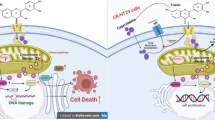
Abstract
T-type calcium channels are involved in a multitude of cellular processes, both physiological and pathological, including cancer. T-type channels are also often aberrantly expressed in different human cancers and participate in the regulation of cell cycle progression, proliferation, migration, and survival. Here, we review the recent literature and discuss the controversies, supporting the role of T-type Ca2+ channels in cancer cells and the proposed use of channels blockers as anticancer agents. A growing number of reports show that pharmacological inhibition or RNAi-mediated downregulation of T-type channels leads to inhibition of cancer cell proliferation and increased cancer cell death. In addition to a single agent activity, experimental results demonstrate that T-type channel blockers enhance the anticancer effects of conventional radio- and chemotherapy. At present, the detailed biological mechanism(s) underlying the anticancer activity of these channel blockers is not fully understood. Recent findings and ideas summarized here identify T-type Ca2+ channels as a molecular target for anticancer therapy and offer new directions for the design of novel therapeutic strategies employing channels blockers. Physiological relevance: T-type calcium channels are often aberrantly expressed or deregulated in cancer cells, supporting their proliferation, survival, and resistance to treatment; therefore, T-type Ca2+ channels could be attractive molecular targets for anticancer therapy.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alison MR, Lin W-R, Lim SML, Nicholson LJ (2012) Cancer stem cells: in the line of fire. Cancer Treat Rev 38(6):589–598
Amorino GP, Parsons SJ (2004) Neuroendocrine cells in prostate cancer. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr 14(4):287–300
Atlas D (2010) Signaling role of the voltage-gated calcium channel as the molecular on/off-switch of secretion. Cell Signal 22(11):1597–1603
Balk SD (1971) Calcium as a regulator of the proliferation of normal, but not of transformed, chicken fibroblasts in a plasma-containing medium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 68(2):271–275
Balkwill F, Mantovani A (2001) Inflammation and cancer: back to Virchow? Lancet 357(9255):539–545
Bertolesi GE, Jollimore CAB, Shi C, Elbaum L, Denovan-Wright EM, Barnes S, Kelly MEM (2003) Regulation of alpha1G T-type calcium channel gene (CACNA1G) expression during neuronal differentiation. Eur J Neurosci 17(9):1802–1810
Bertolesi GE, Shi C, Elbaum L, Jollimore C, Rozenberg G, Barnes S, Kelly MEM (2002) The Ca(2+) channel antagonists mibefradil and pimozide inhibit cell growth via different cytotoxic mechanisms. Mol Pharmacol 62(2):210–219
Bilici D, Akpinar E, Gürsan N, Dengiz GO, Bilici S, Altaş S (2001) Protective effect of T-type calcium channel blocker in histamine-induced paw inflammation in rat. Pharmacol Res Off J Ital Pharmacol Soc 44(6):527–531
Boynton AL, Whitfield JF, Isaacs RJ, Tremblay RG (1977) Different extracellular calcium requirements for proliferation of nonneoplastic, preneoplastic, and neoplastic mouse cells. Cancer Res 37(8 Pt 1):2657–2661
Bringmann A, Schopf S, Reichenbach A (2000) Developmental regulation of calcium channel-mediated currents in retinal glial (Müller) cells. J Neurophysiol 84(6):2975–2983
Capiod T (2011) Cell proliferation, calcium influx and calcium channels. Biochimie 93(12):2075–2079
Carbone E, Lux HD (1984) A low voltage-activated, fully inactivating Ca channel in vertebrate sensory neurones. Nature 310(5977):501–502
Chemin J, Nargeot J, Lory P (2004) Ca(v)3.2 calcium channels control an autocrine mechanism that promotes neuroblastoma cell differentiation. Neuroreport 15(4):671–675
Clapham DE (2007) Calcium signaling. Cell 131(6):1047–1058
Das A, Pushparaj C, Bahí N, Sorolla A, Herreros J, Pamplona R, Vilella R, Matias-Guiu X, Martí RM, Cantí C (2012) Functional expression of voltage-gated calcium channels in human melanoma. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res 25(2):200–212
