Abstract
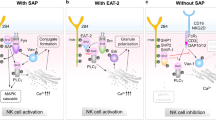
Signaling lymphocytic activation molecule (SLAM)-associated protein (SAP) is an adaptor molecule containing a Src homology 2 (SH2) domain. SAP is expressed in T cells and natural killer (NK) cells and binds to the cytoplasmic domains of SLAM family receptors, resulting in the subsequent recruitment of Fyn. The SAP (SH2D1A) gene is located on the X chromosome and is responsible for X-linked lymphoproliferative disease, characterized by higher susceptibility to Epstein-Barr virus infection. The SAP-mediated signal is not only essential for the development of NKT cells, i.e. unconventional CD1d-restricted T cells with invariant Vα14 T cell receptors, but also for the regulation of the function of NK cells and conventional T cells. The role of SAP-mediated signaling in the induction of autoimmune diseases has been analyzed using animal models such as lupus, hepatitis, and graft-versus-host disease and is considered important in their pathogenesis in humans. In this review we highlight the current findings on SAP-mediated signaling in hematopoietic cells and discuss its importance in autoimmune diseases and immunological disorders.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SLAM:
-
Signaling lymphocytic activation molecule
- SAP:
-
SLAM-associated protein
- XLP:
-
X-linked lymphoproliferative disease
- NK:
-
Natural killer
- EBV:
-
Epstein-Barr virus
- GVHD:
-
Graft-versus-host disease
- Ig:
-
Immunoglobulin
- ITSM:
-
Immunoreceptor tyrosine-based switching motif
- DC:
-
Dendritic cell
- SNP:
-
Single-nucleotide polymorphism
- SH2:
-
Src homology 2
- EAT-2:
-
Ewing’s sarcoma-activated transcript-2
- ERT:
-
EAT-2-related transducer
- AICD:
-
Activation-induced cell death
- MR-1:
-
MHC-related 1
- MAIT:
-
Mucosal-associated invariant T
- XIAP:
-
X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis
- SLE:
-
Systemic lupus erythematosus
- RA:
-
Rheumatoid arthritis
- FasL:
-
Fas ligand
- ConA:
-
Concanavalin A
- MHC:
-
Major histocompatibility complex
- mHC:
-
Minor histocompatibility complex
- BMT:
-
Bone marrow transplantation
References
Adachi M, Watanabe-Fukunaga R, Nagata S (1993) Aberrant transcription caused by the insertion of an early transposable element in an intron of the Fas antigen gene of lpr mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:1756–1760
Adams KM, Holmberg LA, Leisenring W et al (2004) Risk factors for syngeneic graft-versus-host disease after adult hematopoietic cell transplantation. Blood 104:1894–1897
Allen RD, Marshall JD, Roths JB et al (1990a) Bone marrow transplantation from mutant lpr/lpr mice. Functional abnormalities rather than alloantigenic differences appear to determine the development of a graft-vs.-host-like syndrome. Eur J Immunol 20:2057–2066
Allen RD, Marshall JD, Roths JB et al (1990b) Differences defined by bone marrow transplantation suggest that lpr and gld are mutations of genes encoding an interacting pair of molecules. J Exp Med 172:1367–1375
Anand S, Wang P, Yoshimura K et al (2006) Essential role of TNF family molecule LIGHT as a cytokine in the pathogenesis of hepatitis. J Clin Invest 116:1045–1051
Andrews BS, Eisenberg RA, Theofilopoulos AN et al (1978) Spontaneous murine lupus-like syndromes. Clinical and immunopathological manifestations in several strains. J Exp Med 148:1198–1215
Cannons J, Yu L, Hill B et al (2004) SAP regulates T(H)2 differentiation and PKC-theta-mediated activation of NF-kappaB1. Immunity 21:693–706
Chan AY, Westcott JM, Mooney JM et al (2006) The role of SAP and the SLAM family in autoimmunity. Curr Opin Immunol 18:656–664
