Abstract
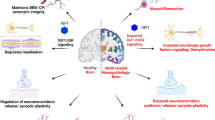
Disturbed trophic support to neurons has long been considered a potential mechanism in neurodegeneration. Recent evidence indicates that intracellular trophic signaling may be compromised in several neurodegenerative diseases. Changes in the levels of insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I), a trophic hormone with multiple neuroprotective actions, have recently been observed in several human neurodegenerative illnesses. Therefore analysis of IGF-I pathways could help provide greater insight into trophic disturbances to neurons. However, neurodegenerative diseases with similar clinical manifestations show either high or low levels of circulating IGF-I. This apparently puzzling observation can be explained if we consider that IGF-I input to target neurons is disrupted by either lower IGF-I availability or by reduced cell sensitivity to IGF-I. The latter disturbance may be associated with high IGF-I levels. We hypothesize that in the majority of neurodegenerative diseases compromised IGF-I support to neurons emerges as part of the pathological cascade during the degenerative process and contributes to neuronal demise. In addition, loss of IGF-I input to specific neuronal populations might be the cause of a small group of neurodegenerative diseases.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AT :
-
Ataxia-telangectasia
- Aβ :
-
Amyloid-β
- IGF :
-
Insulin-like growth factor
- IGFBP :
-
Insulin-like growth factors binding protein
- IRS :
-
Insulin receptor substrate protein
- LID :
-
Liver IGF-1 deficiency
- SCA :
-
Spinocerebellar ataxia
- TNF :
-
Tumor necrosis factor
References
Dudek H, Datta SR, Franke TF, Birnbaum MJ, Yao R, Cooper GM, Segal RA, Kaplan DR, Greenberg ME (1997) Regulation of neuronal survival by the serine-threonine protein kinase Akt. Science 275:661–665
Dore S, Kar S, Quirion R (1997) Rediscovering an old friend, IGF-I: potential use in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Trends Neurosci 20:326–331
Gasparini L, Netzer WJ, Greengard P, Xu H (2002) Does insulin dysfunction play a role in Alzheimer’s disease? Trends Pharmacol Sci 23:288–293
Pierce SB, Costa M, Wisotzkey R, Devadhar S, Homburger SA, Buchman AR, Ferguson KC, Heller J, Platt DM, Pasquinelli AA, Liu LX, Doberstein SK, Ruvkun G (2001) Regulation of DAF-2 receptor signaling by human insulin and ins-1, a member of the unusually large and diverse C. elegans insulin gene family. Genes Dev 15:672–686
Peruzzi F, Prisco M, Dews M, Salomoni P, Grassilli E, Romano G, Calabretta B, Baserga R (1999) Multiple signaling pathways of the insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor in protection from apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol 19:7203–7215
Bondy CA, Cheng CM (2002) Insulin-like growth factor-1 promotes neuronal glucose utilization during brain development and repair processes. Int Rev Neurobiol 51:189–217
Carro E, Nunez A, Busiguina S, Torres-Aleman I (2000) Circulating insulin-like growth factor I mediates effects of exercise on the brain. J Neurosci 20:2926–2933
Carro E, Trejo JL, Nuñez A, Torres-Aleman I (2003) Brain repair and neuroprotection by serum insulin-like growth factor I. Mol Neurobiol 27:153–162
Hellstrom A, Carlsson B, Niklasson A, Segnestam K, Boguszewski M, de Lacerda L, Savage M, Svensson E, Smith L, Weinberger D, Albertsson WK, Laron Z (2002) IGF-I is critical for normal vascularization of the human retina. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87:3413–3416
Carro E, Trejo JL, Gomez-Isla T, LeRoith D, Torres-Aleman I (2002) Serum insulin-like growth factor I regulates brain amyloid-beta levels. Nat Med 8:1390–1397
Castro-Alamancos MA, Torres-Aleman I (1993) Long-term depression of glutamate-induced gamma-aminobutyric acid release in cerebellum by insulin-like growth factor I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 90:7386–7390
Nunez A, Carro E, Torres-Aleman I (2003) Insulin-like growth factor I modifies electrophysiological properties of rat brain stem neurons. J Neurophysiol 89:3008–3017
Jones JI, Clemmons DR (1995) Insulin-like growth factors and their binding proteins: biological actions. Endocr Rev 16:3–34
Firth SM, Baxter RC (2002) Cellular actions of the insulin-like growth factor binding proteins. Endocr Rev 23:824–854