Das A, Pushparaj C, Herreros J, Nager M, Vilella R, Portero M, Pamplona R, Matias-Guiu X, Martí R, Cantí C (2013) T-type calcium channel blockers inhibit autophagy and promote apoptosis of malignant melanoma cells. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res 26(6):874–85
Del Toro R, Levitsky KL, López-Barneo J, Chiara MD (2003) Induction of T-type calcium channel gene expression by chronic hypoxia. J Biol Chem 278(25):22316–22324
Di Sant’Agnese PA (2001) Neuroendocrine differentiation in prostatic carcinoma: an update on recent developments. Ann Oncol Off J Eur Soc Med Oncol / ESMO 12(Suppl 2):S135–140
Dziegielewska B, Brautigan DL, Larner JM, Dziegielewski J (2013) T-type Ca2+ channel inhibition induces p53 dependent cell growth arrest and apoptosis through activation of p38-MAPK in colon cancer cells. Molecular Cancer Research: MCR. http://mcr.aacrjournals.org/content/early/2013/12/20/1541-7786.MCR-13-0485.abstract. Accessed 30 Dec 2013
Eller P, Berjukov S, Wanner S, Huber I, Hering S, Knaus HG, Toth G, Kimball SD, Striessnig J (2000) High affinity interaction of mibefradil with voltage-gated calcium and sodium channels. Br J Pharmacol 130(3):669–677
Fallon MT (2013) Neuropathic pain in cancer. Br J Anaesth 111(1):105–111
Fearon IM, Randall AD, Perez-Reyes E, Peers C (2000) Modulation of recombinant T-type Ca2+ channels by hypoxia and glutathione. Pflügers Archiv Eur J Physiol 441(2-3):181–188
Fisseler-Eckhoff A, Demes M (2012) Neuroendocrine tumors of the lung. Cancers 4(3):777–798
Fixemer T, Remberger K, Bonkhoff H (2002) Apoptosis resistance of neuroendocrine phenotypes in prostatic adenocarcinoma. Prostate 53(2):118–123
Flatters SJL, Bennett GJ (2004) Ethosuximide reverses paclitaxel- and vincristine-induced painful peripheral neuropathy. Pain 109(1-2):150–161
Gackière F, Bidaux G, Delcourt P, Van Coppenolle F, Katsogiannou M, Dewailly E, Bavencoffe A, Van Chuoï-Mariot MT, Mauroy B, Prevarskaya N, Mariot P (2008) CaV3.2 T-type calcium channels are involved in calcium-dependent secretion of neuroendocrine prostate cancer cells. J Biol Chem 283(15):10162–10173
Goel S, Duda DG, Xu L, Munn LL, Boucher Y, Fukumura D, Jain RK (2011) Normalization of the vasculature for treatment of cancer and other diseases. Physiol Rev 91(3):1071–1121
Gray LS, Macdonald TL (2006) The pharmacology and regulation of T type calcium channels: new opportunities for unique therapeutics for cancer. Cell Calcium 40(2):115–120
Gray LS, Schiff D, Macdonald TL (2013) A model for the regulation of T-type Ca(2+) channels in proliferation: roles in stem cells and cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther 13(5):589–595
Haverstick DM, Heady TN, Macdonald TL, Gray LS (2000) Inhibition of human prostate cancer proliferation in vitro and in a mouse model by a compound synthesized to block Ca2+ entry. Cancer Res 60(4):1002–1008
Heady TN, Gomora JC, Macdonald TL, Perez-Reyes E (2001) Molecular pharmacology of T-type Ca2+ channels. Jpn J Pharmacol 85(4):339–350
Heo JH, Seo HN, Choe YJ, Kim S, Oh CR, Kim YD, Rhim H, Choo DJ, Kim J, Lee JY (2008) T-type Ca2+ channel blockers suppress the growth of human cancer cells. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 18(14):3899–3901
Hirooka K, Bertolesi GE, Kelly MEM, Denovan-Wright EM, Sun X, Hamid J, Zamponi GW, Juhasz AE, Haynes LW, Barnes S (2002) T-Type calcium channel alpha1G and alpha1H subunits in human retinoblastoma cells and their loss after differentiation. J Neurophysiol 88(1):196–205
Huang L, Keyser BM, Tagmose TM, Hansen JB, Taylor JT, Zhuang H, Zhang M, Ragsdale DS, Li M (2004) NNC 55-0396 [(1S,2S)-2-(2-(N-[(3-benzimidazol-2-yl)propyl]-N-methylamino)ethyl)-6-fluoro-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-1-isopropyl-2-naphtyl cyclopropanecarboxylate dihydrochloride]: a new selective inhibitor of T-type calcium channels. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 309(1):193–199