Chen G, Tai AK, Lin M et al (2007) Increased proliferation of CD8+ T cells in SAP-deficient mice is associated with impaired activation-induced cell death. Eur J Immunol 37:663–674
Chu JL, Drappa J, Parnassa A et al (1993) The defect in Fas mRNA expression in MRL/lpr mice is associated with insertion of the retrotransposon, ETn. J Exp Med 178:723–730
Chu JL, Ramos P, Rosendorff A et al (1995) Massive upregulation of the Fas ligand in lpr and gld mice: implications for Fas regulation and the graft-versus-host disease-like wasting syndrome. J Exp Med 181:393–398
Crotty S, Kersh E, Cannons J et al (2003) SAP is required for generating long-term humoral immunity. Nature 421:282–287
Croxford JL, Miyake S, Huang YY et al (2006) Invariant V(alpha)19i T cells regulate autoimmune inflammation. Nat Immunol 7:987–994
Cunninghame Graham DS, Vyse TJ, Fortin PR et al (2008) Association of LY9 in UK and Canadian SLE families. Genes Immun 9:93–102
Czar M, Kersh E, Mijares L et al (2001) Altered lymphocyte responses and cytokine production in mice deficient in the X-linked lymphoproliferative disease gene SH2D1A/DSHP/SAP. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:7449–7454
Davidson WF, Dumont FJ, Bedigian HG et al (1986) Phenotypic, functional, and molecular genetic comparisons of the abnormal lymphoid cells of C3H-lpr/lpr and C3H-gld/gld mice. J Immunol 136:4075–4084
Diao H, Kon S, Iwabuchi K et al (2004) Osteopontin as a mediator of NKT cell function in T cell-mediated liver diseases. Immunity 21:539–550
Eberl G, Lowin-Kropf B, MacDonald H (1999) Cutting edge: NKT cell development is selectively impaired in Fyn- deficient mice. J Immunol 163:4091–4094
Engel P, Eck MJ, Terhorst C (2003) The SAP and SLAM families in immune responses and X-linked lymphoproliferative disease. Nat Rev Immunol 3:813–821
Fujiwara M, Kariyone A (1984) One-way occurrence of graft-versus-host disease in bone marrow chimaeras between congenic MRL mice. Immunology 53:251–256
Furukawa H, Ono M (2005) The polymorphisms and the expression patterns of the SLAM family receptor genes in the lupus prone mice. Clin Immunol Allergol 44:429–433
Furukawa H, Kitazawa H, Kaneko I et al (2009) Role of 2B4-mediated signals in the pathogenesis of a murine hepatitis model independent of Fas and Valpha14 NKT cells. Immunology 128(suppl 1):e151–e158
Glazier A, Tutschka PJ, Farmer ER et al (1983) Graft-versus-host disease in cyclosporin A-treated rats after syngeneic and autologous bone marrow reconstitution. J Exp Med 158:1–8
Hess AD, Horwitz L, Beschorner WE et al (1985) Development of graft-vs.-host disease-like syndrome in cyclosporine-treated rats after syngeneic bone marrow transplantation. I. Development of cytotoxic T lymphocytes with apparent polyclonal anti-Ia specificity, including autoreactivity. J Exp Med 161:718–730
Hron J, Caplan L, Gerth A et al (2004) SH2D1A regulates T-dependent humoral autoimmunity. J Exp Med 200:261–266
Isomaki P, Aversa G, Cocks B et al (1997) Increased expression of signaling lymphocytic activation molecule in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and its role in the regulation of cytokine production in rheumatoid synovium. J Immunol 159:2986–2993
Ito MR, Terasaki S, Itoh J et al (1997) Rheumatic diseases in an MRL strain of mice with a deficit in the functional Fas ligand. Arthritis Rheum 40:1054–1063
Jennings P, Chan A, Schwartzberg P et al (2008) Antigen-specific responses and ANA production in B6.Sle1b mice: a role for SAP. J Autoimmun 31:345–353
Jordan M, Fletcher J, Pellicci D et al (2007) Slamf1, the NKT cell control gene Nkt1. J Immunol 178:1618–1627
