Abstract
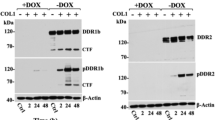
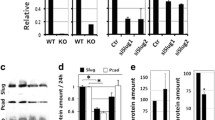
The non-receptor tyrosine kinase Syk is a well-characterized hematopoietic signal transducer, which is also expressed in non-hematopoietic cells. In epithelial cells, the function of Syk is not wholly known. It interacts with the receptor tyrosine kinase DDR1 and is frequently lost from metastatic mammary tumors. Here, using genetic tracing, we demonstrate Syk expression in murine mammary epithelium, myoepithelium and skin epithelium, but not in intestinal or lung epithelia. Investigating possible functions of Syk, we found a substantial suppression of cell mobility that depended on Syk kinase activity in trans-well migration and wounding assays. Co-expression of DDR1 resulted in constitutive interaction and strong activation of Syk kinase. Most importantly, Syk-mediated migration inhibition was blocked in the presence of DDR1, while conversely DDR1 knockdown restored migration inhibition. Our study identifies Syk as a potent inhibitor of epithelial migration and describes a first functional consequence of the interaction with the collagen receptor DDR1.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Comoglio PM, Trusolino L (2005) Cancer: the matrix is now in control. Nat Med 11:1156–1159
Sada K, Takano T, Yanagi S, Yamamura H (2001) Structure and function of Syk protein-tyrosine kinase. J Biochem 130:177–186
Fluck M, Zurcher G, Andres AC, Ziemiecki A (1995) Molecular characterization of the murine Syk protein tyrosine kinase cDNA, transcripts and protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 213:273–281
Coopman PJ, Mueller SC (2006) The Syk tyrosine kinase: a new negative regulator in tumor growth and progression. Cancer Lett 241:159–173
Mocsai A, Ruland J, Tybulewicz VL (2010) The SYK tyrosine kinase: a crucial player in diverse biological functions. Nat Rev Immunol 10:387–402
Moroni M, Soldatenkov V, Zhang L, Zhang Y, Stoica G, Gehan E, Rashidi B, Singh B, Ozdemirli M, Mueller SC (2004) Progressive loss of Syk and abnormal proliferation in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res 64:7346–7354
Yuan Y, Liu H, Sahin A, Dai JL (2005) Reactivation of SYK expression by inhibition of DNA methylation suppresses breast cancer cell invasiveness. Int J Cancer 113:654–659
Dejmek J, Leandersson K, Manjer J, Bjartell A, Emdin SO, Vogel WF, Landberg G, Andersson T (2005) Expression and signaling activity of Wnt-5a/discoidin domain receptor-1 and Syk plays distinct but decisive roles in breast cancer patient survival. Clin Cancer Res 11:520–528
Toyama T, Iwase H, Yamashita H, Hara Y, Omoto Y, Sugiura H, Zhang Z, Fujii Y (2003) Reduced expression of the Syk gene is correlated with poor prognosis in human breast cancer. Cancer Lett 189:97–102
Coopman PJ, Do MT, Barth M, Bowden ET, Hayes AJ, Basyuk E, Blancato JK, Vezza PR, McLeskey SW, Mangeat PH, Mueller SC (2000) The Syk tyrosine kinase suppresses malignant growth of human breast cancer cells. Nature 406:742–747
Li J, Sidell N (2005) Growth-related oncogene produced in human breast cancer cells and regulated by Syk protein-tyrosine kinase. Int JCancer 117:14–20
Wang L, Devarajan E, He J, Reddy SP, Dai JL (2005) Transcription repressor activity of spleen tyrosine kinase mediates breast tumor suppression. Cancer Res 65:10289–10297
Zyss D, Montcourrier P, Vidal B, Anguille C, Merezegue F, Sahuquet A, Mangeat PH, Coopman PJ (2005) The Syk tyrosine kinase localizes to the centrosomes and negatively affects mitotic progression. Cancer Res 65:10872–10880
Vogel W, Gish GD, Alves F, Pawson T (1997) The discoidin domain receptor tyrosine kinases are activated by collagen. Mol Cell 1:13–23
Di ME, Cutuli N, Guerra L, Cancedda R, De LM (1993) Molecular cloning of trkE, a novel trk-related putative tyrosine kinase receptor isolated from normal human keratinocytes and widely expressed by normal human tissues. J Biol Chem 268:24290–24295
Alves F, Vogel W, Mossie K, Millauer B, Hofler H, Ullrich A (1995) Distinct structural characteristics of discoidin I subfamily receptor tyrosine kinases and complementary expression in human cancer. Oncogene 10:609–618
