Abstract
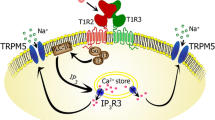
Sweet-tasting compounds are recognized by a heterodimeric receptor composed of the taste receptor, type 1, members 2 (T1R2) and 3 (T1R3) located in the mouth. This receptor is also expressed in the gut where it is involved in intestinal absorption, metabolic regulation, and glucose homeostasis. These metabolic functions make the sweet taste receptor a potential novel therapeutic target for the treatment of obesity and related metabolic dysfunctions such as diabetes. Existing sweet taste inhibitors or blockers that are still in development would constitute promising therapeutic agents. In this review, we will summarize the current knowledge of sweet taste inhibitors, including a sweet-taste-suppressing protein named gurmarin, which is only active on rodent sweet taste receptors but not on that of humans. In addition, their potential applications as therapeutic tools are discussed.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arai K, Ishima R, Morikawa S, Miyasaka A, Imoto T, Yoshimura S, Aimoto S, Akasaka K (1995) Three-dimensional structure of gurmarin, a sweet taste-suppressing polypeptide. J Biomol NMR 5:297–305
Assadi-Porter FM, Maillet EL, Radek JT, Quijada J, Markley JL, Max M (2010) Key amino acid residues involved in multi-point binding interactions between brazzein, a sweet protein, and the T1R2-T1R3 human sweet receptor. J Mol Biol 398:584–599
Behrens M, Meyerhof W (2011) Gustatory and extragustatory functions of mammalian taste receptors. Physiol Behav 105:4–13
Behrens M, Meyerhof W, Hellfritsch C, Hofmann T (2011) Sweet and umami taste: natural products, their chemosensory targets, and beyond. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 50:2220–2242
Bonsor DA, Sundberg EJ (2011) Dissecting protein-protein interactions using directed evolution. Biochemistry 50:2394–2402
Carugo O, Lu S, Luo J, Gu X, Liang S, Strobl S, Pongor S (2001) Structural analysis of free and enzyme-bound amaranth alpha-amylase inhibitor: classification within the knottin fold superfamily and analysis of its functional flexibility. Protein Eng 14:639–646
Chandrashekar J, Hoon MA, Ryba NJ, Zuker CS (2006) The receptors and cells for mammalian taste. Nature 444:288–294
Craik DJ, Daly NL, Waine C (2001) The cystine knot motif in toxins and implications for drug design. Toxicon 39:43–60
Cregg JM, Cereghino JL, Shi J, Higgins DR (2000) Recombinant protein expression in Pichia pastoris. Mol Biotechnol 16:23–52
Cui M, Jiang P, Maillet E, Max M, Margolskee RF, Osman R (2006) The heterodimeric sweet taste receptor has multiple potential ligand binding sites. Curr Pharm Des 12:4591–4600
Diamant H, Oakley B, Stroem L, Wells C, Zotterman Y (1965) A Comparison of neural and psychophysical responses to taste stimuli in man. Acta Physiol Scand 64:67–74
DuBois GE (2008) Chemistry of gustatory stimuli. In: Firestein S, Beauchamp GK (eds) The senses : a comprehensive reference, vol 4. Elsevier, pp 27–74
Dubois GE, Prakash I (2012) Non-caloric sweeteners, sweetness modulators, and sweetener enhancers. Annu Rev Food Sci Technol 3:353–380
Dyer J, Salmon KS, Zibrik L, Shirazi-Beechey SP (2005) Expression of sweet taste receptors of the T1R family in the intestinal tract and enteroendocrine cells. Biochem Soc Trans 33:302–305
Fletcher JI, Chapman BE, Mackay JP, Howden ME, King GF (1997) The structure of versutoxin (delta-atracotoxin-Hv1) provides insights into the binding of site 3 neurotoxins to the voltage-gated sodium channel. Structure 5:1525–1535
Fletcher JI, Dingley AJ, Smith R, Connor M, Christie MJ, King GF (1999) High-resolution solution structure of gurmarin, a sweet-taste-suppressing plant polypeptide. Eur J Biochem 264:525–533