Kaneko Y, Harada M, Kawano T et al (2000) Augmentation of Valpha14 NKT cell-mediated cytotoxicity by interleukin 4 in an autocrine mechanism resulting in the development of concanavalin A-induced hepatitis. J Exp Med 191:105–114
Kawachi I, Maldonado J, Strader C et al (2006) MR1-restricted V alpha 19i mucosal-associated invariant T cells are innate T cells in the gut lamina propria that provide a rapid and diverse cytokine response. J Immunol 176:1618–1627
Komori H, Furukawa H, Mori S et al (2006) A signal adaptor SLAM-associated protein regulates spontaneous autoimmunity and Fas-dependent lymphoproliferation in MRL-Faslpr lupus mice. J Immunol 176:395–400
Kumar K, Li L, Yan M et al (2006) Regulation of B cell tolerance by the lupus susceptibility gene Ly108. Science 312:1665–1669
Latchman Y, McKay P, Reiser H (1998) Identification of the 2B4 molecule as a counter-receptor for CD48. J Immunol 161:5809–5812
Latif T, Pohlman B, Kalaycio M et al (2003) Syngeneic graft-versus-host disease: a report of two cases and literature review. Bone Marrow Transpl 32:535–539
Latour S, Veillette A (2003) Molecular and immunological basis of X-linked lymphoproliferative disease. Immunol Rev 192:212–224
Latour S, Roncagalli R, Chen R et al (2003) Binding of SAP SH2 domain to FynT SH3 domain reveals a novel mechanism of receptor signalling in immune regulation. Nat Cell Biol 5:149–154
Ma CS, Nichols KE, Tangye SG (2007) Regulation of cellular and humoral immune responses by the SLAM and SAP families of molecules. Annu Rev Immunol 25:337–379
Massaguer A, Perez-Del-Pulgar S, Engel P et al (2002) Concanavalin-A-induced liver injury is severely impaired in mice deficient in P-selectin. J Leukoc Biol 72:262–270
Matsuda JL, Gapin L (2005) Developmental program of mouse Valpha14i NKT cells. Curr Opin Immunol 17:122–130
Morra M, Lu J, Poy F et al (2001) Structural basis for the interaction of the free SH2 domain EAT-2 with SLAM receptors in hematopoietic cells. EMBO J 20:5840–5852
Mosbach-Ozmen L, Loor F (1987) Bone marrow transfers in X-irradiated mice congenic at the lpr locus: some paradoxical effects. Thymus 9:197–210
Nguyen C, Limaye N, Wakeland E (2002) Susceptibility genes in the pathogenesis of murine lupus. Arthritis Res 4:S255–S263
Nichols KE, Hom J, Gong SY et al (2005) Regulation of NKT cell development by SAP, the protein defective in XLP. Nat Med 11:340–345
Perkins DL, Michaelson J, Glaser RM et al (1987) Selective elimination of non-lpr lymphoid cells in mice undergoing lpr-mediated graft-vs-host disease. J Immunol 139:1406–1413
Piguet PF, Izui S, Janin-Mercier A et al (1987) Interstitial pneumonitis and hepatitis after transfer of bone marrow cells bearing the lpr gene to irradiated recipients: a disease due to large granular leucocytes? Scand J Immunol 26:603–610
Rigaud S, Fondaneche M, Lambert N et al (2006) XIAP deficiency in humans causes an X-linked lymphoproliferative syndrome. Nature 444:110–114
Roncagalli R, Taylor J, Zhang S et al (2005) Negative regulation of natural killer cell function by EAT-2, a SAP-related adaptor. Nat Immunol 6:1002–1010
Roths JB, Murphy ED, Eicher EM (1984) A new mutation, gld, that produces lymphoproliferation and autoimmunity in C3H/HeJ mice. J Exp Med 159:1–20
Sawada S, Takei M (2005) Epstein-Barr virus etiology in rheumatoid synovitis. Autoimmun Rev 4:106–110
Sayos J, Wu C, Morra M et al (1998) The X-linked lymphoproliferative-disease gene product SAP regulates signals induced through the co-receptor SLAM. Nature 395:462–469
Suzuki A, Yamada R, Kochi Y et al (2008) Functional SNPs in CD244 increase the risk of rheumatoid arthritis in a Japanese population. Nat Genet 40:1224–1229
Tagawa Y, Kakuta S, Iwakura Y (1998) Involvement of Fas/Fas ligand system-mediated apoptosis in the development of concanavalin A-induced hepatitis. Eur J Immunol 28:4105–4113