Ischenko I, Seeliger H, Schaffer M, Jauch K-W, Bruns CJ (2008) Cancer stem cells: how can we target them? Curr Med Chem 15(30):3171–3184
Jaggi AS, Singh N (2012) Mechanisms in cancer-chemotherapeutic drugs-induced peripheral neuropathy. Toxicology 291(1-3):1–9
Jang, SJ, Choi HW, Choi DL, Cho S, Rim H.-K, Choi H.-E, Kim K-S, Huang M, Rhim H, Lee K-T, Lee JY (2013) In vitro cytotoxicity on human ovarian cancer cells by T-type calcium channel blockers. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 23(24):6656–62
Joksovic PM, Nelson MT, Jevtovic-Todorovic V, Patel MK, Perez-Reyes E, Campbell KP, Chen C-C, Todorovic SM (2006) CaV3.2 is the major molecular substrate for redox regulation of T-type Ca2+ channels in the rat and mouse thalamus. J Physiol 574(2):415–430
Kahl CR, Means AR (2003) Regulation of cell cycle progression by calcium/calmodulin-dependent pathways. Endocr Rev 24(6):719–736
Kang HB, Rim H-K, Park JY, Choi HW, Choi DL, Seo J-H, Chung K-S, Huh G, Kim J, Choo DJ, Lee K-T, Lee JY (2012) In vivo evaluation of oral anti-tumoral effect of 3,4-dihydroquinazoline derivative on solid tumor. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 22(2):1198–1201
Keir ST, Friedman HS, Reardon DA, Bigner DD, Gray LA (2013) Mibefradil, a novel therapy for glioblastoma multiforme: cell cycle synchronization and interlaced therapy in a murine model. J Neuro-oncol 111(2):97–102
Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation (2013) Human protein atlas. www.proteinatlas.org. Accessed 15 Nov 2013
Kundu JK, Surh Y-J (2008) Inflammation: gearing the journey to cancer. Mutat Res 659(1-2):15–30
Kwon SY, Bae YK, Gu MJ, Choi JE, Kang SH, Lee SJ, Kim A, Jung HR, Kang SH, Oh HK, Park JY (2013) Neuroendocrine differentiation correlates with hormone receptor expression and decreased survival in patients with invasive breast carcinoma. http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/his.12306/abstract. Accessed 30 Dec 2013
Lijnen P, Fagard R, Petrov V (1999) Mibefradil-induced inhibition of proliferation of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 33(4):595–604
Li W, Zhang S-L, Wang N, Zhang B-B, Li M (2011) Blockade of T-type Ca(2+) channels inhibits human ovarian cancer cell proliferation. Cancer Investig 29(5):339–346
Li Y, Liu S, Lu F, Zhang T, Chen H, Wu S, Zhuang H (2009) A role of functional T-type Ca2+ channel in hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation. Oncol Rep 22(5):1229–1235
Life Technologies Corporation (2013) https://www.oncomine.com/resource/main.html#d:212;dso:geneOverex;dt:dataset;ec[2];epv:150001.151078,3508;et:over;f:2502825;g:8912;gt:boxplot;p:77321987;pg:1;pvf:3518,7696;scr:datasets;ss:all;v:17. Accessed 15 Nov 2013
Lory P, Bidaud I, Chemin J (2006) T-type calcium channels in differentiation and proliferation. Cell Calcium 40(2):135–146
Louhivuori LM, Louhivuori V, Wigren H-K, Hakala E, Jansson LC, Nordström T, Castrén ML, Akerman KE (2013) Role of low voltage activated calcium channels in neuritogenesis and active migration of embryonic neural progenitor cells. Stem Cells Dev 22(8):1206–1219
Lu F, Chen H, Zhou C, Liu S, Guo M, Chen P, Zhuang H, Xie D, Wu S (2008) T-type Ca2+ channel expression in human esophageal carcinomas: a functional role in proliferation. Cell Calcium 43(1):49–58
Lu F, Chen H, Zhou C, Wu S (2005) Is there a role for T-type Ca2+ channel in glioma cell proliferation? Cell Calcium 38(6):593–595, author reply 597
Mariot P, Vanoverberghe K, Lalevee N, Rossier MF, Prevarskaya N (2002) Overexpression of an alpha 1H (Cav3.2) T-type calcium channel during neuroendocrine differentiation of human prostate cancer cells. J Biol Chem 277(13):10824–10833
Mehrke G, Zong XG, Flockerzi V, Hofmann F (1994) The Ca(++)-channel blocker Ro 40–5967 blocks differently T-type and L-type Ca++ channels. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 271(3):1483–1488
Mishra SK, Hermsmeyer K (1994) Selective inhibition of T-type Ca2+ channels by Ro 40–5967. Circ Res 75(1):144–148
