Abstract
Rationale
Previous studies have shown that selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors, activators of the cortex, apparently improved language functional recovery after brain damage rather than simply affective disorders.
Objective
Our aim was to determine whether venlafaxine (an agonist of both norepinephrine and 5-hydroxytryptamine) could modulate language cortex function.
Methods
A double-blind, crossover, randomized design was used to compare two 7-day treatment sessions with either venlafaxine (75 mg per day) or placebo. A functional magnetic resonance imaging experiment and two language function tests were performed on eight healthy males (mean age, 28.25 ± 3.15 years) at the end of each session, i.e., study entry, after venlafaxine, and after placebo (days 0, 7, and 18). Hyperactivation (venlafaxine minus placebo >0) or hypoactivation (placebo minus venlafaxine >0) by venlaxafine was assessed on the basis of the activation–baseline contrast.
Results
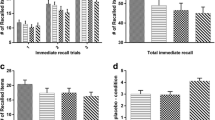
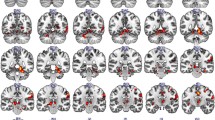
The naming score (P < .001) and spontaneous language fluency (P < .001) were significantly higher after venlafaxine than after placebo. Functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) showed that (1) picture naming activated the left posterior gyrus frontalis medius and the bilateral fusiform gyrus and the bilateral outer occipital lobes, (2) hyperactivation was observed in the adjoining area of posterior upper Broca area and premotor area in the dominant hemisphere in venlafaxine session (after venlafaxine), (3) the hyperactivation of the left gyrus frontalis medius on fMRI and the increase in naming test score were positively correlated, and (4) by contrast, we observed hypoactivation in the temporo–parieto–occipital region in venlafaxine session (after venlafaxine). This improvement may be related to increased phonics-related output in the frontal language cortex of the dominant hemisphere.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berends HI, Nijlant JM, Moviq KL, Van Putten MJ, Jannink MJ, Ijzerman MJ (2009) The clinical use of drugs influencing neurotransmitters in the brain to promote motor recovery after stroke; a Cochrane systematic review. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med 45:621–630
Bütefisch CM, Davis BC, Sawaki L, Waldvogel D, Classen J, Kopylev L, Cohen LG (2002) Modulation of use-dependent plasticity by d-amphetamine. Ann Neurol 51:59–68
Cabeza R, Nyberg L (2000) Imaging cognition II: an empirical review of 275 PET and fMRI studies. J Cogn Neurosci 12:1–47
Cao Y, Vikingstad EM, George KP, Johnson AF, Welch KM (1999) Cortical language activation in stroke patients recovering from aphasia with functional MRI. Stroke 30:2331–2340
De Boissezon X, Peran P, de Boysson C, Démonet JF (2007) Pharmacotherapy of aphasia: myth or reality? J Brain Lang 102:114
Del-Ben CM, Deakin JF, McKie S, Delvai NA, Williams SR, Elliott R, Dolan M, Anderson IM (2005) The effect of citalopram pretreatment on neuronal responses to neuropsychological tasks in normal volunteers: an FMRI study. Neuropsychopharmarmacology 30:1724–1734
Deleon J, Gottesman RF, Kleinman JT, Newhart M, Davis C, Heidler-Gary J, Lee A, Hillis AE (2007) Neural regions essential for distinct cognitive processes underlying picture naming. Brain 130:1408–1422
Duman RS, Nakagawa S, Malberg J (2001) Regulation of adult neurogenesis by antidepressant treatment. Neuropsychopharmarmacology 25:836–844
Feeney DM, Sutton RL (1987) Pharmacotherapy for recovery of function after brain injury. Crit Rev Neurobiol 3:135–137
Fernandez B, Cardebat D, Demonet JF, Joseph PA, Mazaux JM, Barat M, Allard M (2004) Functional MRI follow-up study of language processes in healthy subjects and during recovery in a case of aphasia. Stroke 35:2171–2176
Gaspar P, Cases O, Maroteaux L (2003) The developmental role of serotonin: news from mouse molecular genetics. Nat Rev Neurosci 4:1002–1012
Gerdelat-Mas A, Loubinoux I, Tombari D, Rascol O, Chollet F, Simonetta-Moreau M (2005) Chronic administration of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) paroxetine modulates human motor cortex excitability in healthy subjects. NeuroImage 27:314–322