Vogel WF, Abdulhussein R, Ford CE (2006) Sensing extracellular matrix: an update on discoidin domain receptor function. Cell Signal 18:1108–1116
Alves F, Saupe S, Ledwon M, Schaub F, Hiddemann W, Vogel WF (2001) Identification of two novel, kinase-deficient variants of discoidin domain receptor 1: differential expression in human colon cancer cell lines. FASEB J 15:1321–1323
Mullenbach E, Walter L, Dressel R (2006) A novel discoidin domain receptor 1 (Ddr1) transcript is expressed in postmeiotic germ cells of the rat testis depending on the major histocompatibility complex haplotype. Gene 372:53–61
Curat CA, Vogel WF (2002) Discoidin domain receptor 1 controls growth and adhesion of mesangial cells. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:2648–2656
Ongusaha PP, Kim JI, Fang L, Wong TW, Yancopoulos GD, Aaronson SA, Lee SW (2003) p53 induction and activation of DDR1 kinase counteract p53-mediated apoptosis and influence p53 regulation through a positive feedback loop. EMBO J 22:1289–1301
Hou G, Vogel W, Bendeck MP (2001) The discoidin domain receptor tyrosine kinase DDR1 in arterial wound repair. J Clin Invest 107:727–735
Kamohara H, Yamashiro S, Galligan C, Yoshimura T (2001) Discoidin domain receptor 1 isoform-a (DDR1alpha) promotes migration of leukocytes in three-dimensional collagen lattices. FASEB J 15:2724–2726
Yoshimura T, Matsuyama W, Kamohara H (2005) Discoidin domain receptor 1: a new class of receptor regulating leukocyte-collagen interaction. Immunol Res 31:219–230
Weiner HL, Huang H, Zagzag D, Boyce H, Lichtenbaum R, Ziff EB (2000) Consistent and selective expression of the discoidin domain receptor-1 tyrosine kinase in human brain tumors. Neurosurgery 47:1400–1409
Wang L, Duke L, Zhang PS, Arlinghaus RB, Symmans WF, Sahin A, Mendez R, Dai JL (2003) Alternative splicing disrupts a nuclear localization signal in spleen tyrosine kinase that is required for invasion suppression in breast cancer. Cancer Res 63:4724–4730
Gatalica Z, Bing Z (2005) Syk tyrosine kinase expression during multistep mammary carcinogenesis. Croat Med J 46:372–376
Ulanova M, Puttagunta L, Marcet-Palacios M, Duszyk M, Steinhoff U, Duta F, Kim MK, Indik ZK, Schreiber AD, Befus AD (2005) Syk tyrosine kinase participates in beta1-integrin signaling and inflammatory responses in airway epithelial cells. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 288:L497–L507
Nakashima H, Natsugoe S, Ishigami S, Okumura H, Matsumoto M, Hokita S, Aikou T (2006) Clinical significance of nuclear expression of spleen tyrosine kinase (Syk) in gastric cancer. Cancer Lett 236:89–94
Bohmer R, Neuhaus B, Buhren S, Zhang D, Stehling M, Bock B, Kiefer F (2010) Regulation of developmental lymphangiogenesis by Syk(+) leukocytes. Dev Cell 18:437–449
Srinivas S, Watanabe T, Lin CS, William CM, Tanabe Y, Jessell TM, Costantini F (2001) Cre reporter strains produced by targeted insertion of EYFP and ECFP into the ROSA26 locus. BMC Dev Biol 1:4
Saouaf SJ, Mahajan S, Rowley RB, Kut SA, Fargnoli J, Burkhardt AL, Tsukada S, Witte ON, Bolen JB (1994) Temporal differences in the activation of three classes of non-transmembrane protein tyrosine kinases following B-cell antigen receptor surface engagement. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:9524–9528
Luangdilok S, Box C, Patterson L, Court W, Harrington K, Pitkin L, Rhys-Evans P, Charoenrat P, Eccles S (2007) Syk tyrosine kinase is linked to cell motility and progression in squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck. Cancer Res 67:7907–7916
Mahabeleshwar GH, Kundu GC (2003) Syk, a protein-tyrosine kinase, suppresses the cell motility and nuclear factor kappa B-mediated secretion of urokinase type plasminogen activator by inhibiting the phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase activity in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 278:6209–6221
Zhang X, Shrikhande U, Alicie BM, Zhou Q, Geahlen RL (2009) Role of the protein tyrosine kinase Syk in regulating cell–cell adhesion and motility in breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res 7:634–644
