klein C, Hedrich K, Ozelius LJ, Vieregge P, Herholz K, Pramstaller PP, Heiss WD (2002) The striatal dopaminergic deficit is dependent on the number of mutant alleles in a family with mutations in the parkin gene: evidence for enzymatic parkin function in humans. Neurosci Lett 323:50–54
Hu CJ, Sung SM, Liu HC, Lee CC, Tsai CH, Chang JG (2000) Polymorphisms of the parkin gene in sporadic Parkinson’s disease among Chinese in Taiwan. Eur Neurol 44:90–93
Ishikawa A, Takahashi H (1998) Clinical and neuropathological aspects of autosomal recessive juvenile parkinsonism. J Neurol 245:4–9
Itier JM, Ibanez P, Mena MA, Abbas N, Cohen-Salmon C, Bohme GA, Laville M, Pratt J, Corti O, Pradier L, Ret G, Joubert C, Periquet M, Araujo F, Negroni J, Casarejos MJ, Canals S, Solano R, Serrano A, Gallego E, Sanchez M, Denefle P, Benavides J, Tremp G, Rooney TA, Brice A, Garcia DY (2003) Parkin gene inactivation alters behaviour and dopamine neurotransmission in the mouse. Hum Mol Genet 12:2277–2291
Kann M, Jacobs H, Mohrmann K, Schumacher K, Hedrich K, Garrels J, Wiegers K, Schwinger E, Pramstaller PP, Breakefield XO, Ozelius LJ, Vieregge P, Klein C (2002) Role of parkin mutations in 111 community-based patients with early-onset parkinsonism. Ann Neurol 51:621–625
Khan NL, Brooks DJ, Pavese N, Sweeney MG, Wood NW, Lees AJ, Piccini P (2002) Progression of nigrostriatal dysfunction in a parkin kindred: an [18F]dopa PET and clinical study. Brain 125:2248–2256
Khan NL, Graham E, Critchley P, Schrag AE, Wood NW, Lees AJ, Bhatia KP, Quinn N (2003) Parkin disease: a phenotypic study of a large case series. Brain 126:1279–1292
Kitada T, Asakawa S, Hattori N, Matsumine H, Yamamura Y, Minoshima S, Yokochi M, Mizuno Y, Shimizu N (1998) Mutations in the parkin gene cause autosomal recessive juvenile parkinsonism. Nature 392:605–608
Langston JW (2002) Parkinson’s disease: current and future challenges. Neurotoxicology 23:443–450
Langston JW, Tan LC (2000) Juvenile parkinsonism: a term in search of an identity. Eur J Neurol 7:465–466
Leroy E, Anastasopoulos D, Konitsiotis S, Lavedan C, Polymeropoulos MH (1998) Deletions in the parkin gene and genetic heterogeneity in a Greek family with early onset Parkinson’s disease. Hum Genet 103:424–427
Lohmann E, Periquet M, Bonifati V, Wood NW, De Michele G, Bonnet AM, Fraix V, Broussolle E, Horstink MW, Vidailhet M, Verpillat P, Gasser T, Nicholl D, Teive H, Raskin S, Rascol O, Destee A, Ruberg M, Gasparini F, Meco G, Agid Y, Durr A, Brice A (2003) How much phenotypic variation can be attributed to parkin genotype? Ann Neurol 54:176–185
Lotharius J, Brundin P (2002) Pathogenesis of Parkinson’s disease: dopamine, vesicles and alpha-synuclein. Nat Rev Neurosci 3:932–942
Lucking CB, Abbas N, Durr A, Bonifati V, Bonnet AM, Broucker T de, De Michele G, Wood NW, Agid Y, Brice A (1998) Homozygous deletions in parkin gene in European and north African families with autosomal recessive juvenile parkinsonism. The European Consortium on Genetic Susceptibility in Parkinson’s Disease and the French Parkinson’s Disease Genetics Study Group. Lancet 352:1355–1356
Lucking CB, Durr A, Bonifati V, Vaughan J, De Michele G, Gasser T, Harhangi BS, Meco G, Denefle P, Wood NW, Agid Y, Brice A (2000) Association between early-onset Parkinson’s disease and mutations in the parkin gene. French Parkinson’s Disease Genetics Study Group. N Engl J Med 342:1560–1567
Maher NE, Currie LJ, Lazzarini AM, Wilk JB, Taylor CA, Saint-Hilaire MH, Feldman RG, Golbe LI, Wooten GF, Myers RH (2002) Segregation analysis of Parkinson disease revealing evidence for a major causative gene. Am J Med Genet 109:191–197
