Abstract
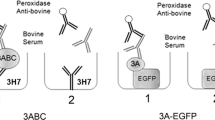
To develop a strategy of differentiating infected from vaccinated animals (DIVA) with foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV), a short (27aa) peptide containing three conserved linear B cell epitopes of the FMDV 3B nonstructural protein was designed. This novel BF peptide was synthesized using a gene splicing by overlap extension protocol with preferred codons for Escherichia coli. The resultant eight tandem repeat multimer (1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 16, 24, and 32BF) were expressed as soluble fusion proteins in E. coli. An indirect ELISA was developed based on the recombinant 8BF protein with the aim of specifically distinguishing antibodies induced by FMDV infection but not those induced by vaccination. Using the cut-off value of 0.3, the sensitivity of the assay was 96.8% and the specificities for naive and vaccinated cattle were 99.8 and 99.0%, respectively. The performance of the newly developed epitope-based ELISA was compared with three commercial NSP ELISA kits. The 8BF-ELISA appears to be a promising DIVA test for FMD control and eradication.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexandersen S, Zhang Z, Donaldson AI, Garland AJ (2003) The pathogenesis and diagnosis of foot-and-mouth disease. J Comp Pathol 129:1–36
Bergmann IE, Malirat V, Neitzert E, Beck E, Panizzutti N, Sanchez C, Falczuk A (2000) Improvement of a serodiagnostic strategy for foot-and-mouth disease virus surveillance in cattle under systematic vaccination: a combined system of an indirect ELISA-3ABC with an enzyme-linked immunoelectrotransfer blot assay. Arch Virol 145:473–489
Brocchi E, Bergmann IE, Dekker A, Paton DJ, Sammin DJ, Greiner M, Grazioli S, De Simone F, Yadin H, Haas B, Bulut N, Malirat V, Neitzert E, Goris N, Parida S, Sorensen K, De Clercq K (2006) Comparative evaluation of six ELISAs for the detection of antibodies to the non-structural proteins of foot-and-mouth disease virus. Vaccine 24:6966–6979
Chen SP, Lee MC, Sun YF, Yang PC (2011) Application of non-structural protein ELISA kits in nationwide FMD surveillance in pigs to demonstrate virus circulation in Taiwan. Vet Microbiol 152:266–269
Chu HS, Park JE, Kim DM, Kim BG, Won JI (2010) The effects of supplementing specific amino acids on the expression of elastin-like polypeptides (ELPs). Protein Expr Purif 74:298–303
Clavijo A, Wright P, Kitching P (2004) Developments in diagnostic techniques for differentiating infection from vaccination in foot-and-mouth disease. Vet J 167:9–22
Cooke JN, Westover KM (2008) Serotype-specific differences in antigenic regions of foot-and-mouth disease virus (FMDV): a comprehensive statistical analysis. Infect Genet Evol 8:855–863
De Diego M, Brocchi E, Mackay D, De Simone F (1997) The non-structural polyprotein 3ABC of foot-and-mouth disease virus as a diagnostic antigen in ELISA to differentiate infected from vaccinated cattle. Arch Virol 142:2021–2033
Gomara MJ, Haro I (2007) Synthetic peptides for the immunodiagnosis of human diseases. Curr Med Chem 14:531–546
Hohlich BJ, Wiesmuller KH, Schlapp T, Haas B, Pfaff E, Saalmuller A (2003) Identification of foot-and-mouth disease virus-specific linear B-cell epitopes to differentiate between infected and vaccinated cattle. J Virol 77:8633–8639
Horton RM, Hunt HD, Ho SN, Pullen JK, Pease LR (1989) Engineering hybrid genes without the use of restriction enzymes: gene splicing by overlap extension. Gene 77:61–68
Inoue T, Parida S, Paton DJ, Linchongsubongkoch W, Mackay D, Oh Y, Aunpomma D, Gubbins S, Saeki T (2006) Development and evaluation of an indirect enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for detection of foot-and-mouth disease virus nonstructural protein antibody using a chemically synthesized 2B peptide as antigen. J Vet Diagn Invest 18:545–552
