Abstract
Rationale
Acute opiate exposure produces a state of dependence in humans and animals, which is revealed by signs and symptoms of withdrawal precipitated by opioid receptor antagonists. The physiological changes that underlie this state of acute dependence develop rapidly and can persist long after the end of chronic opiate exposure.
Objectives
The purpose of this investigation was to determine the persistence of acute dependence after a single morphine exposure in rodents, focusing on changes in behavior thought to reflect the negative emotional consequences of withdrawal.
Methods
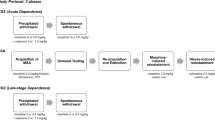
The acoustic startle reflex and conditioned place aversion were measured following naloxone administration at different time points after a single morphine exposure.
Results
Naloxone administration produced significant potentiation of acoustic startle—a form of anxiety-like behavior—for at least 80 days after one exposure to morphine. In contrast, naloxone produced a conditioned place aversion 24 h but not 20 days after one morphine exposure.
Conclusions
Together with existing literature, these results suggest acute as well as chronic opiate exposure leave rodents persistently vulnerable to express anxiety-like behavior in response to opioid receptor antagonists or stressful experience. The adaptations in brain function that underlie this protracted state of dependence may provide a foundation for the escalation of withdrawal severity that develops over repeated opiate exposure, and increase the likelihood of progression from casual drug use to compulsive drug abuse.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams JU, Holtzman SG (1990) Pharmacologic characterization of the sensitization to the rate-decreasing effects of naltrexone induced by acute opioid pretreatment in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 253:483–489
Araki H, Kawakami KY, Jin C, Suemaru K, Kitamura Y, Nagata M, Futagami K, Shibata K, Kawasaki H, Gomita Y (2004) Nicotine attenuates place aversion induced by naloxone in single-dose, morphine-treated rats. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 171:398–404
Aston-Jones G, Harris GC (2004) Brain substrates for increased drug seeking during protracted withdrawal. Neuropharmacology 47(Suppl 1):167–179
Azar MR, Jones BC, Schulteis G (2003) Conditioned place aversion is a highly sensitive index of acute opioid dependence and withdrawal. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 170:42–50
Baker TB, Piper ME, McCarthy DE, Majeskie MR, Fiore MC (2004) Addiction motivation reformulated: an affective processing model of negative reinforcement. Psychol Rev 111:33–51
Barr JL, Renner KJ, Forster GL (2010) Withdrawal from chronic amphetamine produces persistent anxiety-like behavior but temporally-limited reductions in monoamines and neurogenesis in the adult rat dentate gyrus. Neuropharmacology 59:395–405
Blatchford KE, Diamond K, Westbrook RF, McNally GP (2005) Increased vulnerability to stress following opiate exposures: behavioral and autonomic correlates. Behav Neurosci 119:1034–1041
Bruchas MR, Land BB, Lemos JC, Chavkin C (2009) CRF1-R activation of the dynorphin/kappa opioid system in the mouse basolateral amygdala mediates anxiety-like behavior. PLoS One 4:e8528
Cabral A, Ruggiero RN, Nobre MJ, Brandao ML, Castilho VM (2009) GABA and opioid mechanisms of the central amygdala underlie the withdrawal-potentiated startle from acute morphine. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 33:334–344
Carlezon WA Jr (2003) Place conditioning to study drug reward and aversion. Methods Mol Med 84:243–249
Celerier E, Laulin JP, Corcuff JB, Le Moal M, Simonnet G (2001) Progressive enhancement of delayed hyperalgesia induced by repeated heroin administration: a sensitization process. J Neurosci 21:4074–4080
Culpepper-Morgan JA, Kreek MJ (1997) Hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis hypersensitivity to naloxone in opioid dependence: a case of naloxone-induced withdrawal. Metabolism 46:130–134
Davis M, Cassella JV, Kehne JH (1988) Serotonin does not mediate anxiolytic effects of buspirone in the fear-potentiated startle paradigm: comparison with 8-OH-DPAT and ipsapirone. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 94:14–20
