Abstract
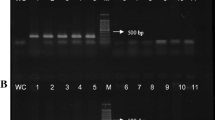
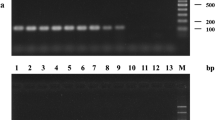
For rapid and sensitive detection of Xanthomonas fragariae, the causal agent of angular leaf spot of strawberry, a nested polymerase chain reaction (Pcr) was developed. A specific fragment was amplified from X fragariae Dna using primers 245A and 245B, described previously (Pooler et al. 1996). The fragment was sequenced and internal primers suitable for nested Pcr were selected. Using this internal pair of primers, a specific fragment was amplified from all of the 14 X. fragariae isolates tested but no fragment was amplified from X. campestris isolates or from unidentified bacteria, which were isolated from strawberry plants. Whereas detection limit of simple Pcr was 20 pg Dna per reaction, nested Pcr was up to a hundred times more sensitive and even from 200 fg Dna per reaction, a fragment was amplified. In addition, fragments amplified by nested Pcr were always clearly detectable on agarose gels, whereas fragments amplified by simple Pcr were only visible as faint bands when template concentrations decreased. Applicability of nested Pcr was tested on samples from naturally infected fields and from nursery plants showing no symptoms by visible inspection. In symptomatic plants, X. fragariae was regularly detected in leaves, especially in old leaves. In the crown, it was only occasionally detected. Simple Pcr was sufficient for confirmation of symptomatic infection and sometimes for detection of X. fragariae in symptomless parts of symptom-bearing plants and in latently infected nursery plants, respectively. However, using more sensitive nested Pcr, latent infections were more frequently detected and Pcr fragments were more clearly visible on agarose gels.
Zusammenfassung
Fur einen möglichst schnellen und sensitiven Nachweis von Xanthomonas fragariae, dem Erreger der Eckigen Blattfleckenkrankheit an Erdbeere, wurde eine verschachtelte Polymerase-Kettenreaktion (nested Pcr) entwickelt. Mit den Primern 245A und 245B (Pooler et al. 1996) wurde ein spezifisches Fragment von X. fragariae Dna amplifiziert. Das Fragment wurde sequenziert und innere Primer, die sich fur eine nested Pcr eignen, wurden ausgewahlt. Mit diesem inneren Primer-Paar wurde an allen 14 getesteten X. fragariae Isolaten ein spezifisches Fragment amplifiziert, an X. campestris Pathovaren und an weiteren nicht identifizierten Bakterien, die von Erdbeerpflanzen isoliert worden waren, wurde dagegen kein Fragment amplifiziert. Während die Nachweisgrenze der einfachen Pcr bei 20 pg Dna pro Pcr-Ansatz lag, wurde mit der neu entwickelten nested Pcr eine bis zu 100 x höhere Sensitivität erzielt und auch mit 200 fg Dna/Ansatz ein nachweisbares Fragment amplifiziert. Darüber hinaus war das Fragment, das mit der nested Pcr amplifiziert wurde stets deutlich auf dem Agarosegel sichtbar, während bei der einfachen Pcr die Bandenstärke des amplifizierten Fragments mit abnehmender Matritzen-Konzentration abnahm. Die Praxistauglichkeit der nested Pcr wurde an Proben aus natürlich befallenen Feldbeständen und an äußerlich gesund aussehenden Jungpflanzen geprüft. X. fragariae wurde regelmäßig in Blättern, insbesondere in älteren Blättern, nachgewiesen. Im Rhizom wurde das Bakterium nur gelegentlich nachgewiesen. Die einfache Pcr war für den Nachweis von Befallssymptomen ausreichend und teilweise wurde auch an symptomlosen Pflanzenteilen von Symptome aufweisenden Pflanzen bzw. an latent infizierten Jungpflanzen X. fragariae nachgewiesen. Mit der sensitiveren nested Pcr wurde latenter Befall häufiger nachgewiesen und die PCR Fragmente waren auf dem Agarosegel deutlicher sichtbar.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literature
Billen, W.: Die Eckige Blattfleckenkrankheit. — Eine neue Gefahr fur den Erdbeeranbau? — Obstbau, 20(2), 74–75, 1995.
