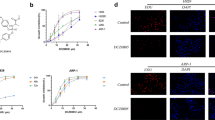
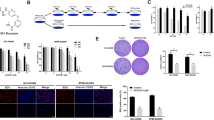
Abstract
NVP-BKM120 is a novel phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor and is currently being investigated in phase I clinical trials in solid tumors. This study aimed to evaluate the therapeutic efficacy of BKM120 in multiple myeloma (MM). BKM120 induces cell growth inhibition and apoptosis in both MM cell lines and freshly isolated primary MM cells. However, BKM120 only shows limited cytotoxicity toward normal lymphocytes. The presence of MM bone marrow stromal cells, insulin-like growth factor, or interleukin-6 does not affect BKM120-induced tumor cell apoptosis. More importantly, BKM120 treatment significantly inhibits tumor growth in vivo and prolongs the survival of myeloma-bearing mice. In addition, BKM120 shows synergistic cytotoxicity with dexamethasone in dexamethasone-sensitive MM cells. Low doses of BKM120 and dexamethasone, each of which alone has limited cytotoxicity, induce significant cell apoptosis in MM.1S and ARP-1. Mechanistic study shows that BKM120 exposure causes cell cycle arrest by upregulating p27 (Kip1) and downregulating cyclin D1 and induces caspase-dependent apoptosis by downregulating antiapoptotic XIAP and upregulating expression of cytotoxic small isoform of Bim, BimS. In summary, our findings demonstrate the in vitro and in vivo anti-MM activity of BKM120 and suggest that BKM120 alone or together with other MM chemotherapeutics, particularly dexamethasone, may be a promising treatment for MM.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kyle RA, Rajkumar SV (2004) Multiple myeloma. N Engl J Med 351:1860–1873
Jagannath S, Kyle RA, Palumbo A, Siegel DS, Cunningham S, Berenson J (2010) The current status and future of multiple myeloma in the clinic. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk 10: 28–43
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J, Thun MJ (2009) Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin 59:225–249
Di Paolo G, De Camilli P (2006) Phosphoinositides in cell regulation and membrane dynamics. Nature 443:651–657
Engelman JA, Luo J, Cantley LC (2006) The evolution of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases as regulators of growth and metabolism. Nat Rev Genet 7:606–619
Engelman JA (2009) Targeting PI3K signalling in cancer: opportunities, challenges and limitations. Nat Rev Cancer 9:550–562
Younes H, Leleu X, Hatjiharissi E, Moreau AS, Hideshima T, Richardson P, Anderson KC, Ghobrial IM (2007) Targeting the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway in multiple myeloma. Clin Cancer Res 13:3771–3775
Hideshima T, Nakamura N, Chauhan D, Anderson KC (2001) Biologic sequelae of interleukin-6 induced PI3-K/Akt signaling in multiple myeloma. Oncogene 20:5991–6000
Descamps G, Pellat-Deceunynck C, Szpak Y, Bataille R, Robillard N, Amiot M (2004) The magnitude of Akt/phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase proliferating signaling is related to CD45 expression in human myeloma cells. J Immunol 173:4953–4959
Harvey RD, Lonial S (2007) PI3 kinase/AKT pathway as a therapeutic target in multiple myeloma. Future Oncol 3:639–647
Salphati L, Pang J, Plise EG, Chou B, Halladay JS, Olivero AG, Rudewicz PJ, Tian Q, Wong S, Zhang X (2011) Preclinical pharmacokinetics of the novel PI3K inhibitor GDC-0941 and prediction of its pharmacokinetics and efficacy in human. Xenobiotica 41:1088–1099
Lannutti BJ, Meadows SA, Herman SE, Kashishian A, Steiner B, Johnson AJ, Byrd JC, Tyner JW, Loriaux MM, Deininger M, et al. (2011) CAL-101, a p110delta selective phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase inhibitor for the treatment of B-cell malignancies, inhibits PI3K signaling and cellular viability. Blood 117:591–594
Zheng Y, Cai Z, Wang S, Zhang X, Qian J, Hong S, Li H, Wang M, Yang J, Yi Q (2009) Macrophages are an abundant component of myeloma microenvironment and protect myeloma cells from chemotherapy drug-induced apoptosis. Blood 114:3625–3628
Zhao L, Wientjes MG, Au JL (2004) Evaluation of combination chemotherapy: integration of nonlinear regression, curve shift, isobologram, and combination index analyses. Clin Cancer Res 10:7994–8004
Lee JJ, Kong M, Ayers GD, Lotan R (2007) Interaction index and different methods for determining drug interaction in combination therapy. J Biopharm Stat 17:461–480
Tai YT, Dillon M, Song W, Leiba M, Li XF, Burger P, Lee AI, Podar K, Hideshima T, Rice AG et al (2008) Anti-CS1 humanized monoclonal antibody HuLuc63 inhibits myeloma cell adhesion and induces antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity in the bone marrow milieu. Blood 112:1329–1337
Gado K, Domjan G, Hegyesi H, Falus A (2000) Role of interleukin-6 in the pathogenesis of multiple myeloma. Cell Biol Int 24:195–209
Frassanito MA, Cusmai A, Iodice G, Dammacco F (2001) Autocrine interleukin-6 production and highly malignant multiple myeloma: relation with resistance to drug-induced apoptosis. Blood 97:483–489