Davis M, Walker DL, Miles L, Grillon C (2010) Phasic vs sustained fear in rats and humans: role of the extended amygdala in fear vs anxiety. Neuropsychopharmacology 35:105–135
Eisenberg RM (1982) Further studies on the acute dependence produced by morphine in opiate naive rats. Life Sci 31:1531–1540
Engelmann JM, Radke AK, Gewirtz JC (2009) Potentiated startle as a measure of the negative affective consequences of repeated exposure to nicotine in rats. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 207:13–25
Gellert VF, Sparber SB (1977) A comparison of the effects of naloxone upon body weight loss and suppression of fixed-ratio operant behavior in morphine-dependent rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 201:44–54
Glover EM, Davis M (2008) Anxiolytic-like effects of morphine and buprenorphine in the rat model of fear-potentiated startle: tolerance, cross-tolerance, and blockade by naloxone. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 198:167–180
Goeldner C, Lutz PE, Darcq E, Halter T, Clesse D, Ouagazzal AM, Kieffer BL (2010) Impaired emotional-like behavior and serotonergic function during protracted abstinence from chronic morphine. Biol Psychiatry 69(3):236–244
Goldberg SR, Schuster CR (1969) Nalorphine: increased sensitivity of monkeys formerly dependent on morphine. Science 166:1548–1549
Harris AC, Gewirtz JC (2004) Elevated startle during withdrawal from acute morphine: a model of opiate withdrawal and anxiety. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 171:140–147
Harris AC, Gewirtz JC (2005) Acute opioid dependence: characterizing the early adaptations underlying drug withdrawal. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 178:353–366
Harris AC, Hanes SL, Gewirtz JC (2004) Potentiated startle and hyperalgesia during withdrawal from acute morphine: effects of multiple opiate exposures. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 176:266–273
Harris AC, Atkinson DM, Aase DM, Gewirtz JC (2006) Double dissociation in the neural substrates of acute opiate dependence as measured by withdrawal-potentiated startle. Neuroscience 139:1201–1210
Harris AC, Rothwell PE, Gewirtz JC (2008) Effects of the NMDA receptor antagonist memantine on the expression and development of acute opiate dependence as assessed by withdrawal-potentiated startle and hyperalgesia. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 196:649–660
Higgins GA, Sellers EM (1994) Antagonist-precipitated opioid withdrawal in rats: evidence for dissociations between physical and motivational signs. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 48:1–8
Hijzen TH, Houtzager SW, Joordens RJ, Olivier B, Slangen JL (1995) Predictive validity of the potentiated startle response as a behavioral model for anxiolytic drugs. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 118:150–154
Holtzman SG (2003) Discrimination of a single dose of morphine followed by naltrexone: substitution of other agonists for morphine and other antagonists for naltrexone in a rat model of acute dependence. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 304:1033–1041
Hyman SE, Malenka RC, Nestler EJ (2006) Neural mechanisms of addiction: the role of reward-related learning and memory. Annu Rev Neurosci 29:565–598
Jin C, Araki H, Nagata M, Suemaru K, Shibata K, Kawasaki H, Hamamura T, Gomita Y (2004) Withdrawal-induced c-Fos expression in the rat centromedial amygdala 24 h following a single morphine exposure. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 175:428–435
Jonkman S, Risbrough VB, Geyer MA, Markou A (2008) Spontaneous nicotine withdrawal potentiates the effects of stress in rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:2131–2138
Kalinichev M, Holtzman SG (2003) Changes in urination/defecation, auditory startle response, and startle-induced ultrasonic vocalizations in rats undergoing morphine withdrawal: similarities and differences between acute and chronic dependence. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 304:603–609
Kalivas PW, O’Brien C (2008) Drug addiction as a pathology of staged neuroplasticity. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:166–180