Bonants, P., M. Hagenaar-De Weerdt, M. van Gent-Pelzer, I. Lacourt, D. Cooke, J. Duncan: Detection and identification of Phytophthora fragariae Hickman by the polymerase chain reaction. — Eur. J. Pl. Pathol. 103, 345–355, 1997.
Bultreys, A., A. Robbe, J.-C. van Schingen: Detection de Xanthomonas fragariae en culture de fraisier en Belgique. — Fruit Belge 68, 202–206, 2000.
CABI/EPPO: Xanthomonas fragariae. — Distribution maps of Quarantine Pests for Europe No. 284. Cab International, Wallingford, Uk, 1998
Civerolo, E. L., A. J. Feliciano, J. A. Melvin, W. D. Gubler: A detached strawberry leaf bioassay for Xanthomonas fragariae. — In: Proceedings 9th International Conference of Plant Pathogenic Bacteria, p. 89–94. Ed. Mahadevan A. University of Madras, India, 1997.
Epstein, A. H.: Angular leaf spot of strawberry. — Pl. Dis. Rep. 50, 167, 1966.
Fernandes, A. M. M., J. F. Pinto-Ganhao: Xanthomonas fragariae Kennedy & King, a bacteriosis new to Portugal. — Rev. Pl. Pathol. 63, 3469 (Abstract), 1984.
Giegerich, R., F. Meyer, C. Schleiermacher: GeneFischer — Software Support for the detection of postulated genes. — In: Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Intelligent Systems for Molecular Biology, Aaai Press, 1996.
Gillings, M. R., P. C. Fahy, J. Bradley: Identification of Xanthomonas fragariae, the cause of an outbreak of angular leaf spot on strawberry in South Australia, and comparison with the cause of previous outbreaks in New South Wales and New Zealand. — Australas. Pl. Path. 27, 97–103, 1998.
Grimm, R., T. Lips, J. Vogelsanger: Eckige Blattfleckenkrankheit der Erdbeere. — Schweiz. Z. Obst- Weinbau 129, 130–131, 1993.
Gurtler, V., V. A. Stanisich: New approaches to typing and identification of bacteria using the 16S- 23S rDna spacer region. — Microbiology 142, 3–16, 1996.
Hartung, J. S., M. R. Pooler: Immunocapture and multiplexed-Pcr assay for Xanthomonas fragariae, causal agent of angular leafspot disease. — Acta Hort. 439, 821–828, 1997.
Hartung, J. S., O. P. Pruvost, I. Villemot, A. Alvarez: Rapid and sensitive colorimetric detection of Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. citri by immunocapture and a nested-polymerase chain reaction assay. — Phytopathology 86, 95–101, 1996.
Hildebrand, D. C., M. N. Schroth, S. Wilhelm: Systemic invasion of strawberry by Xanthomonas fragariae causing vascular collapse. — Phytopathology 57, 1260–1261, 1967.
Kennedy, B. W., T. H. King: Angular leaf spot of strawberry caused by Xanthomonas fragariae sp. nov. — Phytopathology 52, 873–875, 1962.
Lee, I.-M., I. M. Bartoszyk, D. E. Gundersen, B. Mogen, R. E. Davis: Nested Pcr for ultrasensitive detection of the potato ring rot bacterium Clavibacter michiganensis subsp. sepedonicus. — Appl. Environ. Microb. 63, 2625–2630, 1997.
Lewers, K. S., J. L. Maas, S. C. Hokanson, C. Gouin, J. S. Hartung: Inheritance of resistance in strawberry to bacterial angular leafspot disease caused by Xanthomonas fragariae. — J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 128, 209–212, 2003.
Litterst, M.: Neue Krankheit im Erdbeeranbau. — Badische Bauernzeitung 49 (13), 28, 1996.
Lopez, M. M., J. M. Aramburu, M. Cambra, V. Borras: Deteccion e identificacion de Xanthomonas fragariae en Espana. — An. Inia/ Ser. Agric. 28, 245–259, 1985.
Maas, J. L.: Compendium of strawberry diseases. 2nd edition, Aps Press, St. Paul, Minnesota, Usa, 1998.
Maas, J. L., M. R. Pooler, G. J. Galletta: Bacterial angular leafspot disease of strawberry: present status and prospects for control. — Adv. Strawberry Res. 14, 18–24, 1995.
