Abstract
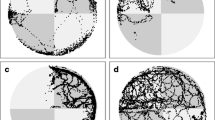
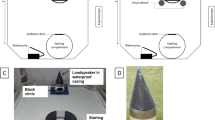
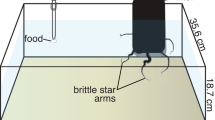
Animals face different threats; to survive, they have to anticipate how to react or how to avoid these. It has already been shown in teleosts that selected regions in the telencephalon, i.e., the medial pallium, are involved in avoidance learning strategies. No such study exists for any chondrichthyan. In nature, an avoidance reaction may vary, ranging from a ‘freeze’ reaction to a startling response and quick escape. This study investigated whether elasmobranchs (Chiloscyllium griseum and C. punctatum) can be conditioned in an aversive classical conditioning paradigm. Upon successful conditioning, the dorsal, medial and lateral pallium were removed (group 1) and performance tested again. In a second group, the same operation was performed prior to training. While conditioning was successful in individuals of both groups, no escape responses were observed. Post-operative performance was assessed and compared between individual and groups to reveal if the neural substrates governing avoidance behavior or tasks learned in a classical conditioning paradigm are located within the telencephalon, as has been shown for teleosts such as goldfish.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agranoff BW, Davis RE, Brink JJ (1965) Memory fixation in the goldfish. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 54:788–793
Agranoff BW, Davis RE, Brink JJ (1966) Chemical studies on memory fixation in goldfish. Brain Res 1:303–309
Akirav I, Maroun M (2007) The role of the medial prefrontal cortex–amygdala circuit in stress effects on the extinction of fear. Neural Plast 2007:1–11
Aronson LR, Herberman R (1960) Persistence of a conditioned response in the cichlid fish, Tilapia macrocephala, after forebrain and cerebellar ablations. Anat Rec 138:332
Behrend ER, Bitterman ME (1963) Sidman avoidance in the fish. J Exp Anal Behav 6:47–52
Bindra D, Anchel H (1963) Immobility as an avoidance response, and its disruption by drugs. J Exp Anal Behav 6:213–218
Bolles R, Popp R (1964) ###Parameters affecting the acquisition of Sidman avoidance1. J Exp Anal Behav 7:315–321
Bovet D, Bovet-Nitti F, Oliverio A (1968) Memory and consolidation mechanisms in avoidance learning of inbred mice. Brain Res 10:168–182
Bradford MR (1995) Comparative aspects of forebrain organization in the ray-finned fishes: touchstones or not? Brain Behav Evol 46:259–274
Broglio C, Gómez A, Durán E, Ocaña FM, Jiménez-Moya F, Rodríguez F, Salas C (2005) Hallmarks of a common forebrain vertebrate plan: specialized pallial areas for spatial, temporal and emotional memory in actinopterygian fish. Brain Res Bull 66:277–281
Carpenter RE, Summers CH (2009) Learning strategies during fear conditioning. Neurobiol Learn Mem 91:415–423
Compagno LJV, Dando M, Fowler S (2005) A field guide to the sharks of the world. Collins, London, pp 65–326
Chandroo K, Duncan IJ, Moccia R (2004) Can fish suffer?: Perspectives on sentience, pain, fear and stress. Appl Anim Behav Sci 86:225–250
Davis M (1992) The role of the amygdala in fear and anxiety. Annu Rev Neurosci 15:353–375
Dunlop R, Millsopp S, Laming P (2006) Avoidance learning in goldfish (Carassius auratus) and trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) and implications for pain perception. Appl Anim Behav Sci 97:255–271
Ebbesson SO (1972) New insights into the organization of the shark brain. Comp Biochem Physiol 42:121–129
Ferrari EAM, Faleiros L, Cerutti SM, Oliveira AM (1999) The functional value of sound and exploratory behaviour in detelencephalated pigeons. Behav Brain Res 101:93–103
Ferreira TL, Moreira KM, Ikeda DC et al (2003) Effects of dorsal striatum lesions in tone fear conditioning and contextual fear conditioning. Brain Res 987:17–24
Flood NC, Overmier JB, Savage GE (1976) Teleost telencephalon and learning: an interpretive review of data and hypotheses. Physiol Behav 16:783–788
Freund G, Walker DW (1971) The effect of aging on acquisition and retention of shuttle box avoidance in mice. Life Sci 10:1343–1349
Gamaro GD, Michalowski MB, Catelli DH et al (1999) Effect of repeated restraint stress on memory in different tasks. Braz J Med Biol Res 32:341–347
Graeber RC, Ebbesson SO (1972) Visual discrimination learning in normal and tectal-ablated nurse sharks (Ginglymostoma cirratum). Comp Biochem Physiol 42:131–139