Shi Y, Yan H, Frost P, Gera J, Lichtenstein A (2005) Mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors activate the AKT kinase in multiple myeloma cells by up-regulating the insulin-like growth factor receptor/insulin receptor substrate-1/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase cascade. Mol Cancer Ther 4:1533–1540
Mitsiades CS, McMillin DW, Klippel S, Hideshima T, Chauhan D, Richardson PG, Munshi NC, Anderson KC (2007) The role of the bone marrow microenvironment in the pathophysiology of myeloma and its significance in the development of more effective therapies. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 21:1007–1034, vii-viii
O'Connor L, Strasser A, O'Reilly LA, Hausmann G, Adams JM, Cory S, Huang DC (1998) Bim: a novel member of the Bcl-2 family that promotes apoptosis. EMBO J 17:384–395
Weber A, Paschen SA, Heger K, Wilfling F, Frankenberg T, Bauerschmitt H, Seiffert BM, Kirschnek S, Wagner H, Hacker G (2007) BimS-induced apoptosis requires mitochondrial localization but not interaction with anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins. J Cell Biol 177:625–636
Dijkers PF, Medema RH, Lammers JW, Koenderman L, Coffer PJ (2000) Expression of the pro-apoptotic Bcl-2 family member Bim is regulated by the forkhead transcription factor FKHR-L1. Curr Biol 10:1201–1204
Deveraux QL, Roy N, Stennicke HR, Van Arsdale T, Zhou Q, Srinivasula SM, Alnemri ES, Salvesen GS, Reed JC (1998) IAPs block apoptotic events induced by caspase-8 and cytochrome c by direct inhibition of distinct caspases. EMBO J 17:2215–2223
Minn AJ, Kettlun CS, Liang H, Kelekar A, Vander Heiden MG, Chang BS, Fesik SW, Fill M, Thompson CB (1999) Bcl-xL regulates apoptosis by heterodimerization-dependent and -independent mechanisms. EMBO J 18:632–643
Yang J, Qian J, Wezeman M, Wang S, Lin P, Wang M, Yaccoby S, Kwak LW, Barlogie B, Yi Q (2006) Targeting beta2-microglobulin for induction of tumor apoptosis in human hematological malignancies. Cancer Cell 10:295–307
Dalton WS (2002) Drug resistance and drug development in multiple myeloma. Semin Oncol 29:21–25
Kastritis E, Palumbo A, Dimopoulos MA (2009) Treatment of relapsed/refractory multiple myeloma. Semin Hematol 46:143–157
Ludwig H, Beksac M, Blade J, Boccadoro M, Cavenagh J, Cavo M, Dimopoulos M, Drach J, Einsele H, Facon T, et al. (2010) Current multiple myeloma treatment strategies with novel agents: a European perspective. Oncologist 15:6–25
Kumar SK, Rajkumar SV, Dispenzieri A, Lacy MQ, Hayman SR, Buadi FK, Zeldenrust SR, Dingli D, Russell SJ, Lust JA et al (2008) Improved survival in multiple myeloma and the impact of novel therapies. Blood 111:2516–2520
Pene F, Claessens YE, Muller O, Viguie F, Mayeux P, Dreyfus F, Lacombe C, Bouscary D (2002) Role of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt and mTOR/P70S6-kinase pathways in the proliferation and apoptosis in multiple myeloma. Oncogene 21:6587–6597
Mitsiades CS, Mitsiades NS, McMullan CJ, Poulaki V, Shringarpure R, Akiyama M, Hideshima T, Chauhan D, Joseph M, Libermann TA et al (2004) Inhibition of the insulin-like growth factor receptor-1 tyrosine kinase activity as a therapeutic strategy for multiple myeloma, other hematologic malignancies, and solid tumors. Cancer Cell 5:221–230
O'Reilly KE, Rojo F, She QB, Solit D, Mills GB, Smith D, Lane H, Hofmann F, Hicklin DJ, Ludwig DL et al (2006) mTOR inhibition induces upstream receptor tyrosine kinase signaling and activates Akt. Cancer Res 66:1500–1508
McMillin DW, Ooi M, Delmore J, Negri J, Hayden P, Mitsiades N, Jakubikova J, Maira SM, Garcia-Echeverria C, Schlossman R et al (2009) Antimyeloma activity of the orally bioavailable dual phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor NVP-BEZ235. Cancer Res 69:5835–5842
Cirstea D, Hideshima T, Rodig S, Santo L, Pozzi S, Vallet S, Ikeda H, Perrone G, Gorgun G, Patel K et al (2010) Dual inhibition of akt/mammalian target of rapamycin pathway by nanoparticle albumin-bound-rapamycin and perifosine induces antitumor activity in multiple myeloma. Mol Cancer Ther 9:963–975
Acknowledgments
We thank our Departmental Myeloma Tissue Bank for patient samples and Alison Woo for providing editorial assistance.
Grant support
This work was supported by the National Cancer Institute R01 CA138402, R01 CA138398, and P50 CA142509, the Leukemia and Lymphoma Society Translational Research Grants, Multiple Myeloma Research Foundation, Commonwealth Foundation for Cancer Research, and the Center for Targeted Therapy of The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 274 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, Y., Yang, J., Qian, J. et al. Novel phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase inhibitor NVP-BKM120 induces apoptosis in myeloma cells and shows synergistic anti-myeloma activity with dexamethasone. J Mol Med 90, 695–706 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-011-0849-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-011-0849-9