Maruyama M, Ikeuchi T, Saito M, Ishikawa A, Yuasa T, Tanaka H, Hayashi S, Wakabayashi K, Takahashi H, Tsuji S (2000) Novel mutations, pseudo-dominant inheritance, and possible familial affects in patients with autosomal recessive juvenile parkinsonism. Ann Neurol 48:245–250
Matsumine H, Yamamura Y, Hattori N, Kobayashi T, Kitada T, Yoritaka A, Mizuno Y (1998) A microdeletion of D6S305 in a family of autosomal recessive juvenile parkinsonism (PARK2). Genomics 49:143–146
Melamed E, Offen D, Shirvan A, Ziv I (2000) Levodopa—an exotoxin or a therapeutic drug? J Neurol 247 (Suppl 2):II135–II139
Mizuno Y, Hattori N, Mori H (1999) Genetics of Parkinson’s disease. Biomed Pharmacother 53:109–116
Mori H, Kondo T, Yokochi M, Matsumine H, Nakagawa-Hattori Y, Miyake T, Suda K, Mizuno Y (1998) Pathologic and biochemical studies of juvenile parkinsonism linked to chromosome 6q. Neurology 51:890–892
Oliveri RL, Zappia M, Annesi G, Bosco D, Annesi F, Spadafora P, Pasqua AA, Tomaino C, Nicoletti G, Pirritano D, Labate A, Gambardella A, Logroscino G, Manobianca G, Epifanio A, Morgante L, Savettieri G, Quattrone A (2001) The parkin gene is not involved in late-onset Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 57:359–362
Oliveira SA, Scott WK, Martin ER, Nance MA, Watts RL, Hubble JP, Koller WC, Pahwa R, Stern MB, Hiner BC, Ondo WG, Allen FH Jr, Scott BL, Goetz CG, Small GW, Mastaglia F, Stajich JM, Zhang F, Booze MW, Winn MP, Middleton LT, Haines JL, Pericak-Vance MA, Vance JM (2003a) Parkin mutations and susceptibility alleles in late-onset Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 53:624–629
Oliveira SA, Scott WK, Nance MA, Watts RL, Hubble JP, Koller WC, Lyons KE, Pahwa R, Stern MB, Hiner BC, Jankovic J, Ondo WG, Allen FH Jr, Scott BL, Goetz CG, Small GW, Mastaglia FL, Stajich JM, Zhang F, Booze MW, Reaves JA, Middleton LT, Haines JL, Pericak-Vance MA, Vance JM, Martin ER (2003b) Association study of parkin gene polymorphisms with idiopathic Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 60:975–980
Pal PK, Leung J, Hedrich K, Samii A, Lieberman A, Nausieda PA, Calne DB, Breakefield XO, Klein C, Stoessl AJ (2002) [18F]-Dopa positron emission tomography imaging in early-stage, non-parkin juvenile parkinsonism. Mov Disord 17:789–794
Pankratz N, Nichols WC, Uniacke SK, Halter C, Murrell J, Rudolph A, Shults CW, Conneally PM, Foroud T, Parkinson Study Group (2003) Genome-wide linkage analysis and evidence of gene-by-gene interactions in a sample of 362 multiplex Parkinson disease families. Hum Mol Genet 20:2599–2608
Periquet M, Lucking C, Vaughan J, Bonifati V, Durr A, De Michele G, Horstink M, Farrer M, Illarioshkin SN, Pollak P, Borg M, Brefel-Courbon C, Denefle P, Meco G, Gasser T, Breteler MM, Wood N, Agid Y, Brice A (2001) Origin of the mutations in the parkin gene in Europe: exon rearrangements are independent recurrent events, whereas point mutations may result from founder effects. Am J Hum Genet 68:617–626
Periquet M, Latouche M, Lohmann E, Rawal N, De Michele G, Ricard S, Teive H, Fraix V, Vidailhet M, Nicholl D, Barone P, Wood NW, Raskin S, Deleuze JF, Agid Y, Durr A, Brice A (2003) Parkin mutations are frequent in patients with isolated early-onset parkinsonism. Brain 126:1271–1278
Petrucelli L, O’Farrell C, Lockhart PJ, Baptista M, Kehoe K, Vink L, Choi P, Wolozin B, Farrer M, Hardy J, Cookson MR (2002) Parkin protects against the toxicity associated with mutant alpha-synuclein: proteasome dysfunction selectively affects catecholaminergic neurons. Neuron 36:1007–1019
Rajput AH, Uitti RJ, Sudhakar S, Rozdilsky B (1989) Parkinsonism and neurofibrillary tangle pathology in pigmented nuclei. Ann Neurol 25:602–606
Rao G, Fisch L, Srinivasan S, D’Amico F, Okada T, Eaton C, Robbins C (2003) Does this patient have Parkinson disease? JAMA 289:347–353