Galindo-Cuspinera V, Breslin PA (2006) The liaison of sweet and savory. Chem Senses 31:221–225
Galindo-Cuspinera V, Winnig M, Bufe B, Meyerhof W, Breslin PA (2006) A TAS1R receptor-based explanation of sweet ‘water-taste’. Nature 441:354–357
Gudermann T, Kalkbrenner F, Schultz G (1996) Diversity and selectivity of receptor-G protein interaction. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 36:429–459
Hamazume Y, Mega T, Ikenaka T (1987) Positions of disulfide bonds in riboflavin-binding protein of hen egg white. J Biochem 101:217–223
Hardy ML, Coulter I, Venuturupalli S, Roth EA, Favreau J, Morton SC, Shekelle P (2001) Ayurvedic interventions for diabetes mellitus: a systematic review. Evid Rep Technol Assess (Summ):2p
Hellekant G, Gopal V (1976) On the effects of gymnemic acid in the hamster and rat. Acta Physiol Scand 98:136–142
Hellekant G, af Segerstad CH, Roberts T, van der Wel H, Brouwer JN, Glaser D, Haynes R, Eichberg JW (1985) Effects of gymnemic acid on the chorda tympani proper nerve responses to sweet, sour, salty and bitter taste stimuli in the chimpanzee. Acta Physiol Scand 124:399–408
Hellekant G, Ninomiya Y, DuBois GE, Danilova V, Roberts TW (1996) Taste in chimpanzee: I. The summated response to sweeteners and the effect of gymnemic acid. Physiol Behav 60:469–479
Hellekant G, Ninomiya Y, Danilova V (1998) Taste in chimpanzees. III: labeled-line coding in sweet taste. Physiol Behav 65:191–200
Ide N, Sato E, Ohta K, Masuda T, Kitabatake N (2009) Interactions of the sweet-tasting proteins thaumatin and lysozyme with the human sweet-taste receptor. J Agric Food Chem 57:5884–5890
Imada T, Misaka T, Fujiwara S, Okada S, Fukuda Y, Abe K (2010) Amiloride reduces the sweet taste intensity by inhibiting the human sweet taste receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 397:220–225
Imoto T, Miyasaka A, Ishima R, Akasaka K (1991) A novel peptide isolated from the leaves of Gymnema sylvestre-I. Characterization and its suppressive effect on the neural responses to sweet taste stimuli in the rat. Comp Biochem Physiol A 100:309–314
Imoto T, Sasamoto K, Ninomiya Y (2001) Beta-cyclodextrin inhibits the sweet taste suppressing activity of gurmarin by the formation of an inclusion complex with aromatic residues in gurmarin. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 79:836–840
Iwasaki K, Sato M (1984) Inhibitory effects of some heavy metal ions on taste nerve responses in mice. Jpn J Physiol 34:907–918
Iwasaki K, Sato M (1986) Inhibition of taste nerve responses to sugars and amino acids by cupric and zinc ions in mice. Chem Senses 11
Jakinovich W Jr (1983) Methyl 4,6-dichloro-4,6-dideoxy-alpha-D-galactopyranoside: an inhibitor of sweet taste responses in gerbils. Science 219:408–410
Jiang P, Ji Q, Liu Z, Snyder LA, Benard LM, Margolskee RF, Max M (2004) The cysteine-rich region of T1R3 determines responses to intensely sweet proteins. J Biol Chem 279:45068–45075
Jiang P, Cui M, Zhao B, Liu Z, Snyder LA, Benard LM, Osman R, Margolskee RF, Max M (2005a) Lactisole interacts with the transmembrane domains of human T1R3 to inhibit sweet taste. J Biol Chem 280:15238–15246
Jiang P, Cui M, Zhao B, Snyder LA, Benard LM, Osman R, Max M, Margolskee RF (2005b) Identification of the cyclamate interaction site within the transmembrane domain of the human sweet taste receptor subunit T1R3. J Biol Chem 280:34296–34305
Katsukawa H, Imoto T, Ninomiya Y (1999) Induction of salivary gurmarin-binding proteins in rats fed gymnema-containing diets. Chem Senses 24:387–392
Keast RS (2003) The effect of zinc on human taste perception. J Food Sci 68:1871–1877
Keast RS, Canty TM, Breslin PA (2004) Oral zinc sulfate solutions inhibit sweet taste perception. Chem Senses 29:513–521