Kim JA, Pollak KA, Hjelmstad GO, Fields HL (2004) A single cocaine exposure enhances both opioid reward and aversion through a ventral tegmental area-dependent mechanism. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:5664–5669
Koob GF, Le Moal M (2008) Addiction and the brain antireward system. Annu Rev Psychol 59:29–53
Koob GF, Maldonado R, Stinus L (1992) Neural substrates of opiate withdrawal. Trends Neurosci 15:186–191
Krystal JH, Webb E, Grillon C, Cooney N, Casal L, Morgan CA 3rd, Southwick SM, Davis M, Charney DS (1997) Evidence of acoustic startle hyperreflexia in recently detoxified early onset male alcoholics: modulation by yohimbine and m-chlorophenylpiperazine (mCPP). Psychopharmacol (Berl) 131:207–215
Land BB, Bruchas MR, Lemos JC, Xu M, Melief EJ, Chavkin C (2008) The dysphoric component of stress is encoded by activation of the dynorphin kappa-opioid system. J Neurosci 28:407–414
Liu J, Schulteis G (2004) Brain reward deficits accompany naloxone-precipitated withdrawal from acute opioid dependence. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 79:101–108
Martin WR, Jasinski DR (1969) Physiological parameters of morphine dependence in man—tolerance, early abstinence, protracted abstinence. J Psychiatr Res 7:9–17
Mullis KB, Perry DC, Finn AM, Stafford B, Sadee W (1979) Morphine persistence in rat brain and serum after single doses. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 208:228–231
Myers KM, Carlezon WA Jr (2009) D-cycloserine facilitates extinction of naloxone-induced conditioned place aversion in morphine-dependent rats. Biol Psychiatry 67:85–87
Nutt JG, Jasinski DR (1974) Methadone-naloxone mixtures for use in methadone maintenance programs I. An evaluation in man of their pharmacological feasibility. II. Demonstration of acute physical dependence. Clin Pharmacol Ther 15:156–166
Nylander I, Vlaskovska M, Terenius L (1995) The effects of morphine treatment and morphine withdrawal on the dynorphin and enkephalin systems in Sprague-Dawley rats. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 118:391–400
Olive MF, Bertolucci M, Evans CJ, Maidment NT (1995) Microdialysis reveals a morphine-induced increase in pallidal opioid peptide release. Neuroreport 6:1093–1096
Parker LA, Joshi A (1998) Naloxone-precipitated morphine withdrawal induced place aversions: effect of naloxone at 24 hours postmorphine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 61:331–333
Parker LA, Cyr JA, Santi AN, Burton PD (2002) The aversive properties of acute morphine dependence persist 48 h after a single exposure to morphine: evaluation by taste and place conditioning. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 72:87–92
Robinson TE, Berridge KC (2003) Addiction. Annu Rev Psychol 54:25–53
Rosenfeld GC, Burks TF (1977) Single-dose tolerance to morphine hypothermia in the rat: differentiation of acute from long-term tolerance. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 202:654–659
Rothwell PE, Thomas MJ, Gewirtz JC (2009) Distinct profiles of anxiety and dysphoria during spontaneous withdrawal from acute morphine exposure. Neuropsychopharmacology 34:2285–2295
Rothwell PE, Gewirtz JC, Thomas MJ (2010) Episodic withdrawal promotes psychomotor sensitization to morphine. Neuropsychopharmacology 35:2579–2589
Rylkova D, Shah HP, Small E, Bruijnzeel AW (2009) Deficit in brain reward function and acute and protracted anxiety-like behavior after discontinuation of a chronic alcohol liquid diet in rats. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 203:629–640
Saal D, Dong Y, Bonci A, Malenka RC (2003) Drugs of abuse and stress trigger a common synaptic adaptation in dopamine neurons. Neuron 37:577–582
Sadee W, Wang D, Bilsky EJ (2005) Basal opioid receptor activity, neutral antagonists, and therapeutic opportunities. Life Sci 76:1427–1437
Sahuque LL, Kullberg EF, McGeehan AJ, Kinder JR, Hicks MP, Blanton MG, Janak PH, Olive MF (2006) Anxiogenic and aversive effects of corticotropin-releasing factor (CRF) in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis in the rat: role of CRF receptor subtypes. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 186:122–132
Satel SL, Kosten TR, Schuckit MA, Fischman MW (1993) Should protracted withdrawal from drugs be included in DSM-IV? Am J Psychiatry 150:695–704