Rawal N, Periquet M, Lohmann E, Lucking CB, Teive HA, Ambrosio G, Raskin S, Lincoln S, Hattori N, Guimaraes J, Horstink MW, Dos Santos BW, Brousolle E, Destee A, Mizuno Y, Farrer M, Deleuze JF, De Michele G, Agid Y, Durr A, Brice A (2003) New parkin mutations and atypical phenotypes in families with autosomal recessive parkinsonism. Neurology 60:1378–1381
Richards RI (2001) Fragile and unstable chromosomes in cancer: causes and consequences. Trends Genet 17:339–345
Satoh J, Kuroda Y (1999) Association of codon 167 Ser/Asn heterozygosity in the parkin gene with sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neuroreport 10:2735–2739
Scott WK, Nance MA, Watts RL, Hubble JP, Koller WC, Lyons K, Pahwa R, Stern MB, Colcher A, Hiner BC, Jankovic J, Ondo WG, Allen FH Jr, Goetz CG, Small GW, Masterman D, Mastaglia F, Laing NG, Stajich JM, Slotterbeck B, Booze MW, Ribble RC, Rampersaud E, West SG, Gibson RA, Middleton LT, Roses AD, Haines JL, Scott BL, Vance JM, Pericak-Vance MA (2001) Complete genomic screen in Parkinson disease: evidence for multiple genes. JAMA 286:2239–2244
Skipper L, Farrer M (2002) Parkinson’s genetics: molecular insights for the new millennium. Neurotoxicology 23:503–514
Smith DI, Huang H, Wang L (1998) Common fragile sites and cancer. Int J Oncol 12:187–196
Spillantini MG, Schmidt ML, Lee VM, Trojanowski JQ, Jakes R, Goedert M (1997) Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature 388:839–840
Sveinbjornsdottir S, Hicks AA, Jonsson T, Petursson H, Gugmundsson G, Frigge ML, Kong A, Gulcher JR, Stefansson K (2000) Familial aggregation of Parkinson’s disease in Iceland. N Engl J Med 343:1765–1770
Tanner CM, Aston DA (2000) Epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease and akinetic syndromes. Curr Opin Neurol 13:427–430
Thobois S, Ribeiro MJ, Lohmann E, Durr A, Pollak P, Rascol O, Guillouet S, Chapoy E, Costes N, Agid Y, Remy P, Brice A, Broussolle E (2003) Young-onset Parkinson disease with and without parkin gene mutations: a fluorodopa F 18 positron emission tomography study. Arch Neurol 60:713–718
Wang M, Hattori N, Matsumine H, Kobayashi T, Yoshino H, Morioka A, Kitada T, Asakawa S, Minoshima S, Shimizu N, Mizuno Y (1999) Polymorphism in the parkin gene in sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 45:655–658
Warrenburg BP van de, Lammens M, Lucking CB, Denefle P, Wesseling P, Booij J, Praamstra P, Quinn N, Brice A, Horstink MW (2001) Clinical and pathologic abnormalities in a family with parkinsonism and parkin gene mutations. Neurology 56:555–557
West AB, Periquet M, Lincoln S, Lucking CB, Nicholl D, Bonifati V, Rawal N, Gasser T, Lohmann E, Deleuze JF, Maraganore D, Levey A, Wood N, Durr A, Hardy J, Brice A, Farrer M (2002a) Complex relationship between Parkin mutations and Parkinson disease. Am J Med Genet 114:584–591
West AB, Maraganore D, Crook J, Lesnick T, Lockhart PJ, Wilkes KM, Kapatos G, Hardy JA, Farrer MJ (2002b) Functional association of the parkin gene promoter with idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Hum Mol Genet 11:2787–2792
West AB, Lockhart PJ, O’Farell C, Farrer MJ (2003) Identification of a novel gene linked to parkin via a bi-directional promoter. J Mol Biol 326:11–19
Yokochi M, Narabayashi H, Iizuka R, Nagatsu T (1984) Juvenile parkinsonism—some clinical, pharmacological, and neuropathological aspects. Adv Neurol 40:407–413
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the Udall Parkinson’s Disease Centers of Excellence for financial support and to Matt Farrer and John Hardy for useful discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
West, A.B., Maidment, N.T. Genetics of parkin-linked disease. Hum Genet 114, 327–336 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-003-1074-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-003-1074-6