Kenakin T (2003) Ligand-selective receptor conformations revisited: the promise and the problem. Trends Pharmacol Sci 24:346–354
Kennedy LM, Saul LR, Seffeka R, Stevens DA (1988) Hodulcin: selective sweetness-reducing principle from Hovenia dulcis leaves. Chem Senses 13:529–543
Kniazeff J, Prezeau L, Rondard P, Pin JP, Goudet C (2011) Dimers and beyond: the functional puzzles of class C GPCRs. Pharmacol Ther 130:9–25
Koizumi A, Nakajima K, Asakura T, Morita Y, Ito K, Shmizu-Ibuka A, Misaka T, Abe K (2007) Taste-modifying sweet protein, neoculin, is received at human T1R3 amino terminal domain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 358:585–589
Kuhn C, Bufe B, Winnig M, Hofmann T, Frank O, Behrens M, Lewtschenko T, Slack JP, Ward CD, Meyerhof W (2004) Bitter taste receptors for saccharin and acesulfame K. J Neurosci 24:10260–10265
Kunishima N, Shimada Y, Tsuji Y, Sato T, Yamamoto M, Kumasaka T, Nakanishi S, Jingami H, Morikawa K (2000) Structural basis of glutamate recognition by a dimeric metabotropic glutamate receptor. Nature 407:971–977
Kurihara Y (1992) Characteristics of antisweet substances, sweet proteins, and sweetness-inducing proteins. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 32:231–252
LaBell F (1989) Sweetness reduction improves flavor delivery, functionality. Food Process: 74–76
Leach MJ (2007) Gymnema sylvestre for diabetes mellitus: a systematic review. J Altern Complement Med 13:977–983
Lemon CH, Imoto T, Smith DV (2003) Differential gurmarin suppression of sweet taste responses in rat solitary nucleus neurons. J Neurophysiol 90:911–923
Li X, Staszewski L, Xu H, Durick K, Zoller M, Adler E (2002) Human receptors for sweet and umami taste. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:4692–4696
Li X, Bachmanov AA, Maehashi K, Li W, Lim R, Brand JG, Beauchamp GK, Reed DR, Thai C, Floriano WB (2011) Sweet taste receptor gene variation and aspartame taste in primates and other species. Chem Senses 36:453–475
Liu HM, Kiuchi F, Tsuda Y (1992) Isolation and structure elucidation of gymnemic acids, antisweet principles of Gymnema sylvestre. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 40:1366–1375
Liu B, Ha M, Meng XY, Kaur T, Khaleduzzaman M, Zhang Z, Jiang P, Li X, Cui M (2011) Molecular mechanism of species-dependent sweet taste toward artificial sweeteners. J Neurosci 31:11070–11076
Mace OJ, Lister N, Morgan E, Shepherd E, Affleck J, Helliwell P, Bronk JR, Kellett GL, Meredith D, Boyd R, Pieri M, Bailey PD, Pettcrew R, Foley D (2009) An energy supply network of nutrient absorption coordinated by calcium and T1R taste receptors in rat small intestine. J Physiol 587:195–210
Maehashi K, Matano M, Kondo A, Yamamoto Y, Udaka S (2007) Riboflavin-binding protein exhibits selective sweet suppression toward protein sweeteners. Chem Senses 32:183–190
Maehashi K, Matano M, Saito M, Udaka S (2010) Extracellular production of riboflavin-binding protein, a potential bitter inhibitor, by Brevibacillus choshinensis. Protein Expr Purif 71:85–90
Maillet EL, Margolskee RF, Mosinger B (2009) Phenoxy herbicides and fibrates potently inhibit the human chemosensory receptor subunit T1R3. J Med Chem 52:6931–6935
Maitrepierre E, Sigoillot M, Le Pessot L, Briand L (2012) Recombinant expression, in vitro refolding, and biophysical characterization of the N-terminal domain of T1R3 taste receptor. Protein Expr Purif 83:75–83
Margolskee RF, Dyer J, Kokrashvili Z, Salmon KS, Ilegems E, Daly K, Maillet EL, Ninomiya Y, Mosinger B, Shirazi-Beechey SP (2007) T1R3 and gustducin in gut sense sugars to regulate expression of Na+-glucose cotransporter 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:15075–15080
