Abstract
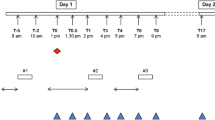
Previous treatment can be a confounding variable in studies with novel antipsychotics. Quetiapine is a new antipsychotic substance with a low affinity for dopamine-2 (D2) receptors. Preliminary SPECT and PET investigations revealed only a low striatal D2 receptor occupancy rate. However, we present two cases of high striatal D2 receptor occupancy (51% and 71%) measured with 123I IBZM SPECT during quetiapine monotherapy. Both patients had previously received continuous treatment with typical neuroleptics. We present evidence that the previous antipsychotic therapy influenced D2 receptor binding of 123I IBZM during quetiapine treatment weeks after cessation of typical neuroleptics. This might be of importance for the design of clinical trials and brain imaging studies in the future.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 14 April 1997 /Final version: 14 May 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tauscher, J., Küfferle, B., Asenbaum, S. et al. Previous treatment as a confounding variable in studies with novel antipsychotics: two cases of high dopamine-2 receptor occupancy with quetiapine. Psychopharmacology 133, 102–105 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130050378
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130050378