Moncharmont C, Levy A, Gilormini M, Bertrand G, Chargari C, Alphonse G, Ardail D, Rodriguez-Lafrasse C, Magné N (2012) Targeting a cornerstone of radiation resistance: cancer stem cell. Cancer Lett 322(2):139–147
Monteith GR, Davis FM, Roberts-Thomson SJ (2012) Calcium channels and pumps in cancer: changes and consequences. J Biol Chem 287(38):31666–31673
Monteith GR, McAndrew D, Faddy HM, Roberts-Thomson SJ (2007) Calcium and cancer: targeting Ca2+ transport. Nat Rev Cancer 7(7):519–530
Nebe B, Kunz F, Peters A, Rychly J, Noack T, Beck R (2004) Induction of apoptosis by the calcium antagonist mibefradil correlates with depolarization of the membrane potential and decreased integrin expression in human lens epithelial cells. Graefe’s Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol = Albrecht Von Graefes Archiv Für Klinische Und Experimentelle Ophthalmologie 242(7):597–604
Nilius B, Hess P, Lansman JB, Tsien RW (1985) A novel type of cardiac calcium channel in ventricular cells. Nature 316(6027):443–446
Nilius B, Talavera K, Verkhratsky A (2006) T-type calcium channels: the never ending story. Cell Calcium 40(2):81–88
Nowycky MC, Fox AP, Tsien RW (1985) Three types of neuronal calcium channel with different calcium agonist sensitivity. Nature 316(6027):440–443
Oguri A, Tanaka T, Iida H, Meguro K, Takano H, Oonuma H, Nishimura S, Morita T, Yamasoba T, Nagai R, Nakajima T (2010) Involvement of CaV3.1 T-type calcium channels in cell proliferation in mouse preadipocytes. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 298(6):C1414–1423
Ohkubo T, Yamazaki J (2012) T-type voltage-activated calcium channel Cav3.1, but not Cav3.2, is involved in the inhibition of proliferation and apoptosis in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells. Int J Oncol 41(1):267–275
Panner A, Cribbs LL, Zainelli GM, Origitano TC, Singh S, Wurster RD (2005) Variation of T-type calcium channel protein expression affects cell division of cultured tumor cells. Cell Calcium 37(2):105–119
Panner A, Wurster RD (2006) T-type calcium channels and tumor proliferation. Cell Calcium 40(2):253–259
Perez-Reyes E (2003) Molecular physiology of low-voltage-activated t-type calcium channels. Physiol Rev 83(1):117–161
Perez-Reyes E, Van Deusen AL, Vitko I (2009) Molecular pharmacology of human Cav3.2 T-type Ca2+ channels: block by antihypertensives, antiarrhythmics, and their analogs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 328(2):621–627
Pluteanu F, Cribbs LL (2009) T-type calcium channels are regulated by hypoxia/reoxygenation in ventricular myocytes. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 297(4):H1304–1313
Potente M, Gerhardt H, Carmeliet P (2011) Basic and therapeutic aspects of angiogenesis. Cell 146(6):873–887
Pottle J, Sun C, Gray L, Li M (2013) Exploiting MCF-7 cells’ calcium dependence with Interlaced Therapy. J Cancer Ther 04(07):32–40
Rim H-K, Lee H-W, Choi IS, Park JY, Choi HW, Choi J-H, Cho Y-W, Lee JY, Lee K-T (2012) T-type Ca2+ channel blocker, KYS05047 induces G1 phase cell cycle arrest by decreasing intracellular Ca2+ levels in human lung adenocarcinoma A549 cells. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 22(23):7123–7126
Rodríguez-Gómez JA, Levitsky KL, López-Barneo J (2012) T-type Ca2+ channels in mouse embryonic stem cells: modulation during cell cycle and contribution to self-renewal. Am J Physiol Cell physiol 302(3):C494–504
Santoni G, Santoni M, Nabissi M (2012) Functional role of T-type calcium channels in tumour growth and progression: prospective in cancer therapy. Br J Pharmacol 166(4):1244–1246
Schmitt R, Clozel JP, Iberg N, Bühler FR (1996) Prevention of neointima formation by mibefradil after vascular injury in rats: comparison with ACE inhibition. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther / Sponsored Int Soc Cardiovasc Pharmacother 10(2):101–105
Seigel GM, Hackam AS, Ganguly A, Mandell LM, Gonzalez-Fernandez F (2007) Human embryonic and neuronal stem cell markers in retinoblastoma. Mol Vis 13(2007):823–832