Masuda K, Koizumi A, Nakajima K, Tanaka T, Abe K, Misaka T, Ishiguro M (2012) Characterization of the modes of binding between human sweet taste receptor and low-molecular-weight sweet compounds. PLoS One 7:e35380
Max M, Shanker YG, Huang L, Rong M, Liu Z, Campagne F, Weinstein H, Damak S, Margolskee RF (2001) Tas1r3, encoding a new candidate taste receptor, is allelic to the sweet responsiveness locus Sac. Nat Genet 28:58–63
Meiselman HL, Halpern BP, Dateo GP (1976) Reduction of sweetness judgments by extracts from the leaves of Ziziphus jujuba. Physiol Behav 17:313–317
Miyasaka A, Imoto T (1995) Electrophysiological characterization of the inhibitory effect of a novel peptide gurmarin on the sweet taste response in rats. Brain Res 676:63–68
Montmayeur JP, Liberles SD, Matsunami H, Buck LB (2001) A candidate taste receptor gene near a sweet taste locus. Nat Neurosci 4:492–498
Muller GW, Culberson JC, Roy G, Ziegler J, Walters DE, Kellogg MS, Schiffman SS, Warwick ZS (1992) Carboxylic acid replacement structure-activity relationships in suosan type sweeteners. A sweet taste antagonist. 1. J Med Chem 35:1747–1751
Murata Y, Nakashima K, Yamada A, Shigemura N, Sasamoto K, Ninomiya Y (2003) Gurmarin suppression of licking responses to sweetener-quinine mixtures in C57BL mice. Chem Senses 28:237–243
Nakashima K, Katsukawa H, Sasamoto K, Ninomiya Y (2001) Behavioral taste similarities and differences among monosodium L-glutamate and glutamate receptor agonists in C57BL mice. J Nutr Sci Vitaminol (Tokyo) 47:161–166
Nelson G, Hoon MA, Chandrashekar J, Zhang Y, Ryba NJ, Zuker CS (2001) Mammalian sweet taste receptors. Cell 106:381–390
Nelson G, Chandrashekar J, Hoon MA, Feng L, Zhao G, Ryba NJ, Zuker CS (2002) An amino-acid taste receptor. Nature 416:199–202
Nie Y, Vigues S, Hobbs JR, Conn GL, Munger SD (2005) Distinct contributions of T1R2 and T1R3 taste receptor subunits to the detection of sweet stimuli. Curr Biol 15:1948–1952
Nie Y, Hobbs JR, Vigues S, Olson WJ, Conn GL, Munger SD (2006) Expression and purification of functional ligand-binding domains of T1R3 taste receptors. Chem Senses 31:505–513
Ninomiya Y, Imoto T (1995) Gurmarin inhibition of sweet taste responses in mice. Am J Physiol 268:R1019–R1025
Ninomiya Y, Inoue M, Imoto T, Nakashima K (1997) Lack of gurmarin sensitivity of sweet taste receptors innervated by the glossopharyngeal nerve in C57BL mice. Am J Physiol 272:R1002–R1006
Ninomiya Y, Inoue M, Imoto T (1998) Reduction of the suppressive effects of gurmarin on sweet taste responses by addition of beta-cyclodextrin. Chem Senses 23:303–307
Ninomiya Y, Imoto T, Sugimura T (1999) Sweet taste responses of mouse chorda tympani neurons: existence of gurmarin-sensitive and -insensitive receptor components. J Neurophysiol 81:3087–3091
Ninomiya Y, Nakashima K, Fukuda A, Nishino H, Sugimura T, Hino A, Danilova V, Hellekant G (2000) Responses to umami substances in taste bud cells innervated by the chorda tympani and glossopharyngeal nerves. J Nutr 130:950S–953S
Noma A, Hiji Y (1972) Effects of chemical modifiers on taste responses in the rat chorda tympani. Jpn J Physiol 22:393–402
Ohkuri T, Yasumatsu K, Horio N, Jyotaki M, Margolskee RF, Ninomiya Y (2009) Multiple sweet receptors and transduction pathways revealed in knockout mice by temperature dependence and gurmarin sensitivity. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 296:R960–R971
Ohmiya K, Ohashi H, Kobayashi T, Shimizu S (1977) Hydrolysis of lactose by immobilized microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol 33:137–146
Ohta K, Masuda T, Tani F, Kitabatake N (2011) The cysteine-rich domain of human T1R3 is necessary for the interaction between human T1R2-T1R3 sweet receptors and a sweet-tasting protein, thaumatin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 406:435–438