Maas, J. L., C. Gouin-Behe, J. S. Hartung, S. C. Hokanson: Sources of resistance for two differentially pathogenic strains of Xanthomonas fragariae in Fragaria genotypes. — HortScience 35, 128–131, 2000.
Mahuku, G. S., P. H. Goodwin: Presence of Xanthomonas fragariae in symptomless strawberry crowns in Ontario detected using a nested polymerase chain reaction (Pcr). — Can. J. Plant Pathol. 19, 366–370, 1997.
Mazzucchi, U., A. Alberghina, A. Dalli: Occurrence of Xanthomonas fragariae Kennedy & King in Italy. — Phytopathol. Z. 76, 367–370, 1973.
Moltmann, E.: Die Eckige Blattfleckenkrankheit (Xanthomonas fragariae) in Baden-Wurttemberg. — Phytomedizin 27(1), 56–57, 1997.
OEPP/EPPO: Eppo Data sheets on quarantine organisms No. 135. Xanthomonas fragariae Kennedy & King. — Bull. Oepp/Eppo Bull. 16, 17–20, 1986.
OEPP/EPPO: Phytosanitary procedure. Xanthomonas fragariae. Detection methods in strawberry plants. — Bull. Oepp/Eppo Bull. 24, 343–346, 1994.
OEPP/EPPO: Certification Scheme No. 11: Pathogen-tested strawberry. — Bull. Oepp/Eppo Bull. 24, 875–889, 1994.
Opgenorth, D. C., C. D. Smart, F. J. Louws, F. J. De Bruijn, B. C. Kirkpatrick: Identification of Xanthomonas fragariae field isolates by rep-Pcr genomic fingerprinting. — Pl. Dis. 80, 868–873, 1996.
Panagopoulos, C. G., P. G. Psallidas, A. S. Alivizatos: A bacterial leafspot of strawberry in Greece caused by Xanthomonas fragariae. — Phytopathol. Z. 91, 33–38, 1978.
Pooler, M. R., D. F. Ritchie, J. S. Hartung: Genetic relationships among strains of Xanthomonas fragariae based on random amplified polymorphic Dna Pcr, repetitive extragenic palindromic Pcr, and enterobacterial repetitive intergenic consensus Pcr data and generation of multiplexed Pcr primers useful for the identification of this phytopathogen. — Appl. Environ. Microb. 62, 3121–3127, 1996.
Poussier, S., J. Luisetti: Specific detection of biovars of Raktonia solanacearum in plant tissues by nested-Pcr-Rflp. — Eur. J. Pl. Pathol. 106, 255–265, 2000.
Rat, B.: Presence en France de la maladie des taches angulaires du fraisier. — Ann. Phytopathol. 6(2), 223, 1974.
Roberts, P. D., R. D. Berger, J. B. Jones, C. K. Chandler, R. E. Stall: Disease progress, yield loss, and control of Xanthomonas fragariae on strawberry plants. — Pl. Dis. 81, 917–921, 1997.
Roberts, P. D., J. B. Jones, C. K. Chandler, R. E. Stall, R. D. Berger: Survival of Xanthomonas fragariae on strawberry in summer nurseries in Florida detected by specific primers and nested polymerase chain reaction. — Pl. Dis. 80, 1283–1288, 1996.
Rowhani A., A. J. Feliciano, T. Lips, W. D. Gubler: Rapid identification of Xanthomonas fragariae in infected strawberry leaves by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. — Pl. Dis. 78, 248–250, 1994.
Schaad, N. W.: Laboratory guide for identification of plant pathogenic bacteria, 2nd edition, Aps Press, St. Paul, Minnesota, Usa, 1988.
Severin, V., C. Stǎncescu, E. Zambrowicz: Angular leaf spot, a new bacterial disease of strawberry in Romania. — Bul. Prot. Plant. 1–2, 21–23, 1985.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zimmermann, C., Hinrichs-Berger, J., Moltmann, E. et al. Nested Pcr (polymerase chain reaction) for detection of Xanthomonas fragariae in symptomless strawberry plants. J Plant Dis Prot 111, 39–51 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03356131
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03356131