Abstract
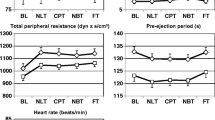
Effects of oral alprazolam (0.5 and 1 mg) and lorazepam (2 mg) on sympathetic adrenomedullary activity and sedation were studied during supine rest, mental load (Color Word Test, CWT) and active standing (OCT), in 12 male volunteers in a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled cross-over design. Compared to placebo, alprazolam significantly increased subjective sedation, reduced plasma adrenaline and noradrenaline concentrations and mean blood pressure (MBP) during supine rest, and attenuated plasma adrenaline responses during the CWT and the OCT; these effects during the CWT and OCT appeared to be dose-dependent. In comparison with lorazepam (2 mg), alprazolam (1 mg) showed reduced MBP levels during supine rest, whereas lorazepam showed a higher heart rate level during supine rest, a reduced plasma noradrenaline response to the OCT and a performance deterioration to the CWT. There were no differences between alprazolam (1 mg) and lorazepam regarding subjective sedation. Although the benzodiazepines were similar regarding their increase of sedation, alprazolam and loraze- pam induced differential effects on sympathetic adrenomedullary activity during rest and stress, whereby suppression of adrenomedullary activity may be specific for alprazolam.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 13 March 1996 / Final version: 6 June 1996
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van den Berg, F., Tulen, J., Boomsma, F. et al. Effects of alprazolam and lorazepam on catecholaminergic and cardiovascular activity during supine rest, mental load and orthostatic challenge. Psychopharmacology 128, 21–30 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130050105
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130050105