Abstract
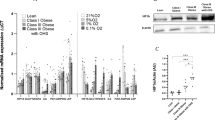
Adipose tissue becomes hypoxic in obesity, and cell culture studies have demonstrated that hypoxia leads to major changes in adipocyte function. Studies on the response of adipocytes to low O2 tension have employed marked hypoxia (1% O2). Here, we have examined the effects of modest hypoxia, utilising differing concentrations of O2 (1–21%), on adipokine production and glucose uptake by human adipocytes. Incubation with 10% O2 (24 h) increased expression of the leptin, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and Angptl4 genes, while leptin expression was elevated even at 15% O2 (compared to ‘normoxia’—21% O2). Overall, there was a concentration-dependent increase in the expression of these genes as O2 fell, with the highest mRNA level evident at 1% O2. Parallel changes were observed in the secretion of leptin, VEGF and IL-6 into the medium, an increased release being evident at 10% O2 (15% O2 for leptin). Adiponectin gene expression was reduced at 15% O2 and below, while adiponectin release was significantly reduced at 5% O2. Both 2-deoxy-d-glucose uptake and lactate release showed progressive increases as O2 concentration fell, being significantly raised at 10% and 5% O2, respectively. The alterations in substrate transport were accompanied by parallel changes in transporter gene expression, GLUT1 and MCT1 mRNA level increasing from 15% and 10% O2, respectively. These results indicate that marked responses to reduced O2 concentration are exhibited by human adipocytes at O2 levels well above those associated with hypoxia and employed in cell culture studies. Adipocytes are sensitive to small changes in O2 tension.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arita Y, Kihara S, Ouchi N, Takahashi M, Maeda K, Miyagawa J, Hotta K, Shimomura I, Nakamura T, Miyaoka K, Kuriyama H, Nishida M, Yamashita S, Okubo K, Matsubara K, Muraguchi M, Ohmoto Y, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y (1999) Paradoxical decrease of an adipose-specific protein, adiponectin, in obesity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 257:79–83
Berg AH, Combs TP, Du X, Brownlee M, Scherer PE (2001) The adipocyte-secreted protein Acrp30 enhances hepatic insulin action. Nat Med 7:947–953
Brahimi-Horn MC, Pouyssegur J (2007) Oxygen, a source of life and stress. FEBS Lett 581:3582–3591
Chen B, Lam KSL, Wang Y, Wu D, Lam MC, Shen J, Wong L, Hoo RLC, Zhang J, Xu A (2006) Hypoxia dysregulates the production of adiponectin and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 independent of reactive oxygen species in adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 341:549–556
Considine RV, Sinha MK, Heiman ML, Kriauciunas A, Stephens TW, Nyce MR, Ohannesian JP, Marco CC, McKee LJ, Bauer TL, Caro JF (1996) Serum immunoreactive leptin concentrations in normal-weight and obese humans. New Engl J Med 334:292–295
Curat CA, Miranville A, Sengenes C, Diehl M, Tonus C, Busse R, Bouloumié A (2004) From blood monocytes to adipose tissue-resident macrophages: induction of diapedesis by human mature adipocytes. Diabetes 53:1285–1292
Festa A, D’Agostino R Jr, Williams K, Karter AJ, Mayer-Davis EJ, Tracy RP, Haffner SM (2001) The relation of body fat mass and distribution to markers of chronic inflammation. Int J Obesity 25:1407–1415
Frühbeck G, Salvador J (2004) Role of adipocytokines in metabolism and disease. Nutr Res 24:803–826
Hausman GJ (1985) The comparative anatomy of adipose tissue. In: Cryer A, Van RLR (eds) New perspectives in adipose tissue: structure, function and development. Butterworths, London, pp 1–21
