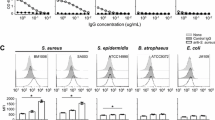
Abstract
Staphylococcus aureus is a leading causative agent of bovine mastitis, which can result in significant economic losses to the dairy industry. However, available vaccines against bovine mastitis do not confer adequate protection, although passive immunization with antibodies may be useful to prevent disease. Hence, we constructed a bovine single-chain variable region fragment (scFv) phage display library using cDNAs from peripheral blood lymphocytes of cows with S. aureus-induced mastitis. After four rounds of selection, eight scFvs that bound S. aureus antigens with high affinity were obtained. The framework regions of the variable domains (VH and VL) of the eight scFvs were highly conserved, and the complementarity-determining regions (CDRs) displayed significant diversity, especially CDR3 of the VH domain. All eight scFvs inhibited S. aureus growth in culture medium. Lactating mice were challenged by injecting S. aureus into the fourth mammary gland. Histopathological analysis showed that treatment with these scFvs prior to bacterial challenge maintained the structure of the mammary acini, decreased infiltration of polymorphonuclear neutrophils, increased levels of interferon-gamma and interleukin-4, and reduced tumor necrosis factor-alpha levels in mammary tissues, as compared with mice treatment with physiological saline (P < 0.05). These novel bovine scFvs may be suitable candidates for therapeutic agents for the prevention of S. aureus-induced bovine mastitis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barkema HW, Schukken YH, Zadoks RN (2006) Invited review: the role of cow, pathogen, and treatment regimen in the therapeutic success of bovine Staphylococcus aureus mastitis. J Dairy Sci 89:1877–1895
Berger S, Hinz D, Bannantine JP, Griffin JFT (2006) Isolation of high-affinity single-chain antibodies against Mycobacterium avium subsp. paratuberculosis surface proteins from sheep with Johne’s disease. Clin Vaccine Immunol 13:1022–1029
Bradley AJ (2002) Bovine mastitis: an evolving disease. Vet J 164:116–128
Brooks BM, Hart CA, Coleman JW (2005) Differential effects of beta-lactams on human IFN-gamma activity. J Antimicrob Chemother 56:1122–1125
Brouillette E, Malouin F (2005) The pathogenesis and control of Staphylococcus aureus-induced mastitis: study models in the mouse. Microbes Infect 7:560–568
Chandler RL (1970) Experimental bacterial mastitis in the mouse. J Med Microbiol 3:273–282
Colcher D, Pavlinkova G, Beresford G, Booth BJ, Choudhury A, Batra SK (1998) Pharmacokinetics and biodistribution of genetically-engineered antibodies. Q J Nucl Med 42:225–241
Elbers ARW, Miltenburg JD, Lange DDE, Crauwels APP, Barkema HW, Schukken YH (1998) Risk factors for clinical mastitis in a random sample of dairy herds from the southern part of The Netherlands. J Dairy Sci 81:420–426
Ghahroudi MA, Desmyter A, Wyns L, Hamers R, Muyldermans S (1997) Selection and identification of single domain antibody fragments from camel heavy-chain antibodies. FEBS Lett 414:521–526
Guo MY, Zhang NS, Li DP, Liang DJ, Liu ZC, Li FY, Fu YH, Cao YG, Deng XM, Yang ZT (2013) Baicalin plays an anti-inflammatory role through reducing nuclear factor-κB and p38 phosphorylation in S. aureus-induced mastitis. Int Immunopharmacol 16:125–130
Holt LJ, Enever C, de Wildt RM, Tomlinson IM (2000) The use of recombinant antibodies in proteomics. Curr Opin Biotechnol 11:445–449
Hoogenboom HR, de Bruine AP, Hufton SE, Hoet RM, Arends JW, Roovers RC (1998) Antibody phage display technology and its applications. Immunotechnol 4:1–20
Hu CM, Gong R, Guo AZ, Chen HC (2010) Protective effect of ligand-binding domain of fibronectin-binding protein on mastitis induced by Staphylococcus aureus in mice. Vaccine 28:4038–4044
Kato M, Hanyu Y (2013) Construction of an scFv library by enzymatic assembly of VL and VH genes. J Immunol Methods 396:15–22
