Abstract
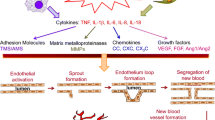
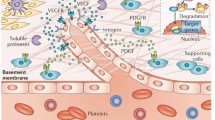
A role for angiogenesis has been described in several rheumatic diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, systemic sclerosis, systemic lupus erythematosus, vasculitides, and osteoarthritis, leading to the possibility that angiogenesis inhibition may be an additional useful therapeutic arm. While the role of anti-angiogenic therapy in rheumatoid arthritis has received attention, it is conceivable that the inhibition of pathological angiogenesis may also be a useful therapeutical approach in other rheumatic diseases. Numerous compounds, such as, for example, various interleukins, antibodies directed against angiogenic factors, peptides, estrogen metabolites, disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs, have been found to have anti-angiogenic properties. However, additional research is needed to obtain a clear understanding of the pathogenic mechanism of angiogenesis and the potential applications of anti-angiogenic therapy in rheumatic diseases.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hanahan D, Folkman J (1996) Patterns and emerging mechanisms of the angiogenic switch during tumorigenesis. Cell 86:353–364
Koch AE (2000) The role of angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis: recent developments. Ann Rheum Dis 59:i65–i71
Szekanecz Z, Koch AE (2009) Angiogenesis and its targeting in rheumatoid arthritis. Vascul Pharmacol 51:1–7
Takahara K, Iioka T, Furukawa K, Uchida T, Nakashima M, Tsukazaki T, Scindo H (2004) Autocrine/paracrine role of the angiopoietin-1 and −2/Tie2 system in cell proliferation and chemotaxis of cultured fibroblastic synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Hum Pathol 35:150–158
Tanaka S, Mori M, Sakamoto Y, Makuuchi M, Sugimachi K, Wands JR (1999) Biologic significance of angiopoietin-2 expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J Clin Invest 103:341–345
Levy NS, Chung S, Furneaux H, Levy AP (1998) Hypoxic stabilization of vascular endothelial growth factor mRNA by the RNA-binding protein HuR. J Biol Chem 273:6417–6423
Park YW, Mo Kang Y, Butterfield J, Detmar M, Goronzy JJ, Weyand CM (2004) Thrombospondin 2 functions as an endogenous regulator of angiogenesis and inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Pathol 165:2087–2098
Yamamoto T (2013) Angiogenic and inflammatory properties of psoriatic arthritis. ISRN Dermatol 2013:630620
Szekanecz Z, Koch AE (2007) Mechanism of disease: angiogenesis in inflammatory diseases. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol 3:635–643
Manetti M, Guiducci S, Ibba-Manneschi L, Matucci-Cerinic M (2011) Impaired angiogenesis in systemic sclerosis: the emerging role of the antiangiogenic VEGF(165)b splice variant. Trends Cardiovasc Med 21:204–210
Manetti M, Guiducci S, Romano E, Ceccarelli C, Bellando-Randone S, Conforti ML, Ibba-Manneschi L, Matucci-Cerinic M (2011) Overexpression of VEGF165b, an inhibitory splice variant of vascular endothelial growth factor, leads to insufficient angiogenesis in patients with systemic sclerosis. Circ Res 109:e14–26
Hernández-Rodríguez J, García-Martínez A, Casademont J, Filella X, Esteban MJ, López-Soto A, Fernández-Solà J, Urbano-Márquez A, Grau JM, Cid MC (2002) A strong initial systemic inflammatory response is associated with higher corticosteroid requirements and longer duration of therapy in patients with giant-cell arteritis. Arthritis Rheum 47:29–35
Halacheva K, Gulubova MV, Manolova I, Petkov D (2002) Expression of ICAM-1, VCAM-1, E-selectin and TNF-alpha on the endothelium of femoral and iliac arteries in thromboangiitis obliterans. Acta Histochem 104:177–184
Bodolay E, Koch AE, Kim J, Szegedi G, Szekanecz Z (2002) Angiogenesis and chemokines in rheumatoid arthritis and other systemic inflammatory rheumatic diseases. J Cell Mol Med 6:357–376
Yacin B, Arda N, Tezel GG, Erman M, Alli N (2006) Expressions of vascular endothelial growth factor and CD34 in oral aphthous lesions of Behcet’s disease. Anal Quant Cytol Histol 28:303–306
Bonnet CS, Walsh DA (2005) Osteoarthritis, angiogenesis and inflammation. Rheumatology (Oxford) 44:7–16
