Abstract.
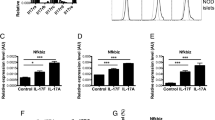
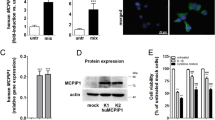
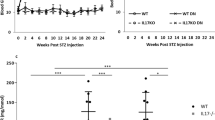
The influence of the proinflammatory cytokine interleukin (IL)-17 on inducible nitric oxide (NO) synthase (iNOS)-mediated NO release was investigated in the mouse insulinoma cell line MIN6 and mouse pancreatic islets. IL-17 markedly augmented iNOS mRNA/protein expression and subsequent NO production induced in MIN6 cells or pancreatic islets by different combinations of interferon-γ, tumor necrosis factor-α, and IL-1β. The induction of iNOS by IL-17 was preceded by phosphorylation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), and inhibition of p38 MAPK activation completely abolished IL-17-stimulated NO release. IL-17 enhanced the NO-dependent toxicity of proinflammatory cytokines toward MIN6 cells, while IL-17-specific neutralizing antibody partially reduced the NO production and rescued insulinoma cells and pancreatic islets from NO-dependent damage induced by activated T cells. Finally, a significant increase in blood IL-17 levels was observed in a multiple low-dose streptozotocin model of diabetes, suggesting that T cell-derived IL-17 might be involved in NO-dependent damage of beta cells in this disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 14 June 2005; received after revision 17 September 2005; accepted 21 September 2005
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miljkovic, D., Cvetkovic, I., Momcilovic, M. et al. Interleukin-17 stimulates inducible nitric oxide synthase-dependent toxicity in mouse beta cells. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 62, 2658 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-005-5259-0
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-005-5259-0