Abstract
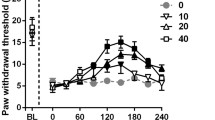
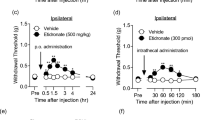
Some antiepileptic drugs are used clinically to relieve neuropathic pain. We have evaluated the effects and investigated the possible mechanisms of action of zonisamide, an antiepileptic drug, on thermal hyperalgesia and tactile allodynia in a murine chronic pain model that was prepared by partial ligation of the sciatic nerve. Subcutaneously administered zonisamide (10 and 30 mg/kg) produced antihyperalgesic and antiallodynic effects in a dose-dependent manner; these effects were manifested by elevation of the withdrawal threshold in response to a thermal (plantar test) or mechanical (von Frey) stimulus, respectively. Similar analgesic effects were obtained in both the plantar and von Frey tests when zonisamide was injected either intracerebroventricularly (i.c.v., 10 and 30 μg) or intrathecally (i.t., 10 and 30 μg). It is thought that this elevation of the thermal and mechanical withdrawal thresholds after local injection of zonisamide is not generated secondarily via impaired motor activity, since zonisamide (30 μg, i.c.v. or i.t.) did not affect locomotor activity, as assessed in sciatic-nerve-ligated mice. Moreover, the nitric oxide synthase inhibitor L-NAME, when injected either i.c.v. or i.t., potentiated the analgesic effects of zonisamide. In contrast, neither i.c.v. nor i.t. zonisamide produced antinociceptive effects against acute thermal and mechanical nociception in non-ligated mice. Together, following peripheral nerve injury, it appears that zonisamide produces centrally mediated antihyperalgesic and antiallodynic effects partly via the blockade of nitric oxide synthesis.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arner S, Meyerson BA (1988) Lack of analgesic effect of opioids on neuropathic and idiopathic forms of pain. Pain 33:11–23
Carlton SM, Zhou S (1998) Attenuation of formalin-induced nociceptive behaviors following local peripheral injection of gabapentin. Pain 76:201–207
Chaplan SR, Bach FW, Pogrel JW, Chung JM, Yaksh TL (1994) Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J Neurosci Methods 53:55–63
Dixon WJ (1980) Efficient analysis of experimental observations. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 20:441–462
Dogrul A, Gardell LR, Ossipov MH, Tulunay FC, Lai J, Porreca F (2003) Reversal of experimental neuropathic pain by T-type calcium channel blockers. Pain 105:159–168
Ferreira J, Santos AR, Calixto JB (1999) The role of systemic, spinal and supraspinal L-arginine-nitric oxide-cGMP pathway in thermal hyperalgesia caused by intrathecal injection of glutamate in mice. Neuropharmacology 38:835–842
Glantz SA (1992) Alternatives to analysis of variance and the t test based on ranks. In: Jeffers JD, Englis MR (eds) Primer of biostatistics, 3rd edn. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 320–371
Hains BC, Klein JP, Saab CY, Craner MJ, Black JA, Waxman SG (2003) Upregulation of sodium channel Nav1.3 and functional involvement in neuronal hyperexcitability associated with central neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury. J Neurosci 23:8881–8892
Hains BC, Saab CY, Klein JP, Craner MJ, Waxman SG (2004) Altered sodium channel expression in second-order spinal sensory neurons contributes to pain after peripheral nerve injury. J Neurosci 24:4832–4839
Haley TJ, McCormick WG (1957) Pharmacological effects produced by intracerebral injection of drugs in the conscious mouse. Br J Pharmacol 12:12–15
Hargreaves K, Dubner R, Brown F, Flores C, Joris J (1988) A new and sensitive method for measuring thermal nociception in cutaneous hyperalgesia. Pain 32:77–88
Hord AH, Denson DD, Chalfoun AG, Azevedo MI (2003) The effect of systemic zonisamide (Zonegran) on thermal hyperalgesia and mechanical allodynia in rats with an experimental mononeuropathy. Anesth Analg 96:1700–1706
Hylden JL, Wilcox GL (1980) Intrathecal morphine in mice: a new technique. Eur J Pharmacol 67:313–316
Ikeda H, Heinke B, Ruscheweyh R, Sandkühler J (2003) Synaptic plasticity in spinal lamina I projection neurons that mediate hyperalgesia. Science 299:1237–1240
Inoue T, Mashimo T, Shibata M, Shibuta S, Yoshiya I (1998) Rapid development of nitric oxide-induced hyperalgesia depends on an alternate to the cGMP-mediated pathway in the rat neuropathic pain model. Brain Res 792:263–270
Kim HK, Park SK, Zhou JL, Taglialatela G, Chung K, Coggeshall RE, Chung JM (2004) Reactive oxygen species (ROS) play an important role in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Pain 111:116–124