Ota M, Shimizu Y, Tonosaki K, Ariyoshi Y (1998) Role of hydrophobic amino acids in gurmarin, a sweetness-suppressing polypeptide. Biopolymers 45:231–238
Pallaghy PK, Duggan BM, Pennington MW, Norton RS (1993) Three-dimensional structure in solution of the calcium channel blocker omega-conotoxin. J Mol Biol 234:405–420
Pandey AK, Yadav S (2010) Variation in gymnemic acid content and non-destructive harvesting of Gymnema sylvestre (Gudmar). Pharmacognosy Res 2:309–312
Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC, Couch GS, Greenblatt DM, Meng EC, Ferrin TE (2004) UCSF Chimera–a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J Comput Chem 25:1605–1612
Pin JP, Galvez T, Prezeau L (2003) Evolution, structure, and activation mechanism of family 3/C G-protein-coupled receptors. Pharmacol Ther 98:325–354
Pronin AN, Tang H, Connor J, Keung W (2004) Identification of ligands for two human bitter T2R receptors. Chem Senses 29:583–593
Rhodes MB, Bennett N, Feeney RE (1959) The flavoprotein-apoprotein system of egg white. J Biol Chem 234:2054–2060
Rondard P, Huang S, Monnier C, Tu H, Blanchard B, Oueslati N, Malhaire F, Li Y, Trinquet E, Labesse G, Pin JP, Liu J (2008) Functioning of the dimeric GABA(B) receptor extracellular domain revealed by glycan wedge scanning. Embo J 27:1321–1332
Roudnitzky N, Bufe B, Thalmann S, Kuhn C, Gunn HC, Xing C, Crider BP, Behrens M, Meyerhof W, Wooding SP (2011) Genomic, genetic and functional dissection of bitter taste responses to artificial sweeteners. Hum Mol Genet 20:3437–3449
Rozengurt N, Wu SV, Chen MC, Huang C, Sternini C, Rozengurt E (2006) Colocalization of the alpha-subunit of gustducin with PYY and GLP-1 in L cells of human colon. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 291:G792–G802
Sainz E, Korley JN, Battey JF, Sullivan SL (2001) Identification of a novel member of the T1R family of putative taste receptors. J Neurochem 77:896–903
Sainz E, Cavenagh MM, LopezJimenez ND, Gutierrez JC, Battey JF, Northup JK, Sullivan SL (2007) The G-protein coupling properties of the human sweet and amino acid taste receptors. Dev Neurobiol 67:948–959
Sako N, Yamamoto T (1999) Analyses of taste nerve responses with special reference to possible receptor mechanisms of umami taste in the rat. Neurosci Lett 261:109–112
Sako N, Tokita K, Sugimura T, Yamamoto T (2003) Synergistic responses of the chorda tympani to mixtures of umami and sweet substances in rats. Chem Senses 28:261–266
Sanematsu K, Yasumatsu K, Yoshida R, Shigemura N, Ninomiya Y (2005) Mouse strain differences in gurmarin-sensitivity of sweet taste responses are not associated with polymorphisms of the sweet receptor gene, Tas1r3. Chem Senses 30:491–496
Schiffman SS, Gatlin CA (1993) Sweeteners: state of knowledge review. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 17:313–345
Schiffman SS, Booth BJ, Sattely-Miller EA, Graham BG, Gibes KM (1999) Selective inhibition of sweetness by the sodium salt of +/-2-(4-methoxyphenoxy)propanoic acid. Chem Senses 24:439–447
Sclafani A, Perez C (1997) Cypha [propionic acid, 2-(4-methoxyphenol) salt] inhibits sweet taste in humans, but not in rats. Physiol Behav 61:25–29
Servant G, Tachdjian C, Tang XQ, Werner S, Zhang F, Li X, Kamdar P, Petrovic G, Ditschun T, Java A, Brust P, Brune N, DuBois GE, Zoller M, Karanewsky DS (2010) Positive allosteric modulators of the human sweet taste receptor enhance sweet taste. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:4746–4751
Shigemura N, Nakao K, Yasuo T, Murata Y, Yasumatsu K, Nakashima A, Katsukawa H, Sako N, Ninomiya Y (2008) Gurmarin sensitivity of sweet taste responses is associated with co-expression patterns of T1r2, T1r3, and gustducin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 367:356–363