Sekiguchi F, Kawabata A (2013) T-type calcium channels: functional regulation and implication in pain signaling. J Pharmacol Sci 122(4):244–250
Sheehan JP, Xu Z, Popp B, Kowalski L, Schlesinger D (2013) Inhibition of glioblastoma and enhancement of survival via the use of mibefradil in conjunction with radiosurgery. J Neurosurg 118(4):830–837
Su AI, Welsh JB, Sapinoso LM, Kern SG, Dimitrov P, Lapp H, Schultz PG, Powell SM, Moskaluk CA, Frierson HF Jr, Hampton GM (2001) Molecular classification of human carcinomas by use of gene expression signatures. Cancer Res 61(20):7388–7393
Taylor JT, Huang L, Pottle JE, Liu K, Yang Y, Zeng X, Keyser BM, Agrawal KC, Hansen JB, Li M (2008) Selective blockade of T-type Ca2+ channels suppresses human breast cancer cell proliferation. Cancer Lett 267(1):116–124
Taylor JT, Zeng X-B, Pottle JE, Lee K, Wang AR, Yi SG, Scruggs JAS, Sikka SS, Li M (2008) Calcium signaling and T-type calcium channels in cancer cell cycling. World J Gastroenterol WJG 14(32):4984–4991
Toyota M, Ho C, Ohe-Toyota M, Baylin SB, Issa JP (1999) Inactivation of CACNA1G, a T-type calcium channel gene, by aberrant methylation of its 5′ CpG island in human tumors. Cancer Res 59(18):4535–4541
Trepel JB (2003) Ion channels as molecular targets in prostate cancer. Clin Prostate Cancer 2(3):188–189
Valerie NCK, Dziegielewska B, Hosing AS, Augustin E, Gray LS, Brautigan DL, Larner JM, Dziegielewski J (2013) Inhibition of T-type calcium channels disrupts Akt signaling and promotes apoptosis in glioblastoma cells. Biochem Pharmacol 85(7):888–897
Vanoverberghe K, Vanden Abeele F, Mariot P, Lepage G, Roudbaraki M, Bonnal JL, Mauroy B, Shuba Y, Skryma R, Prevarskaya N (2004) Ca2+ homeostasis and apoptotic resistance of neuroendocrine-differentiated prostate cancer cells. Cell Death Differ 11(3):321–330
Viana F, Van den Bosch L, Missiaen L, Vandenberghe W, Droogmans G, Nilius B, Robberecht W (1997) Mibefradil (Ro 40–5967) blocks multiple types of voltage-gated calcium channels in cultured rat spinal motoneurones. Cell Calcium 22(4):299–311
Wang D, Hirase T, Inoue T, Node K (2006) Atorvastatin inhibits angiotensin II-induced T-type Ca2+ channel expression in endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 347(2):394–400
Wang L, Bhattacharjee A, Zuo Z, Hu F, Honkanen RE, Berggren PO, Li M (1999) A low voltage-activated Ca2+ current mediates cytokine-induced pancreatic beta-cell death. Endocrinology 140(3):1200–1204
Wilson WR, Hay MP (2011) Targeting hypoxia in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 11(6):393–410
Zhang Y, Cribbs LL, Satin J (2000) Arachidonic acid modulation of alpha1H, a cloned human T-type calcium channel. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 278(1):H184–193
Zhang Y, Zhang J, Jiang D, Zhang D, Qian Z, Liu C, Tao J (2012) Inhibition of T-type Ca(2+) channels by endostatin attenuates human glioblastoma cell proliferation and migration. Br J Pharmacol 166(4):1247–1260
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by the University of Virginia P30 CA44579, by a pilot funding from the James and Rebecca Craig Fund (to JD), and by the University of Virginia Department of Radiation Oncology George P. Amorino pilot grant (to BD and JD).
Conflict of interest
Dr. Lloyd S. Gray is a cofounder of and consultant to Tau Therapeutics LLC. Dr. Jaroslaw Dziegielewski has received research contract funding from Tau Therapeutics LLC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article is published as part of the Special Issue on T-type (Cav3) calcium channels in health and disease.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dziegielewska, B., Gray, L.S. & Dziegielewski, J. T-type calcium channels blockers as new tools in cancer therapies. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 466, 801–810 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-014-1444-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-014-1444-z