Hosogai N, Fukuhara A, Oshima K, Miyata Y, Tanaka S, Segawa K, Furukawa S, Tochino Y, Komuro R, Matsuda M, Shimomura I (2007) Adipose tissue hypoxia in obesity and its impact on adipocytokine dysregulation. Diabetes 56:901–911
Hotamisligil GS (2006) Inflammation and metabolic disorders. Nature 444:860–867
Karpe F, Fielding BA, Ilic V, Macdonald IA, Summers LKM, Frayn KN (2002) Impaired postprandial adipose tissue blood flow response is related to aspects of insulin sensitivity. Diabetes 51:2467–2473
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2ΔΔct method. Methods 25:402–408
Lolmède K, de Saint D, Front V, Galitzky J, Lafontan M, Bouloumié A (2003) Effects of hypoxia on the expression of proangiogenic factors in differentiated 3T3-F442A adipocytes. Int J Obesity 27:1187–1195
Ostlund RE, Yang JW, Klein S, Gingerich R (1996) Relation between plasma leptin concentration and body fat, gender, diet, age, and metabolic covariates. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 81:3909–3913
Ouchi N, Kihara S, Arita Y, Maeda K, Kuriyama H, Okamoto Y, Hotta K, Nishida M, Takahashi M, Nakamura T, Yamashita S, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y (1999) Novel modulator for endothelial adhesion molecules: adipocyte-derived plasma protein adiponectin. Circulation 100:2473–2476
Ouchi N, Kihara S, Arita Y, Okamoto Y, Maeda K, Kuriyama H, Hotta K, Nishida M, Takahashi M, Muraguchi M, Ohmoto Y, Nakamura T, Yamashita S, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y (2000) Adiponectin, an adipocyte-derived plasma protein, inhibits endothelial NF-kappa B signaling through a cAMP-dependent pathway. Circulation 102:1296–1301
Pasarica M, Sereda OR, Redman LM, Albarado DC, Hymel DT, Roan LE, Rood JC, Burk DH, Smith SR (2009) Reduced adipose tissue oxygenation in human obesity: evidence for rarefaction, macrophage chemotaxis, and inflammation without an angiogenic response. Diabetes 58:718–725
Patel SA, Simon MC (2008) Biology of hypoxia-inducible factor-2α in development and disease. Cell Death Differ 15:628–634
Pérez de Heredia F, Wood IS, Trayhurn P (2010) Hypoxia stimulates lactate release and modulates monocarboxylate transporter (MCT1, MCT2, and MCT4) expression in human adipocytes. Pflügers Arch Eur J Physiol 459:509–518
Rajala MW, Scherer PE (2003) The adipocyte—at the crossroads of energy homeostasis, inflammation, and atherosclerosis. Endocrinology 144:3765–3773
Rausch ME, Weisberg SP, Vardhana P, Tortorielllo DV (2008) Obesity in C57BL/6J mice is characterised by adipose tissue hypoxia and cytotoxic T-cell infiltration. Int J Obesity 32:451–463
Regazzetti C, Peraldi P, Gremeaux T, Najem-Lendom R, Ben-Sahra I, Cormont M, Bost F, Le Marchand-Brustel Y, Tanti J-F, Giorgetti-Peraldi S (2009) Hypoxia decreases insulin signaling pathways in adipocytes. Diabetes 58:95–103
Rocha S (2007) Gene regulation under low oxygen: holding your breath for transcription. Trends Biochem Sci 32:389–397
Rosen ED, Spiegelman BM (2006) Adipocytes as regulators of energy balance and glucose homeostasis. Nature 444:847–853
Semenza GL (2001) HIF-1 and mechanisms of hypoxia sensing. Curr Opin Cell Biol 13:167–171
Semenza GL (2003) Targeting HIF-1 for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 3:721–732
Skurk T, Alberti-Huber C, Herder C, Hauner H (2007) Relationship between adipocyte size and adipokine expression and secretion. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92:1023–1033
Tanaka T, Wiesener M, Bernhardt W, Eckardt KU, Warnecke C (2009) The human HIF (hypoxia-inducible factor)-3α gene is a HIF-1 target gene and may modulate hypoxic gene induction. Biochem J 424:143–151