Hernandez-Sanchez C, Blakesley V, Kalebic T, Helman L, LeRoith D (1995) The role of the tyrosine kinase domain of the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor in intracellular signaling, cellular proliferation, and tumorigenesis. J Biol Chem 270:29176–29181
Greene MW, Garofalo RS (2002) Positive and negative regulatory role of insulin receptor substrate 1 and 2 (IRS-1 and IRS-2) serine/threonine phosphorylation. Biochemistry 41:7082–7091
Aguirre V, Werner ED, Giraud J, Lee YH, Shoelson SE, White MF (2002) Phosphorylation of Ser307 in insulin receptor substrate-1 blocks interactions with the insulin receptor and inhibits insulin action. J Biol Chem 277:1531–1537
Burgaud JL, Baserga R (1996) Intracellular transactivation of the insulin-like growth factor I receptor by an epidermal growth factor receptor. Exp Cell Res 223:412–419
Busiguina S, Fernandez AM, Barrios V, Clark R, Tolbert DL, Berciano J, Torres-Aleman I (2000) Neurodegeneration is associated to changes in serum insulin-like growth factors. Neurobiol Dis 7:657–665
Chen HK, Fernandez-Funez P, Acevedo SF, Lam YC, Kaytor MD, Fernandez MH, Aitken A, Skoulakis EM, Orr HT, Botas J, Zoghbi HY (2003) Interaction of akt-phosphorylated ataxin-1 with 14-3-3 mediates neurodegeneration in spinocerebellar ataxia type 1. Cell 113:457–468
Humbert S, Bryson EA, Cordelieres FP, Connors NC, Datta SR, Finkbeiner S, Greenberg ME, Saudou F (2002) The IGF-1/Akt pathway is neuroprotective in Huntington’s disease and involves Huntingtin phosphorylation by Akt. Dev Cell 2:831–837
D’Ercole AJ, Ye P, Calikoglu AS, Gutierrez-Ospina G (1996) The role of the insulin-like growth factors in the central nervous system. Mol Neurobiol 13:227–255
Yakar S, Liu JL, Stannard B, Butler A, Accili D, Sauer B, LeRoith D (1999) Normal growth and development in the absence of hepatic insulin-like growth factor I. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:7324–7329
Torres-Aleman I (1999) Insulin-like growth factors as mediators of functional plasticity in the adult brain. Horm Metab Res 31:114–119
Wyss-Coray T, Mucke L (2002) Inflammation in neurodegenerative disease-a double-edged sword. Neuron 35:419
Venters HD, Tang Q, Liu Q, VanHoy RW, Dantzer R, Kelley KW (1999) A new mechanism of neurodegeneration: a proinflammatory cytokine inhibits receptor signaling by a survival peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:9879–9884
Ikonomidou C, Turski L (1995) Excitotoxicity and neurodegenerative diseases. Curr Opin Neurol 8:487–497
Garcia-Galloway E, Arango C, Pons S, Torres-Aleman I (2003) Glutamate excitotoxicity attenuates insulin-like growth factor I pro-survival signaling. Mol Cell Neurosci (in press)
Xie L, Helmerhorst E, Taddei K, Plewright B, Van Bronswijk W, Martins R (2002) Alzheimer’s beta-amyloid peptides compete for insulin binding to the insulin receptor. J Neurosci 22:RC221
Ullrich A, Gray A, Tam AW, Yang-Feng T, Tsubokawa M, Collins C, Henzel W, Le Bon T, Kathuria S, Chen E (1986) Insulin-like growth factor I receptor primary structure: comparison with insulin receptor suggests structural determinants that define functional specificity. EMBO J 5:2503–2512
Jain S, Golde DW, Bailey R, Geffner ME (1998) Insulin-like growth factor-I resistance. Endocr Rev 19:625–646
Schwartz M, Moalem G, Leibowitz-Amit R, Cohen IR (1999) Innate and adaptive immune responses can be beneficial for CNS repair. Trends Neurosci 22:295–299
Benbassat CA, Lazarus DD, Cichy SB, Evans TM, Moldawer LL, Lowry SF, Unterman TG (1999) Interleukin-1 alpha (IL-1 alpha) and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF alpha) regulate insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1 (IGFBP-1) levels and mRNA abundance in vivo and in vitro. Horm Metab Res 31:209–215
Fan J, Wojnar MM, Theodorakis M, Lang CH (1996) Regulation of insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I mRNA and peptide and IGF-binding proteins by interleukin-1. Am J Physiol 270:R621–R629
Lelbach A, Scharf JG, Ramadori G (2001) Regulation of insulin-like growth factor-I and of insulin-like growth factor binding protein-1, -3 and -4 in cocultures of rat hepatocytes and Kupffer cells by interleukin-6. J Hepatol 35:558–567
