Abstract
Background
Creating an aesthetically pleasing umbilicus may be challenging due to various factors that involve the patient limitations and suboptimal techniques available to the surgeon. Although many techniques aim to locate the umbilicus after abdominoplasty, none are ideal. The authors use a new technique involving a stainless steel spherical device for definite location of the new neo-umbilicus site.
Methods
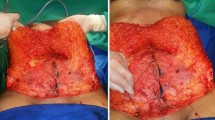
Abdominoplasty with full muscle plication and umbilicoplasty was performed to test the effectiveness of this new technique that involves a stainless steel marble called the Umbilicator. It has a diameter of 1.5 cm and three 2-mm holes drilled 120° apart in an equilateral triangle. The Umbilicator is secured to the inferior and superior dermis of the umbilical stalk to help identify the future location of the umbilicus on the abdominal skin. Once the marble is secured, the superior abdominal flap is redraped and trimmed, the suture is repaired, and the location of the umbilicus is determined by feeling for the smooth spherical surface bump with gentle downward pressure on the overlying abdominal skin located within the proximity of the umbilicus.
Results
The result of this technique produced a definitive means of identifying and delivering the umbilical stalk during abdominoplasty. This technique has been performed in 23 consecutive abdominoplasty procedures with no difficulties locating the umbilical stalk and no infections resulting from the procedure.
Conclusions
Accurate identification of the umbilicus provides the ability to create an aesthetically pleasing neo-umbilicus, thus optimizing abdominoplasty results.
Level of Evidence IV
This journal requires that authors assign a level of evidence to each article. For a full description of these Evidence-Based Medicine ratings, please refer to the Table of Contents or the online Instructions to Authors www.springer.com/00266.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Craig SB, Faller MS, Puckett CL (2008) In search of the ideal female umbilicus. Plast Reconstr Surg 121:356e–357e
Dubou R, Ousterhout DK (1978) Placement of the umbilicus in an abdominoplasty. Plast Reconstr Surg 61:291–293
Delerm A (1982) Refinements in abdominoplasty with emphasis on reimplantation of the umbilicus. Plast Reconstr Surg 70:632–637
Shoukas J, Christopoulos N, Kouris G, Polley J (2009) Umbilical quest: a new technique for accurately identifying the new position of the umbilicus in abdominoplasty using a lockwood marker. Plast Reconstr Surg J 123:120e–121e
Al-shaham A (2009) Neoumbilicoplasty is a useful adjuvant procedure in abdominoplasty. Can J Plast Surg 17:e20–e23
Choudhary S, Taams KO (1998) Umbilicoscuplture: a concept revisited. Br J Plast Surg 51:538–541
Bartsich SA, Schwartz MH (2003) Purse-string method for immediate umbilical reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg J 112:1652–1655
Abhyankar SV, Rajguru AG, Patil PA (2006) Anatomical localization of the umbilicus: an Indian study. Plast Reconstr Surg 117:1153
Grant B (1965) Grant’s method of anatomy. Williams & Wilkins, Baltimore, MD
Dick ET (1970) Umbilicoplasty as a treatment for persistent umbilical infection. Aust N Z J Surg 39:380
Acknowledgments
The funding for the research and the creation of this report was provided solely by us without funding from any outside organization or entity. No outside organizations or entities assisted us in any form with the creation of this report.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mowlavi, A., Huynh, P.M., Huynh, D.C. et al. A New Technique Involving a Spherical Stainless Steel Device to Optimize Positioning of the Umbilicus. Aesth Plast Surg 36, 1062–1065 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-012-9924-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00266-012-9924-z