Goedkoop AY, Kraan MC, Picavet DI, de Rie MA, Teunissen MB, Bos JD, Tak PP (2004) Deactivation of endothelium and reduction in angiogenesis in psoriatic skin and synovium by low dose infliximab therapy in combination with stable methotrexate therapy: a prospective single-centre study. Arthritis Res Ther 6:R326–R334
Markham T, Mullan R, Golden-Mason L, Rogers S, Bresnihan B, Fitzgerald O, Fearon U, Veale DJ (2006) Resolution of endothelial activation and down-regulation of Tie2 receptor in psoriatic skin after infliximab therapy. J Am Acad Dermatol 54:1003–1012
Chen Y, Donnelly E, Kobayashi H, Debusk LM, Lin PC (2005) Gene therapy targeting the Tie2 function ameliorates collagen-induced arthritis and protects against bone destruction. Arthritis Rheum 52:1585–1594
Koch AE (2003) Angiogenesis as a target in rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 62:ii60–ii67
D’Amato RJ, Loughnan MS, Flynn E, Folkman J (1994) Thalidomide is an inhibitor of angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:4082–4085
Versapuech J, Beylot-Barry M, Doutre MS, Beylot C (2000) Subacute cutaneous lupus. Evolutive and therapeutic features of a series of 24 cases. Presse Med 29:1596–1599
Brik R, Shamali H, Bergman R (2001) Successful thalidomide treatment of severe infantile Behçet disease. Pediatr Dermatol 18:143–145
Ribatti D, Vacca A (2005) Therapeutic renaissance of thalidomide in the treatment of haematological malignancies. Leukemia 19:1525–1531
Siegle I, Klein T, Backman JT, Saal JG, Nusing RM, Fritz P (1998) Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in human synovial tissue. Arthritis Rheum 41:122–129
Vane JR, Mitchell JA, Appleton I, Tomlinson A, Bishop-Bailey D, Croxtall J, Willoughby DA (1994) Inducible isoforms of cyclooxygenase and nitric oxide synthase in inflammation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:2046–2050
Woods JM, Mogollon A, Amin MA, Martinez RJ, Koch AE (2003) The role of COX-2 in angiogenesis and rheumatoid arthritis. Exp Mol Pathol 74:282–290
Eliceiri BP, Cheresh DA (1998) The role of alphav integrins during angiogenesis. Mol Med 4:741–750
Takahashi H, Kato K, Miyake K, Hirai Y, Yoshino S, Shimada T (2005) Adeno-associated virus vector-mediated anti-angiogenic gene therapy for collagen-induced arthritis in mice. Clin Exp Rheumatol 23:455–461
Yue L, Shen YX, Feng LJ, Chen FH, Yao HW, Liu LH, Wu Q, Wang H (2007) Blockage of the formation of new blood vessels by recombinant human endostatin contributes to the regression of rat adjuvant arthritis. Eur J Pharmacol 567:166–170
Yamaguchi Y, Takihara T, Chambers RA, Veraldi KL, Larregina AT, Feghali-Bostwick CA (2012) A peptide derived from endostatin ameliorates organ fibrosis. Sci Transl Med 4(136):136ra71
Wang CR, Chen SY, Shiau AL, Wu CL, Jou IM, Chao L, Chao J (2007) Upregulation of kallistatin expression in rheumatoid joints. J Rheumatol 34:2171–2176
Wang CR, Chen SY, Wu CL, Liu MF, Jin YT, Chao L, Chao J (2005) Prophylactic adenovirus-mediated human kallistatin gene therapy suppresses rat arthritis by inhibiting angiogenesis and inflammation. Arthritis Rheum 52:1319–1324
Rico MC, Castaneda JL, Manns JM, Uknis AB, Sainz IM, Safadi FF, Popoff SN, Dela Cadena RA (2007) Amelioration of inflammation, angiogenesis and CTGF expression in an arthritis model by a TSP-1-derived peptide treatment. J Cell Physiol 211:504–512
Bessis N, Boissier MC (1998) Gene therapy in rheumatoid polyarthritis: perspectives. Presse Med 27:580–582
Saito M, Murata T, Watanabe K et al (2005) Adenoviral vector-mediated gene transfer of IL-13R_2 chain followed by IL-13 cytotoxin treatment offers potent targeted therapy for cytotoxin-resistant cancers. Int J Cancer 116:1–8
Haas CS, Amin MA, Allen BB, Ruth JH, Haines GK III, Woods JM, Koch AE (2006) Inhibition of angiogenesis by interleukin-4 gene therapy in rat adjuvant-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 54:2402–2414
Haas CS, Amin MA, Ruth JH, Allen BL, Ahmed S, Pakozdi A, Woods JM, Shahrara S, Koch AE (2007) In vivo inhibition of angiogenesis by interleukin-13 gene therapy in a rat model of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 56:2535–2548
Afuwape AO, Feldmann M, Paleolog EM (2003) Adenoviral delivery of soluble VEGF receptor 1 (sFlt-1) abrogates disease activity in murine collagen-induced arthritis. Gene Ther 10:1950–1960
Carmeliet P, Ferreira V, Breier G et al (1996) Abnormal blood vessel development and lethality in embryos lacking a single VEGF allele. Nature 380:435–439