Law DA, Nannizzi-Alaimo L, Ministri K, Hughes PE, Forsyth J, Turner M, Shattil SJ, Ginsberg MH, Tybulewicz VL, Phillips DR (1999) Genetic and pharmacological analyses of Syk function in alphaIIbbeta3 signaling in platelets. Blood 93:2645–2652
Inoue O, Suzuki-Inoue K, Dean WL, Frampton J, Watson SP (2003) Integrin alpha2beta1 mediates outside-in regulation of platelet spreading on collagen through activation of Src kinases and PLCgamma2. J Cell Biol 160:769–780
Larive RM, Urbach S, Poncet J, Jouin P, Mascre G, Sahuquet A, Mangeat PH, Coopman PJ, Bettache N (2009) Phosphoproteomic analysis of Syk kinase signaling in human cancer cells reveals its role in cell–cell adhesion. Oncogene 28:2337–2347
Singh A, Greninger P, Rhodes D, Koopman L, Violette S, Bardeesy N, Settleman J (2009) A gene expression signature associated with “K-Ras addiction” reveals regulators of EMT and tumor cell survival. Cancer Cell 15:489–500
Jonsson M, Andersson T (2001) Repression of Wnt-5a impairs DDR1 phosphorylation and modifies adhesion and migration of mammary cells. J Cell Sci 114:2043–2053
Hou G, Vogel WF, Bendeck MP (2002) Tyrosine kinase activity of discoidin domain receptor 1 is necessary for smooth muscle cell migration and matrix metalloproteinase expression. Circ Res 90:1147–1149
Katz E, Dubois-Marshall S, Sims AH, Faratian D, Li J, Smith ES, Quinn JA, Edward M, Meehan RR, Evans EE, Langdon SP, Harrison DJ (2010) A gene on the HER2 amplicon, C35, is an oncogene in breast cancer whose actions are prevented by inhibition of Syk. Br J Cancer 103:401–410
Evans EE, Henn AD, Jonason A, Paris MJ, Schiffhauer LM, Borrello MA, Smith ES, Sahasrabudhe DM, Zauderer M (2006) C35 (C17orf37) is a novel tumor biomarker abundantly expressed in breast cancer. Mol Cancer Ther 5:2919–2930
Katz E, Lareef MH, Rassa JC, Grande SM, King LB, Russo J, Ross SR, Monroe JG (2005) MMTV Env encodes an ITAM responsible for transformation of mammary epithelial cells in three-dimensional culture. J Exp Med 201:431–439
Grande SM, Katz E, Crowley JE, Bernardini MS, Ross SR, Monroe JG (2006) Cellular ITAM-containing proteins are oncoproteins in nonhematopoietic cells. Oncogene 25:2748–2757
Kiefer F, Tibbles LA, Anafi M, Janssen A, Zanke BW, Lassam N, Pawson T, Woodgett JR, Iscove NN (1996) HPK1, a hematopoietic protein kinase activating the SAPK/JNK pathway. EMBO J 15:7013–7025
Acknowledgments
This work was supported in part by grants from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (Ki492/2-1, SFB 629) and the Max Planck Society to F.K., the Fritz-Thyssen Stiftung für Wissenschaftsförderung to B.N. and from the National Cancer Institute of Canada and the Canada Research Chair Program to W.F.V.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
B. Neuhaus and S. Bühren contributed equally to this work.
Wolfgang F. Vogel (deceased on 5 December 2007).
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
18_2011_676_MOESM1_ESM.pdf
Suppl. Fig. 1. Syk is not expressed in murine epithelial cells of the intestinum or the airway epithelium of the lungs. To genetically trace Syk expression in murine epithelial cells of the intestinum or lung, cryosections of tissue samples derived from Syk-CreΔ/+ //R26R-YFP/YFP double transgenic mice were prepared and counterstained for YFP (Alexa 488, green) and E-cadherin (Alexa 568, red). (a–e) Syk promotor activity, indicated by YFP staining, was neither detected in the columnar epithelium of the intestinum (a–c) nor in the airway epithelium of the lungs (D + E). Syk-positive cells in the lacteal of the intestine (asterisk) and surrounding lung alveolar epithelium (arrowhead) served as positive controls (PDF 881 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Neuhaus, B., Bühren, S., Böck, B. et al. Migration inhibition of mammary epithelial cells by Syk is blocked in the presence of DDR1 receptors. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 68, 3757–3770 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-011-0676-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-011-0676-8