Kim P, Pau CP (2001) Comparing tandem repeats and multiple antigenic peptides as the antigens to detect antibodies by enzyme immunoassay. J Immunol Methods 257:51–54
Lee F, Jong MH, Yang DW (2006) Presence of antibodies to non-structural proteins of foot-and-mouth disease virus in repeatedly vaccinated cattle. Vet Microbiol 115:14–20
Lu Z, Cao Y, Guo J, Qi S, Li D, Zhang Q, Ma J, Chang H, Liu Z, Liu X, Xie Q (2007) Development and validation of a 3ABC indirect ELISA for differentiation of foot-and-mouth disease virus infected from vaccinated animals. Vet Microbiol 125:157–169
Lu Z, Zhang X, Fu Y, Cao Y, Tian M, Sun P, Li D, Liu Z, Xie Q (2010) Expression of the major epitope regions of 2C integrated with the 3AB non-structural protein of foot-and-mouth disease virus and its potential for differentiating infected from vaccinated animals. J Virol Methods 170:128–133
Mackay DK, Forsyth MA, Davies PR, Berlinzani A, Belsham GJ, Flint M, Ryan MD (1998) Differentiating infection from vaccination in foot-and-mouth disease using a panel of recombinant, non-structural proteins in ELISA. Vaccine 16:446–459
Oem JK, Chang BS, Joo HD, Yang MY, Kim GJ, Park JY, Ko YJ, Kim YJ, Park JH, Joo YS (2007) Development of an epitope-blocking-enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay to differentiate between animals infected with and vaccinated against foot-and-mouth disease virus. J Virol Methods 142:174–181
Parida S, Cox SJ, Reid SM, Hamblin P, Barnett PV, Inoue T, Anderson J, Paton DJ (2005) The application of new techniques to the improved detection of persistently infected cattle after vaccination and contact exposure to foot-and-mouth disease. Vaccine 23:5186–5195
Rao X, Hu J, Li S, Jin X, Zhang C, Cong Y, Hu X, Tan Y, Huang J, Chen Z, Zhu J, Hu F (2005) Design and expression of peptide antibiotic hPAB-beta as tandem multimers in Escherichia coli. Peptides 26:721–729
Shen F, Chen PD, Walfield AM, Ye J, House J, Brown F, Wang CY (1999) Differentiation of convalescent animals from those vaccinated against foot-and-mouth disease by a peptide ELISA. Vaccine 17:3039–3049
Sorensen KJ, de Stricker K, Dyrting KC, Grazioli S, Haas B (2005) Differentiation of foot-and-mouth disease virus infected animals from vaccinated animals using a blocking ELISA based on baculovirus expressed FMDV 3ABC antigen and a 3ABC monoclonal antibody. Arch Virol 150:805–814
Sorensen KJ, Madsen KG, Madsen ES, Salt JS, Nqindi J, Mackay DK (1998) Differentiation of infection from vaccination in foot-and-mouth disease by the detection of antibodies to the non-structural proteins 3D, 3AB and 3ABC in ELISA using antigens expressed in baculovirus. Arch Virol 143:1461–1476
Sorensen MA, Kurland CG, Pedersen S (1989) Codon usage determines translation rate in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol 207:365–377
Sun T, Lu P, Wang X (2004) Localization of infection-related epitopes on the non-structural protein 3ABC of foot-and-mouth disease virus and the application of tandem epitopes. J Virol Methods 119:79–86
Zhong Z, Xu Z, Peng L, Huang L, Fang X, Cen P (2006) Tandem repeat mhBD2 gene enhance the soluble fusion expression of hBD2 in Escherichia coli. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 71:661–667
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a grant from the Earmarked Fund for China Agriculture Research System (No. CARS-37). The authors would like to express their gratitude to Dr. Weiling Yu (Animal Diseases Research Institute, Canadian Food Inspection Agency) for providing cattle sera.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Mingchun Gao and Runxiang Zhang contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, M., Zhang, R., Li, M. et al. An ELISA based on the repeated foot-and-mouth disease virus 3B epitope peptide can distinguish infected and vaccinated cattle. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 93, 1271–1279 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3815-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-011-3815-0