Li FQ, Aitken R (2004) Cloning of porcine scFv antibodies by phage display and expression in Escherichia coli. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 97:39–51
Li Y, Cockburn W, Kilpatrick JB, Whitelam GC (2000) High affinity scFvs from a single rabbit immunized with multiple haptens. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 268:398–404
Mamo W, Jonsson P, Muller HP (1995) Opsonization of Staphylococcus aureus with a fibronectin-binding protein antiserum induces protection in mice. Microb Pathog 19:49–55
McCafferty J, Griffiths AD, Winter G, Chiswell DJ (1990) Phage antibodies: filamentous phage displaying antibody variable domains. Nat 348:552–554
Middleton JR (2008) Staphylococcus aureus antigens and challenges in vaccine development. Expert Rev Vaccines 7:805–815
Milenic DE, Yokota T, Filpula DR, Finkelman MA, Dodd SW, Wood JF, Whitlow M, Snoy P, Schlom J (1991) Construction, binding properties, metabolism, and tumor targeting of a single chain Fv derived from the pancarcinoma monoclonal antibody CC49. Cancer Res 51:6363–6371
Pesanti EL, Lorenzo JA (1998) Osteoclasts and effects of interleukin 4 in development of chronic osteomyelitis. Clin Orthop 355:290–299
Saini SS, Farrugia W, Ramsland PA, Kaushik AK (2003) Bovine IgM antibodies with exceptionally long complementarity-determining region 3 of the heavy chain share unique structural properties conferring restricted VH + Vlambda pairings. Int Immunol 15:845–853
Shinefield HR, Black S (2005) Prevention of Staphylococcus aureus infections: advances in vaccine development. Expert Rev Vaccines 4:669–676
Smith GP (1985) Filamentous fusion phage: novel expression vectors that display cloned antigens on the virion surface. Sci 228:1315–1317
Tan GY, Bai LQ, Zhong JJ (2013) Exogenous 1,4-butyrolactone stimulates A-factor-like cascade and validamycin biosynthesis in Streptomyces hygroscopicus 5008. Biothchnol Bioeng 110:2984–2993
Vincent JL, Sun Q, Dubois MJ (2002) Clinical trials of immunomodulatory therapies in severe sepsis and septic shock. Clin Infect Dis 34:1084–1093
Wang M, Zhang Y, Li BQ, Zhu JG (2015) Construction of scFv that bind both fibronectin-binding protein A and clumping factor A of Stapylococcus aureus. Res in Vet Sci 100:109–114
Yokota T, Milenic DE, Whitlow M, Schlom J (1992) Rapid tumor penetration of a single-chain Fv and comparison with other immunoglobulin forms. Cancer Res 52:3402–3408
Zhao YX, Nilsson IM, Tarkowski A (1998) The dual role of interferon-gamma in experimental Staphylococcus aureus septicemia versus arthritis. Immunol 93:80–85
Zhen YH, Jin LJ, Li XY, Guo J, Li Z, Zhang BJ, Fang R, Xu YP (2009) Efficacy of specific egg yolk immunoglobulin (IgY) to bovine mastitis caused by Staphylococcus aureus. Vet Microbiol 133:317–322
Zwick MB, Wang M, Poignard P, Stienler G, Katinger H, Burton DR, Parren PWHI (2001) Neutralization synergy of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 primary isolates by cocktails of broadly neutralizing antibodies. J Virol 75:12198–12208
Acknowledgments
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
This study was supported by a grant from the National Supporting Projects for Science and Techniques (Grant Number: 2012BAD12B00).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This study was conducted in accordance with all applicable international, national, and institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 474 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, M., Zhang, Y. & Zhu, J. Anti-Staphylococcus aureus single-chain variable region fragments provide protection against mastitis in mice. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 100, 2153–2162 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-7045-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-015-7045-8