Graeber RC, Ebbesson SO, Jane JA (1973) Visual discrimination in sharks without optic tectum. Science 180:413–415
Hofmann MH (2001) The role of the fish telencephalon in sensory information processing. In: Kapoor BG, Hara TJ (eds) Sensory biology of jawed fishes: new insights. Oxford & IBH Publishing Co. Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi, pp 255–274
Horner JL, Longo N, Bitterman ME (1961) A shuttle box for fish and a control circuit of general applicability. Am J Psychol 74:114–120
Hunt HF, Brady JV (1951) Some effects of electro-convulsive shock on a conditioned emotional response (“anxiety”). J Comp Physiol 44:88–98
Jackson RL, Alexander J, Maier SF (1980) Learned helplessness, inactivity, and associative deficits: effects of inescapable shock on response choice escape learning. J Exp Psychol Anim Behav Proc 6:1–20
Kalmijn AJ (1988) Detection of weak electric fields. In: Atema J, Fay RR, Popper RN, Tavolga WN (eds) Sensory biology of aquatic animals. Springer, New York, pp 151–186
Kaplan BYH, Aronson LR (1967) Effect of forebrain ablation on the performance of a conditioned avoidance response in the teleost fish, Tilapia H. macrocephala. Anim Behav 15:438–448
Kelly JC, Nelson DR (1975) Hearing thresholds of the horn shark, Heterodontus francisci. J Acoust Soc Am 58:905–909
Maren S (2001) Neurobiology of pavlovian fear conditioning. Annu Rev Neurosci 224:897–931
Maren S, Fanselow MS (1997) Electrolytic lesions of the fimbria/fornix, dorsal hippocampus, or entorhinal cortex produce anterograde deficits in contextual fear conditioning in rats. Neurobiol Learn Mem 67:142–149
Maren S, Holt WG (2000) The hippocampus and contextual memory retrieval in Pavlovian conditioning. Behav Brain Res 110:97–108
Maren S, Holt WG (2004) Hippocampus and Pavlovian fear conditioning in rats: muscimol infusions into the ventral, but not dorsal, hippocampus impair the acquisition of conditional freezing to an auditory conditional stimulus. Behav Neurosci 118:97–110
Martí-Nicolovius M, Portell-Cortés I, Morgado-Bernal I (1988) Improvement of shuttle-box avoidance following post-training treatment in paradoxical sleep deprivation platforms in rats. Physiol Behav 43:93–98
Mineka S (1979) The role of fear in theories of avoidance learning, flooding, and extinction. Psychol Bull 86:985–1010
Morgan MA, Romanski LM, LeDoux JE (1993) Extinction of emotional learning: contribution of medial prefrontal cortex. Neurosci Lett 163:109–113
Nelson DR (1967) Hearing thresholds, frequency discrimination, and acoustic orientation in the lemon shark, Negaprion brevirostris (POEY). Bull Mar Sci 17:714–768
Nieuwenhuys R (2009) The forebrain of actinopterygians revisited. Brain Behav Evol 73:229–252
Northcutt RG (1981) Evolution of the telencephalon in nonmammals. Annu Rev Neurosci 4:301–350
Northcutt RG (2008) Forebrain evolution in bony fishes. Brain Res Bull 75:191–205
O’Connell CP, Abel DC, Gruber SH et al (2011) Response of juvenile lemon sharks, Negaprion brevirostris, to a magnetic barrier simulating a beach net. Ocean Coast Manage 54:225–230
Otto T, Cousens G, Rajewski K (1997) Odor-guided fear conditioning in rats: 1. Acquisition, retention, and latent inhibition. Behav Neurosci 111:1257–1264
Otto T, Cousens G, Herzog C (2000) Behavioral and neuropsychological foundations of olfactory fear conditioning. Behav Brain Res 110:119–128
Overmier JB, Papini MR (1986) Factors modulating the effects of teleost telencephalon ablation on retention, relearning, and extinction of instrumental avoidance behavior. Behav Neurosci 100:190–199
Overmier JB, Starkman N (1974) Transfer of control of avoidance behavior in normal and telencephalon ablated goldfish (Carassius auratus). Physiol Behav 12:605–608
Owen EH, Logue SF, Rasmussen DL, Wehner JM (1997) Assessment of learning by the Morris water task and fear conditioning in inbred mouse strains and F1 hybrids: implications of genetic background for single gene mutations and quantitative trait loci analyses. Neuroscience 80:1087–1099
Pavlov IP (1928) Lectures on conditioned reflexes: twenty five years of objective study of the higher nervous activity (behaviour) of animals, pp 103–204
Portavella M, Vargas JP (2005) Emotional and spatial learning in goldfish is dependent on different telencephalic pallial systems. Eur J Neurosci 21:2800–2806