Trayhurn P (2005) Endocrine and signalling role of adipose tissue: new perspectives on fat. Acta Physiol Scand 184:285–293
Trayhurn P, Beattie JH (2001) Physiological role of adipose tissue: white adipose tissue as an endocrine and secretory organ. Proc Nutr Soc 60:329–339
Trayhurn P, Wang B, Wood IS (2008) Hypoxia in adipose tissue: a basis for the dysregulation of tissue function in obesity? Br J Nutr 100:227–235
Trayhurn P, Wood IS (2004) Adipokines: Inflammation and the pleiotropic role of white adipose tissue. Br J Nutr 92:347–355
Wang B, Wood IS, Trayhurn P (2007) Dysregulation of the expression and secretion of inflammation-related adipokines by hypoxia in human adipocytes. Pflügers Archiv Eur J Physiol 455:479–492
Wang B, Wood IS, Trayhurn P (2008) Hypoxia induces leptin gene expression and secretion in human preadipocytes: differential effects of hypoxia on adipokine expression by preadipocytes. J Endocrinol 198:127–134
Wang B, Wood IS, Trayhurn P (2008) PCR arrays identify metallothionein-3 as a highly hypoxia-inducible gene in human adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 368:88–93
Weisberg SP, McCann D, Desai M, Rosenbaum M, Leibel RL, Ferrante AW Jr (2003) Obesity is associated with macrophage accumulation in adipose tissue. J Clin Invest 112:1796–1808
Wood IS, Wang B, Lorente-Cebrián S, Trayhurn P (2007) Hypoxia increases expression of selective facilitative glucose transporters (GLUT) and 2-deoxy-d-glucose uptake in human adipocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 361:468–473
Xu H, Barnes GT, Yang Q, Tan G, Yang D, Chou CJ, Sole J, Nichols A, Ross JS, Tartaglia LA, Chen H (2003) Chronic inflammation in fat plays a crucial role in the development of obesity-related insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 112:1821–1830
Yamauchi T, Kamon J, Waki H, Terauchi Y, Kubota N, Hara K, Mori Y, Ide T, Murakami K, Tsuboyama-Kasaoka N, Ezaki O, Akanuma Y, Gavrilova O, Vinson C, Reitman ML, Kagechika H, Shudo K, Yoda M, Nakano Y, Tobe K, Nagai R, Kimura S, Tomita M, Froguel P, Kadowaki T (2001) The fat-derived hormone adiponectin reverses insulin resistance associated with both lipoatrophy and obesity. Nat Med 7:941–946
Ye J (2008) Emerging role of adipose tissue hypoxia in obesity and insulin resistance. Int J Obesity 33:54–66
Ye J, Gao Z, Yin J, He Q (2007) Hypoxia is a potential risk factor for chronic inflammation and adiponectin reduction in adipose tissue of ob/ob and dietary obese mice. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 293:E1118–E1128
Yin J, Gao Z, He Q, Zhou D, Guo Z, Ye J (2009) Role of hypoxia in obesity-induced disorders of glucose and lipid metabolism in adipose tissue. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 296:E333–E342
Yudkin JS (2003) Adipose tissue, insulin action and vascular disease: inflammatory signals. Int J Obesity 27(Suppl 3):S25–S28
Zhang X, Lam KSL, Ye H, Chung SK, Zhou M, Wang Y, Xu A (2010) Adipose tissue-specific inhibition of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α induces obesity and glucose intolerance by impeding energy expenditure in mice. J Biol Chem 285:32869–32877
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council (UK) for grant support. PT is a member of COST BM0602.
Disclosures
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wood, I.S., Stezhka, T. & Trayhurn, P. Modulation of adipokine production, glucose uptake and lactate release in human adipocytes by small changes in oxygen tension. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 462, 469–477 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-011-0985-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-011-0985-7