Heemskerk VH, Daemen MA, Buurman WA (1999) Insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1) and growth hormone (GH) in immunity and inflammation. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 10:5–14
Schmitd RE, Dorsey DA, Beaudet LN, Plurad SB, Parvin CA, Miller MS (1999) Insulin-like growth factor I reverses experimental diabetic autonomic neuropathy. Am J Pathol 155:1651–1660
Peretz S, Jensen R, Baserga R, Glazer PM (2001) ATM-dependent expression of the insulin-like growth factor-I receptor in a pathway regulating radiation response. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:1676–1681
Okamura-Oho Y, Miyashita T, Ohmi K, Yamada M (1999) Dentatorubral-pallidoluysian atrophy protein interacts through a proline-rich region near polyglutamine with the SH3 domain of an insulin receptor tyrosine kinase substrate. Hum Mol Genet 8:947–957
Ostlund P, Lindegren H, Pettersson C, Bedecs K (2001) Up-regulation of functionally impaired insulin-like growth factor-1 receptor in scrapie infected neuroblastoma cells. J Biol Chem 276:36110–36115
Bulleit RF, Cui H (1998) Methylmercury antagonizes the survival-promoting activity of insulin-like growth factor on developing cerebellar granule neurons. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 153:161–168
Hallak H, Seiler AE, Green JS, Henderson A, Ross BN, Rubin R (2001) Inhibition of insulin-like growth factor-I signaling by ethanol in neuronal cells. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 25:1058–1064
Wilczak N, de Vos RA, De Keyser J (2003) Free insulin-like growth factor (IGF)-I and IGF binding proteins 2:5, and 6 in spinal motor neurons in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Lancet 361:1007–1011
Barrett TG, Bundey SE, Macleod AF (1995) Neurodegeneration and diabetes: UK nationwide study of Wolfram (DIDMOAD) syndrome. Lancet 346:1458–1463
Ristow M, Giannakidou E, Hebinck J, Busch K, Vorgerd M, Kotzka J, Knebel B, Mueller-Berghaus J, Epplen C, Pfeiffer A, Kahn CR, Doria A, Krone W, Mueller-Wieland D (1998) An association between NIDDM and a GAA trinucleotide repeat polymorphism in the X25/frataxin (Friedreich’s ataxia) gene. Diabetes 47:851–854
Wertman E, Zilber N, Abramsky O (1992) An association between multiple sclerosis and type I diabetes mellitus. J Neurol 239:43–45
Trejo JL, Carro E, Torres-Aleman I (2001) Circulating insulin-like growth factor I mediates exercise-induced increases in the number of new neurons in the adult hippocampus. J Neurosci 21:1628–1634
Mustafa A, Lannfelt L, Lilius L, Islam A, Winblad B, Adem A (1999) Decreased plasma insulin-like growth factor-I level in familial Alzheimer’s disease patients carrying the Swedish APP 670/671 mutation. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 10:446–451
Tham A, Nordberg A, Grissom FE, Carlsson-Skwirut C, Viitanen M, Sara VR (1993) Insulin-like growth factors and insulin-like growth factor binding proteins in cerebrospinal fluid and serum of patients with dementia of the Alzheimer type. J Neural Transm Park Dis Dement Sect 5:165–176
Schwab S, Spranger M, Krempien S, Hacke W, Bettendorf M (1997) Plasma insulin-like growth factor I and IGF binding protein 3 levels in patients with acute cerebral ischemic injury. Stroke 28:1744–1748
Torres-Aleman I, Barrios V, Lledo A, Berciano J (1996) The insulin-like growth factor I system in cerebellar degeneration. Ann Neurol 39:335–342
Torres-Aleman I, Barrios V, Berciano J (1998) The peripheral insulin-like growth factor system in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 50:772–776
Deutschle M, Blum WF, Strasburger CJ, Schweiger U, Weber B, Korner A, Standhardt H, Gotthardt U, Schmider J, Pflaum CD, Heuser I (1997) Insulin-like growth-factor-I (IGF-I) plasma concentrations are increased in depressed patients. Psychoneuroendocrinology 22:493–503
Huang TS, Wang YH, Lien IN (1995) Suppression of the hypothalamus-pituitary somatrope axis in men with spinal cord injuries. Metabolism 44:1116–1120
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Trejo, J.L., Carro, E., Garcia-Galloway, E. et al. Role of insulin-like growth factor I signaling in neurodegenerative diseases. J Mol Med 82, 156–162 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-003-0499-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-003-0499-7