Shiyovich A, Sztarkier I, Nesher L (2010) Toxic hepatitis induced by Gymnema sylvestre, a natural remedy for type 2 diabetes mellitus. Am J Med Sci 340:514–517
Sigoillot M, Brockhoff A, Lescop E, Poirier N, Meyerhof W, Briand L (2012) Optimization of the production of gurmarin, a sweet-taste-suppressing protein, secreted by the methylotrophic yeast Pichia pastoris. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol
Somenarain L, Jakinovich W Jr (1990) Antagonism of the gerbil’s sweetener and Polycose gustatory responses by copper chloride. Brain Res 522:83–89
Uchida Y, Sato T (1997) Changes in outward K+ currents in response to two types of sweeteners in sweet taste transduction of gerbil taste cells. Chem Senses 22:163–169
Vlahopoulos V, Jakinovich W Jr (1986a) Antagonism of the gerbil's sucrose taste response by p-nitrophenyl alpha-D-glucopyranoside and chloramphenicol. J Neurosci 6:2611–2615
Vlahopoulos V, Jakinovich W Jr (1986b) A structure-activity study on the sucrose taste antagonist methyl 4,6-dichloro-4,6-dideoxy-alpha-D-galactopyranoside. J Neurosci 6:2604–2610
Warren RP, Warren RM, Weninger MG (1969) Inhibition of the sweet taste by Gymnema sylvestre. Nature 223:94–95
Winnig M (2006) Struktur-Wirkungsbeziehungen der Süßgeschmacksrezeptoren des Menschen und der Ratte. Universität Potsdam, Potsdam
Winnig M, Bufe B, Meyerhof W (2005) Valine 738 and lysine 735 in the fifth transmembrane domain of rTas1r3 mediate insensitivity towards lactisole of the rat sweet taste receptor. BMC Neurosci 6:22
Winnig M, Bufe B, Kratochwil NA, Slack JP, Meyerhof W (2007) The binding site for neohesperidin dihydrochalcone at the human sweet taste receptor. BMC Struct Biol 7
Xu H, Staszewski L, Tang H, Adler E, Zoller M, Li X (2004) Different functional roles of T1R subunits in the heteromeric taste receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:14258–14263
Yamada A, Nakamura Y, Sugita D, Shirosaki S, Ohkuri T, Katsukawa H, Nonaka K, Imoto T, Ninomiya Y (2006) Induction of salivary kallikreins by the diet containing a sweet-suppressive peptide, gurmarin, in the rat. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 346:386–392
Yasumatsu K, Kusuhara Y, Shigemura N, Ninomiya Y (2007) Recovery of two independent sweet taste systems during regeneration of the mouse chorda tympani nerve after nerve crush. Eur J Neurosci 26:1521–1529
Yasumatsu K, Ohkuri T, Sanematsu K, Shigemura N, Katsukawa H, Sako N, Ninomiya Y (2009) Genetically-increased taste cell population with G(alpha)-gustducin-coupled sweet receptors is associated with increase of gurmarin-sensitive taste nerve fibers in mice. BMC Neurosci 10:152
Zawalich WS (1973) Depression of gustatory sweet response by alloxan. Comp Biochem Physiol A Comp Physiol 44:903–909
Zhang F, Klebansky B, Fine RM, Liu H, Xu H, Servant G, Zoller M, Tachdjian C, Li X (2010) Molecular mechanism of the sweet taste enhancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:4752–4757
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the Agence Nationale de la Recherche ANR-09-ALIA-010 (LB) and the German Research Foundation ME 1024/7-1 (WM), a studentship from the Institut National de la Recherche Agronomique, and the Burgundy council (MS). We thank Simon Foster for the critical reading of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Maud Sigoillot and Anne Brockhoff contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sigoillot, M., Brockhoff, A., Meyerhof, W. et al. Sweet-taste-suppressing compounds: current knowledge and perspectives of application. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 96, 619–630 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4387-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-012-4387-3