Abstract
Purpose
The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) is one of the four human epidermal receptors. The efficacy and safety of EGFR-targeted therapies for treating non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) remained controversial. The aim of this study was to systematically evaluate EGFR-targeted therapies plus chemotherapy for advanced NSCLC.
Methods
Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, PubMed, and Embase were searched for relevant studies. Quantitative analysis was carried out to evaluate survival, response, and toxicity of EGFR-targeted therapies.
Results
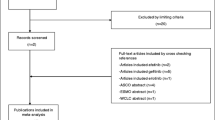
Ten randomized controlled trials (RCTs) involving 5,936 patients were identified out of 107 studies. There was no statistical difference in overall (OS) and 1-year (OYS) survival rate when small-molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitors (TKIs) plus platinum-based doublet chemotherapy (PBDC) were compared with PBDC alone. However, progression-free survival [hazard ratio (HR) = 0.87, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.76–0.99] and overall response rate (ORR) were marginally improved. Prolonged OS (HR = 0.87, 95% CI 0.78–0.96) and increased ORR and OYS were found when cetuximab plus PBDC was compared with PBDC alone. Adverse events in the combination arms were similar in incidence to those of the chemotherapy-alone arms, with the exception of an increased incidence of rash and diarrhea.
Conclusions
Cetuximab adds benefits to NSCLC patients compared with PBDC alone. Small-molecule TKIs plus PBDC lead to a slightly additive efficacy compared with PBDC alone.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E et al (2008) Cancer statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin 58:71–96
Molina JR, Yang P, Cassivi SD et al (2008) Non-small cell lung cancer: epidemiology, risk factors, treatment, and survivorship. Mayo Clin Proc 83:584–594
Stinchcombe TE, Socinski MA (2009) Current treatments for advanced stage non-small cell lung cancer. Proc Am Thorac Soc 6:233–241
Schiller JH, Harrington D, Belani CP et al (2002) Comparison of four chemotherapy regimens for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 346:92–98
Grunwald V, Hidalgo M (2002) The epidermal growth factor receptor: a new target for anticancer therapy. Curr Probl Cancer 26:109–164
Brandes AA, Franceschi E, Tosoni A et al (2008) Epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors in neuro-oncology: hopes and disappointments. Clin Cancer Res 14:957–960
Saif MW, Merikas I, Tsimboukis S et al (2008) Erlotinib-induced skin rash. Pathogenesis, clinical significance and management in pancreatic cancer patients. Jop 9:267–274
Mok TS, Wu YL, Yu CJ et al (2009) Randomized, placebo-controlled, phase II study of sequential erlotinib and chemotherapy as first-line treatment for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 27:5080–5087
Herbst RS, Prager D, Hermann R et al (2005) TRIBUTE: a phase III trial of erlotinib hydrochloride (OSI-774) combined with carboplatin and paclitaxel chemotherapy in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 23:5892–5899
Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carroll D et al (1996) Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? Control Clin Trials 17:1–12
Parmar MK, Torri V, Stewart L (1998) Extracting summary statistics to perform meta-analyses of the published literature for survival endpoints. Stat Med 17:2815–2834
Gatzemeier U, Pluzanska A, Szczesna A et al (2007) Phase III study of erlotinib in combination with cisplatin and gemcitabine in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: the Tarceva Lung Cancer Investigation Trial. J Clin Oncol 25:1545–1552
Giaccone G, Herbst RS, Manegold C et al (2004) Gefitinib in combination with gemcitabine and cisplatin in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a phase III trial–INTACT 1. J Clin Oncol 22:777–784
Herbst RS, Giaccone G, Schiller JH et al (2004) Gefitinib in combination with paclitaxel and carboplatin in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a phase III trial–INTACT 2. J Clin Oncol 22:785–794
Heymach JV, Paz-Ares L, De Braud F et al (2008) Randomized phase II study of vandetanib alone or with paclitaxel and carboplatin as first-line treatment for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 26:5407–5415
Lynch TJ, Patel T, Dreisbach L et al (2010) Cetuximab and first-line taxane/carboplatin chemotherapy in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: results of the randomized multicenter phase III trial BMS099. J Clin Oncol 28:911–917
Pirker R, Pereira JR, Szczesna A et al (2009) Cetuximab plus chemotherapy in patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer (FLEX): an open-label randomised phase III trial. Lancet 373:1525–1531
Rosell R, Robinet G, Szczesna A et al (2008) Randomized phase II study of cetuximab plus cisplatin/vinorelbine compared with cisplatin/vinorelbine alone as first-line therapy in EGFR-expressing advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol 19:362–369
Butts CA, Bodkin D, Middleman EL et al (2007) Randomized phase II study of gemcitabine plus cisplatin or carboplatin [corrected], with or without cetuximab, as first-line therapy for patients with advanced or metastatic non small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 25:5777–5784
Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S et al (2009) Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med 361:947–957
Hotta K, Ueoka H, Kiura K, Tabata M, Ogino A, Umemura S (2005) Safety and efficacy of gefitinib treatment in elderly patients with non-small-cell lung cancer: Okayama Lung Cancer Study Group experience. Acta Oncol 44:717–722
Koyama N, Yasuto J, Takabe K, Yoshizawa M, Usui Y, Inase N (2006) The characterization of gefitinib sensitivity and adverse events in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Anticancer Res 26:4519–4526
D’Addario G, Pintilie M, Leighl NB, Feldd R, Cerny T, Shepherd FA (2005) Platinum-based versus non-platinum-based chemotherapy in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis of the published literature. J Clin Oncol 23:2926–2936
Kunkel MW, Hook KE, Howard CT et al (1996) Inhibition of the epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase by PD153035 in human A431 tumors in athymic nude mice. Invest New Drugs 13:295–302
Akita RW, Sliwkowski MX (2003) Preclinical studies with Erlotinib (Tarceva). Semin Oncol 30:15–24
Baselga J (2004) Combining the anti-EGFR agent gefitinib with chemotherapy in non-small-cell lung cancer: how do we go from INTACT to impact? J Clin Oncol 22:759–761
Liu L, Cao Y, Tan A et al (2010) Cetuximab-based therapy versus non-cetuximab therapy for advanced cancer: a meta-analysis of 17 randomized controlled trials. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 65:849–861
Chia-Hsuin Chang K-YC, Yinong Young-Xu, Tobias Kurth, John Orav E, Pan-Chyr Yang, Arnold Chan K (2008) The safety and efficacy of gefitinib versus platinum-based doublets chemotherapy as the first-line treatment for advanced non-small-cell lung cancer patients in East Asia: A meta-analysi. Lung Cancer 62:242–252
Rajeswaran A, Trojan A, Burnand B et al (2008) Efficacy and side effects of cisplatin- and carboplatin-based doublet chemothera\peutic regimens versus non-platinum-based doublet chemotherapeutic regimens as first line treatment of metastatic non-small cell lung carcinoma: a systematic review of randomized controlled trials. Lung Cancer 59:1–11
McDonald MA, Simpson SH, Ezekowitz JA et al (2005) Angiotensin receptor blockers and risk of myocardial infarction: systematic review. BMJ 331:873
Conflict of Interest
All authors declare no potential conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Peng Chen, Long Wang, and Bing Liu contributed equally to this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, P., Wang, L., Liu, B. et al. EGFR-targeted therapies combined with chemotherapy for treating advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a meta-analysis. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 67, 235–243 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-010-0965-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00228-010-0965-4