Schulteis G, Markou A, Gold LH, Stinus L, Koob GF (1994) Relative sensitivity to naloxone of multiple indices of opiate withdrawal: a quantitative dose-response analysis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 271:1391–1398
See RE, Waters RP (2010) Pharmacologically-induced stress: a cross-species probe for translational research in drug addiction and relapse. Am J Transl Res 3:81–89
Shoblock JR, Maidment NT (2006) Constitutively active micro opioid receptors mediate the enhanced conditioned aversive effect of naloxone in morphine-dependent mice. Neuropsychopharmacology 31:171–177
Shoblock JR, Maidment NT (2007) Enkephalin release promotes homeostatic increases in constitutively active mu opioid receptors during morphine withdrawal. Neuroscience 149:642–649
Smith RJ, Aston-Jones G (2008) Noradrenergic transmission in the extended amygdala: role in increased drug-seeking and relapse during protracted drug abstinence. Brain Struct Funct 213:43–61
Stine SM, Grillon CG, Morgan CA 3rd, Kosten TR, Charney DS, Krystal JH (2001) Methadone patients exhibit increased startle and cortisol response after intravenous yohimbine. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 154:274–281
Stine SM, Southwick SM, Petrakis IL, Kosten TR, Charney DS, Krystal JH (2002) Yohimbine-induced withdrawal and anxiety symptoms in opioid-dependent patients. Biol Psychiatry 51:642–651
Stinus L, Caille S, Koob GF (2000) Opiate withdrawal-induced place aversion lasts for up to 16 weeks. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 149:115–120
Tzschentke TM (1998) Measuring reward with the conditioned place preference paradigm: a comprehensive review of drug effects, recent progress and new issues. Prog Neurobiol 56:613–672
Tzschentke TM (2007) Measuring reward with the conditioned place preference (CPP) paradigm: update of the last decade. Addict Biol 12:227–462
Ungless MA, Whistler JL, Malenka RC, Bonci A (2001) Single cocaine exposure in vivo induces long-term potentiation in dopamine neurons. Nature 411:583–587
Valdez GR, Roberts AJ, Chan K, Davis H, Brennan M, Zorrilla EP, Koob GF (2002) Increased ethanol self-administration and anxiety-like behavior during acute ethanol withdrawal and protracted abstinence: regulation by corticotropin-releasing factor. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 26:1494–1501
Vanderschuren LJ, Schmidt ED, De Vries TJ, Van Moorsel CA, Tilders FJ, Schoffelmeer AN (1999) A single exposure to amphetamine is sufficient to induce long-term behavioral, neuroendocrine, and neurochemical sensitization in rats. J Neurosci 19:9579–9586
Vanderschuren LJ, De Vries TJ, Wardeh G, Hogenboom FA, Schoffelmeer AN (2001) A single exposure to morphine induces long-lasting behavioural and neurochemical sensitization in rats. Eur J Neurosci 14:1533–1538
Walker DL, Davis M (2002) Quantifying fear potentiated startle using absolute versus proportional increase scoring methods: implications for the neurocircuitry of fear and anxiety. Psychopharmacol (Berl) 164:318–328
White-Gbadebo D, Holtzman SG (1994) Acute sensitization to opioid antagonists. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 47:559–566
Zhang Z, Schulteis G (2008) Withdrawal from acute morphine dependence is accompanied by increased anxiety-like behavior in the elevated plus maze. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 89:392–403
Zhao Y, Weiss F, Zorrilla EP (2007) Remission and resurgence of anxiety-like behavior across protracted withdrawal stages in ethanol-dependent rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 31:1505–1515
Acknowledgments
We thank Kimberly Beach, Tory Schaaf, and Angela Walker for technical assistance, Gail Towers for diligent animal husbandry, and members of the Gewirtz and Thomas labs for stimulating discussions. This work was supported by funding from the University of Minnesota Graduate School and grants from the National Institute on Drug Abuse (DA023750 to PER and DA018784 to JCG).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rothwell, P.E., Thomas, M.J. & Gewirtz, J.C. Protracted manifestations of acute dependence after a single morphine exposure. Psychopharmacology 219, 991–998 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2425-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2425-y