Portavella M, Depaulis A, Vergnes M (1993) 22–28 kHz ultrasonic vocalizations associated with defensive reactions in male rats do not result from fear or aversion. Psychopharmacology 111:190–194
Portavella M, Vargas JP, Torres B, Salas C (2002) The effects of telencephalic pallial lesions on spatial, temporal, and emotional learning in goldfish. Brain Res Bull 57:397–399
Portavella M, Salas C, Vargas JP, Papini MR (2003) Involvement of the telencephalon in spaced-trial avoidance learning in the goldfish (Carassius auratus). Physiol Behav 80:49–56
Portavella M, Torres B, Salas C (2004a) Avoidance response in goldfish: emotional and temporal involvement of medial and lateral telencephalic pallium. J Neurosci 24:2335–2342
Portavella M, Torres B, Salas C, Papini MR (2004b) Lesions of the medial pallium, but not of the lateral pallium, disrupt spaced-trial avoidance learning in goldfish (Carassius auratus). Neurosci Lett 362:75–78
Richter-Levin G (2004) The amygdala, the hippocampus, and emotional modulation of memory. Neuroscientist 10:31–39
Rodríguez F, López JC, Vargas JP, Gómez Y et al (2002) Conservation of spatial memory function in the pallial forebrain of reptiles and ray-finned fishes. J Neurosci 22:2894–2903
Rodríguez F, Durán E, Gómez A et al (2005) Cognitive and emotional functions of the teleost fish cerebellum. Brain Res Bull 66:365–370
Rooney DJ, Laming PR (1988) Effects of telencephalic ablation on habituation of arousal responses, within and between daily training sessions in goldfish. Behav Neurol Biol 49:83–96
Sagvolden T (1975) Acquisition of two-way active avoidance following septal lesions in the rat: effect of intensity of discontinuous shock. Behav Biol 14:59–74
Salas C, Broglio C, Durán E et al (2006) Neuropsychology of learning and memory in teleost fish. Zebrafish 3:157–171
Sanders MJ, Wiltgen BJ, Fanselow MS (2003) The place of the hippocampus in fear conditioning. Eur J Pharmacol 463:217–223
Scobie S (1970) The response–shock–shock–shock interval and unsignalled avoidance in goldfish. J Exp Anal Behav 2:219–224
Seligman MEP (1972) Learned helplessness. Annu Rev Med 23:407–412
Seligman MEP, Maier SF, Geer JH (1968) Alleviation of learned helplessness in the dog. J Abnorm Psychol 73:256–262
Shashoua VE, Hesse GW (1989) Classical conditioning leads to changes in extracellular concentrations of ependymin in goldfish brain. Brain Res 484:333–339
Springer AD, Schoel WM, Klinger PD, Agranoff BW (1975) Anterograde and retrograde effects of electroconvulsive shock and of puromycin on memory formation in the goldfish. Behav Biol 13:467–481
Squire L (2004) Memory systems of the brain: a brief history and current perspective. Neurobiol Learn Mem 82:171–177
Thorndike EL (1898) Animal intelligence: an experimental study of the associative processes in animals. Psychol Rev Monogr Suppl 2:1–109
Tricas TC, New JG (1998) Sensitivity and response dynamics of elasmobranch electrosensory primary afferent neurons to near threshold fields. J Comp Physiol A 182:89–101
Vargas JP, López JC, Portavella M (2009) What are the functions of fish brain pallium? Brain Res Bull 79:436–440
Wilensky AE, Schafe GE, LeDoux JE (1999) Functional inactivation of the amygdala before but not after auditory fear conditioning prevents memory formation. J Neurosci 19:1–5
Yoshida M, Okamura I, Uematsu K (2004) Involvement of the cerebellum in classical fear conditioning in goldfish. Behav Brain Res 153:143–148
Yue S, Moccia RD, Duncan IJH (2004) Investigating fear in domestic rainbow trout, (Oncorhynchus mykiss), using an avoidance learning task. Appl Anim Behav Sci 87:343–354
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank M. Hofmann for technical support and helpful comments on the experimental setup. The research reported herein was performed under the guidelines established by the current German animal protection law (Landesamt für Natur, Umwelt und Verbraucherschutz NRW, 8.87-50.10.37.09.198).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schwarze, S., Bleckmann, H. & Schluessel, V. Avoidance conditioning in bamboo sharks (Chiloscyllium griseum and C. punctatum): behavioral and neuroanatomical aspects. J Comp Physiol A 199, 843–856 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-013-0847-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00359-013-0847-1