Gernsbacher MA, Kaschak MP (2003) Neuroimaging studies of language production and comprehension. Annu Rev Psychol 54:91–114
Grabowski TJ, Damasio H, Damasio AR (1998) Premotor and prefrontal correlates of category-related lexical retrieval. NeuroImage 7:232–243
Horsfield SA, Rosse RB, Tomasino V, Schwartz BL, Mastropaolo J, Deutsch SI (2002) Fluoxetine's effects on cognitive performance in patients with traumatic brain injury. Int J Psychiatry Med 32:337–244
Kan IP, Thompson-Schill SL (2004) Effect of name agreement on prefrontal activity during overt and covert picture naming. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci 4:43–57
Kohn SE, Goodglass H (1985) Picture-naming in aphasia. Brain Lang 24:266–283
Levitt P, Harvey JA, Friedman E, Simansky K, Murphy EH (1997) New evidence for neurotransmitter influences on brain development. Trends Neurosci 20:269–274
Lipton SA, Kater SB (1989) Neurotransmitter regulation of neuronal outgrowth, plasticity and survival. Trends Neurosci 12:265–270
Loubinoux I, Tombari D, Pariente J, Gerdelat-Mas A, Franceries X, Cassol E, Rascol O, Pastor J, Chollet F (2005) Modulation of behavior and cortical motor activity in healthy subjects by a chronic administration of a serotonin enhancer. NeuroImage 27:299–313
Martin RC (2003) Language processing: functional organization and neuroanatomical basis. Annu Rev Psychol 54:85–89
Mattson MP, Maudsley S, Martin B (2004) BDNF and 5-HT: a dynamic duo in age-related neuronal plasticity and neurodegenerative disorders. Trends in Neurosicence 27:589–594
Mechelli A, Sartori G, Orlandi P, Price CJ (2006) Semantic relevance explains category effects in medial fusiform gyri. NeuroImage 30:992–1002
Murtha S, Chertkow H, Beauregard M, Evans A (1999) The neural substrate of picture naming. Cogn Neurosci 11:399–423
Noppeney U (2008) The neural systems of tool and action semantics: a perspective from functional imaging. J Physiol Paris 102:40–49
Péran P, Démonet JF, Cardebat D (2008) Paroxetine-induced modulation of cortical activity supporting language representations of action. Psychopharmacol 195:487–496
Price CJ, Devlin JT (2003) The myth of the visual word form area. NeuroImage 19:473–481
Raboyeau G, Marcotte K, Adrover-Roig D, Ansaldo AI (2010) Brain activation and lexical learning: the impact of learning phase and word type. NeuroImage 49:2850–2861
Sarkisyan G, Hedlund PB (2009) The 5-HT7 receptor is involved in allocentric spatial memory information processing. Behav Brain Res 202:26–31
Schweizer E, Theielen RJ, Frazer A (1997) Venlafaxine: a novel antidepressant compound. Exp Opin Invest Drugs 6:65–78
Struder HK, Weicker H (2001) Physiology and pathophysiology of the serotonergic system and its implications on mental and physical performance. Int J Sports Med 22:467–481
Tanaka Y (2007) Pharmacotherapy for aphasia. Rinsho Shinkeigaku 47:859–861
Vigneau M, Beaucousin V, Hervé PY, Duffau H, Crivello F, Houdé O, Mazoyer B, Tzourio-Mazoyer N (2006) Meta-analyzing left hemisphere language areas: phonology, semantics, and sentence processing. NeuroImage 30:1414–1432
Vitalis T, Parnavelas J (2003) The role of serotonin in early cortical development. Exp Neurol 25:245–256
Völlm B, Richardson P, McKie S, Elliott R, Deakin JF, Anderson IM (2006) Serotonergic modulation of neuronal responses to behavioral inhibition and reinforcing stimuli: an fMRI study in healthy volunteers. Eur J Neurosci 23:552–560
Walker-Batson D, Curtis S, Natarajan R (2001) A double-blind, placebo-controlled study of the use of amphetamine in the treatment of aphasia. Stroke 32:2093–2098
Acknowledgments
Our experiments comply with the current laws of China. We would like to acknowledge Dr. Li-min Wang (Department of Neurosurgery, General Hospital of Guangzhou Military Command of PLA) for participating in the design of fMRI paradigm in this study. The study was also supported by Guangzhou Science and Technology Key Project (No. 122732961131543).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, Q., Liu, Y., Li, CY. et al. The modulation of venlafaxine on cortical activation of language area in healthy subjects with fMRI study. Psychopharmacology 223, 417–425 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-012-2730-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-012-2730-0