Whitesell L, Lindquist SL (2005) HSP90 and the chaperoning of cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 5:761–772
Kaur G, Belotti D, Burger AM et al (2004) Antiangiogenic properties of 17-(dimethylaminoethylamino)-17-demethoxygeldanamycin: an orally bioavailable heat shock protein 90 modulator. Clin Cancer Res 10:4813–4821
Liu YV, Baek JH, Zhang H, Diez R, Cole RN, Semenza GL (2007) RACK1 competes with HSP90 for binding to HIF-1α and is required for O(2)-independent and HSP90 inhibitor-induced degradation of HIF-1α. Mol Cell 25:207–217
Sun J, Liao JK (2004) Induction of angiogenesis by heat shock protein 90 mediated by protein kinase Akt and endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 24:2238–2244
Nagy G, Koncz A, Telarico T, Fernandez D, Ersek B, Buzás E, Perl A (2010) Central role of nitric oxide in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Res Ther 12:210
Jhaveri K, Taldone T, Modi S, Chiosis G (2012) Advances in the clinical development of heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) inhibitors in cancers. Biochim Biophys Acta 1823:742–755
Rice JW, Veal JM, Fadden RP, Barabasz AF, Partridge JM, Barta TE, Dubois LG, Huang KH, Mabbett SR, Silinski MA, Steed PM, Hall SE (2008) Small molecule inhibitors of Hsp90 potently affect inflammatory disease pathways and exhibit activity in models of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 58:3765–3775
Ireson CR, Chander SK, Purohit A, Perera S, Newman SP, Parish D et al (2004) Pharmacokinetics and efficacy of 2-methoxyoestradiol and 2-methoxyoestradiol-bis-sulphamate in vivo in rodents. Br J Cancer 90:932–937
Khong TL, Larsen H, Raatz Y, Paleolog E (2007) Angiogenesis as a therapeutic target in arthritis: learning the lessons of the colorectal cancer experience. Angiogenesis 10:243–258
Moertel CG, Schutt AJ, Reitemeier RJ, Hahn RG (1972) Phase II study of camptothecin (NSC-100880) in the treatment of advanced gastrointestinal cancer. Cancer Chemother Rep 56:95–101
Jackson JK, Higo T, Hunter WL, Burt HM (2008) Topoisomerase inhibitors as anti-arthritic agents. Inflamm Res 57:126–134
Koo OM, Rubinstein I, Onyüksel H (2011) Actively targeted low-dose camptothecin as a safe, long-acting, disease-modifying nanomedicine for rheumatoid arthritis. Pharm Res 28:776–787
Pache M, Schwarz HA, Kaiser HJ, Wuest P, Kloti M, Dubler B, Flammer J (2002) Elevated plasma endothelin-1 levels and vascular dysregulation in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Med Sci Monit 8:CR616–CR619
Julkunen H, Saijonmaa O, Gronhagen-Riska C, Teppo AM, Fyhrquist F (1991) Raised plasma concentrations of endothelin-1 in systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann Rheum Dis 50:526–527
Melendez AJ (2008) Sphingosine kinase signalling in immune cells: potential as novel therapeutic targets. Biochim Biophys Acta 1784:66–75
Kitano M, Hla T, Sekiguchi M, Kawahito Y, Yoshimura R, Miyazawa K, Iwasaki T, Sano H, Saba JD, Tam YY (2006) Sphingosine 1-phosphate/sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 1 signaling in rheumatoid synovium: regulation of synovial proliferation and inflammatory gene expression. Arthritis Rheum 54:742–753
Matsuura M, Imayoshi T, Chiba K, Okumoto T (2000) Effect of FTY720, a novel immunosuppressant, on adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats. Inflamm Res 49:404–410
Sheikh A, Naqvi SH, Naqvi SH, Sheikh K (2012) Itraconazole: its possible role in inhibiting angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis. Med Hypotheses 79:313–314
Aftab BT, Dobromilskaya I, Liu JO, Rudin CM (2011) Itraconazole inhibits angiogenesis and tumor growth in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Res 71:6764–6772
Bainbridge J, Sivakumar B, Paleolog E (2006) Angiogenesis as a therapeutic target in arthritis: lessons from oncology. Curr Pharm Des 12:2631–2644
Competing interests
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maruotti, N., Cantatore, F.P. & Ribatti, D. Putative effects of potentially anti-angiogenic drugs in rheumatic diseases. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 70, 135–140 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-013-1605-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-013-1605-6