Mabuchi T, Matsumura S, Okuda-Ashitaka E, Kitano T, Kojima H, Nagano T, Minami T, Ito S (2003) Attenuation of neuropathic pain by the nociceptin/orphanin FQ antagonist JTC-801 is mediated by inhibition of nitric oxide production. Eur J Neurosci 17:1384–1392
Masuda Y, Utsui Y, Shiraishi Y, Karasawa T, Yoshida K, Shimizu M (1979) Relationships between plasma concentrations of diphenylhydantoin, phenobarbital, carbamazepine, and 3-sulfamoylmethyl-1,2-benzisoxazole (AD-810), a new anticonvulsant agent, and their anticonvulsant or neurotoxic effects in experimental animals. Epilepsia 2:623–633
Masuda Y, Ishizaki M, Shimizu M (1998) Zonisamide: Pharmacology and clinical efficacy in epilepsy. CNS Drug Rev 4:341–360
Matthews EA, Dickenson AH (2001) Effects of ethosuximide, a T-type Ca2+ channel blocker, on dorsal horn neuronal responses in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 415:141–149
Mori A, Noda Y, Packer L (1998) The anticonvulsant zonisamide scavenges free radicals. Epilepsy Res 30:153–158
Munger BL, Bennett GJ, Kajander KC (1992) An experimental painful peripheral neuropathy due to nerve constriction. I. Axonal pathology in the sciatic nerve. Exp Neurol 118:204–214
Muscoli C, Mollace V, Wheatley J, Masini E, Ndengele M, Wang ZQ, Salvemini D (2004) Superoxide-mediated nitration of spinal manganese superoxide dismutase: a novel pathway in N-methyl-d-aspartate-mediated hyperalgesia. Pain 111:96–103
Nagatani Y, Tanabe M, Honda M, Ono H (2005) Both spinal nitric oxide-cGMP pathway and free radicals mediate maintenance of neuropathic pain in mice. J Pharmacol Sci 97[Suppl]:204P
Noda Y, Mori A, Packer L (1999) Zonisamide inhibits nitric oxide synthase activity induced by N-methyl-d-aspartate and buthionine sulfoximine in the rat hippocampus. Res Commun Mol Pathol Pharmacol 105:23–33
Pappagallo M (2003) Newer antiepileptic drugs: possible uses in the treatment of neuropathic pain and migraine. Clin Ther 25:2506–2538
Ruscheweyh R, Sandkühler J (2003) Epileptiform activity in rat spinal dorsal horn in vitro has common features with neuropathic pain. Pain 105:327–338
Sakaue A, Honda M, Tanabe M, Ono H (2003) Antiepileptic drug zonisamide is effective in the neuropathic pain model in mice. J Pharmacol Sci 91[Suppl]:105P
Sakaue A, Honda M, Tanabe M, Ono H (2004) Antinociceptive effects of sodium channel-blocking agents on acute pain in mice. J Pharmacol Sci 95:181–188
Seltzer Z, Dubner R, Shir Y (1990) A novel behavioral model of neuropathic pain disorders produced in rats by partial sciatic nerve injury. Pain 43:205–218
Suzuki S, Kawakami K, Nishimura S, Watanabe Y, Yagi K, Seino M, Miyamoto K (1992) Zonisamide blocks T-type calcium channel in cultured neurons of rat cerebral cortex. Epilepsy Res 12:21–27
Tanabe M, Takasu K, Kasuya N, Shimizu S, Honda M, Ono H (2005) Role of descending noradrenergic system and spinal α2-adrenergic receptors in the effects of gabapentin on thermal and mechanical nociception after partial nerve injury in the mouse. Br J Pharmacol 144:703–714
Tao F, Tao YX, Mao P, Zhao C, Li D, Liaw WJ, Raja SN, Johns RA (2003) Intact carrageenan-induced thermal hyperalgesia in mice lacking inducible nitric oxide synthase. Neuroscience 120:847–854
Tao F, Tao YX, Zhao C, Dore S, Liaw WJ, Raja SN, Johns RA (2004) Differential roles of neuronal and endothelial nitric oxide synthases during carrageenan-induced inflammatory hyperalgesia. Neuroscience 128:421–430
Tegeder I, Del Turco D, Schmidtko A, Sausbier M, Feil R, Hofmann F, Deller T, Ruth P, Geisslinger G (2004) Reduced inflammatory hyperalgesia with preservation of acute thermal nociception in mice lacking cGMP-dependent protein kinase I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:3253–3257
Todorovic SM, Rastogi AJ, Jevtovic-Todorovic V (2003) Potent analgesic effects of anticonvulsants on peripheral thermal nociception in rats. Br J Pharmacol 140:255–260
Urban MO, Gebhart GF (1999) Supraspinal contributions to hyperalgesia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:7687–7692
Yang L, Zhang FX, Huang F, Lu YJ, Li GD, Bao L, Xiao HS, Zhang X (2004) Peripheral nerve injury induces trans-synaptic modification of channels, receptors and signal pathways in rat dorsal spinal cord. Eur J Neurosci 19:871–883
Acknowledgements
We thank Dainippon Pharmaceutical for the kind gift of zonisamide.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanabe, M., Sakaue, A., Takasu, K. et al. Centrally mediated antihyperalgesic and antiallodynic effects of zonisamide following partial nerve injury in the mouse. Naunyn Schmied Arch Pharmacol 372, 107–114 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-005-0006-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-005-0006-5