Takahashi T, Tanaka M, Brannan CI et al (1994) Generalized lymphoproliferative disease in mice, caused by a point mutation in the Fas ligand. Cell 76:969–976
Takahashi T, Yagi T, Kakinuma S et al (1997) Suppression of autoimmune disease and of massive lymphadenopathy in MRL/Mp-lpr/lpr mice lacking tyrosine kinase Fyn (p59fyn). J Immunol 159:2532–2541
Takeda K, Hayakawa Y, Van Kaer L et al (2000) Critical contribution of liver natural killer T cells to a murine model of hepatitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:5498–5503
Takei M, Ishiwata T, Mitamura K et al (2001) Decreased expression of signaling lymphocytic-activation molecule-associated protein (SAP) transcripts in T cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Int Immunol 13:559–565
Theofilopoulos AN, Balderas RS, Gozes Y et al (1985) Association of lpr gene with graft-vs.-host disease-like syndrome. J Exp Med 162:1–18
Tiegs G, Hentschel J, Wendel A (1992) A T cell-dependent experimental liver injury in mice inducible by concanavalin A. J Clin Invest 90:196–203
Toyabe S, Seki S, Iiai T et al (1997) Requirement of IL-4 and liver NK1+ T cells for concanavalin A-induced hepatic injury in mice. J Immunol 159:1537–1542
Vaux D, Silke J (2005) IAPs, RINGs and ubiquitylation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6:287–297
Veillette A (2006) Immune regulation by SLAM family receptors and SAP-related adaptors. Nat Rev Immunol 6:56–66
Veillette A, Dong Z, Latour S (2007) Consequence of the SLAM-SAP signaling pathway in innate-like and conventional lymphocytes. Immunity 27:698–710
Wandstrat A, Nguyen C, Limaye N et al (2004) Association of extensive polymorphisms in the SLAM/CD2 gene cluster with murine lupus. Immunity 21:769–780
Watanabe-Fukunaga R, Brannan CI, Copeland NG et al (1992) Lymphoproliferation disorder in mice explained by defects in Fas antigen that mediates apoptosis. Nature 356:314–317
Wu C, Nguyen K, Pien G et al (2001) SAP controls T cell responses to virus and terminal differentiation of TH2 cells. Nat Immunol 2:410–414
Yin L, Al-Alem U, Liang J et al (2003) Mice deficient in the X-linked lymphoproliferative disease gene sap exhibit increased susceptibility to murine gammaherpesvirus-68 and hypo-gammaglobulinemia. J Med Virol 71:446–455
Yu KO, Porcelli SA (2005) The diverse functions of CD1d-restricted NKT cells and their potential for immunotherapy. Immunol Lett 100:42–55
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Hiroyuki Nishimura (Wakayama Medical University) for fruitful discussions, Ms Fumiko Date, Dr. Izumi Kaneko, Mr. Koichi Kikuchi, Mr. Yuichi Kitagawa, Dr. Yusuke Okubo, Ms Naoko Shibata, Mr. Kaname Uchida, and Ms Naomi Yamaki (Tohoku University) for providing technical assistance for the study at Tohoku University, and Ms Noriko Fujisawa and Ms Emi Yura (Tohoku University) for secretarial assistance. The study at Tohoku University was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports, and Culture of Japan to Hiroshi Furukawa (no. 16790221) and Masao Ono (nos. 16390113, 19390108, and 19659096). This paper is dedicated to the memory of Dr. Hiroaki Komori.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Hiroaki Komori: deceased.
About this article
Cite this article
Furukawa, H., Tohma, S., Kitazawa, H. et al. Role of SLAM-Associated Protein in the Pathogenesis of Autoimmune Diseases and Immunological Disorders. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 58, 37–44 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00005-009-0060-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00005-009-0060-7