Abstract
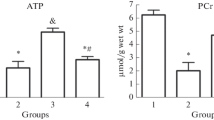
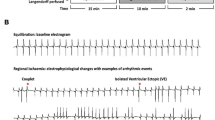
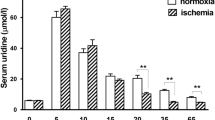
In this study, the effects of ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) on ischemia/reperfusion injury were investigated on isolated heart perfusion model. Hearts were perfused with oxygenated Krebs-Henseleit solution (pH 7.4, 37°C) on a Langendorff apparatus. After equilibration, isolated hearts were treated with UDCA 20 to 160 μM or vehicle (0.04% DMSO) for 10 min before the onset of ischemia. After global ischemia (30 min), ischemic hearts were reperfused and allowed to recover for 30 min. The physiological (i.e. heart rate, left ventricular developed pressure, coronary flow, double product and time to contracture formation) and biochemical (lactate dehydrogenase; LDH) parameters were evaluated. In vehicle-treated group, time to contracture formation was 21.4 min during ischemia, LVDP was 18.5 mmHg at the endpoint of reperfusion and LDH activity in total reperfusion effluent was 54.0 U/L. Cardioprotective effects of UDCA against ischemia/reperfusion consisted of a reduced TTC (EC25=97.3 μM), reduced LDH release and enhanced recovery of cardiac contractile function during reperfusion. Especially, the treatments of UDCA 80 and 160 μM significantly increased LVDP and reduced LDH release. Our findings suggest that UDCA ameliorates ischemia/reperfusion-induced myocardial damage.
Similar content being viewed by others
References Cited
Bernstein E. A., Eberli F. R. and Silverman A. M., Beneficial effects of felodifine on myocardial and coronary function during low flow ischemia and reperfusion.Cardiovasc.Drugs Ther., 10, 167–168 (1996).
Beuers, U., Nathanson, M. H. and Boyer, J. L., Effects of tauroursodeoxycholic acid on cytosolic Ca2+ signals in isolated rat hepatocytes.Gastroenterology, 104, 604–612 (1993).
Braunwald, E. and Kloner, R. A., Myocardial reperfusion: a double edged sword?J. Clin. Invest, 76, 1713–1719 (1985).
Ceriana, P., Effect of myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion on granulocyte elastase release.Anaesth. Int. Care, 20, 187–190 (1992).
Chien, K. R., Willerson, J. T. and Buja, L. M., Phospholipid alteration and membrane injury during myocardial ischemia. In:Advances in Myocardiology, edited by Harris, P. and Poole-Wilson. New York: Plenum, vol. 5, 347–352 (1985).
Drew, R. and Priestly, B. C., Choleretic and cholestatic effects of infused bile salts in the rat.Experientia, 35, 809–811 (1978).
Forman, M. B., Puett, D. W. and Virmani, R., Endothelial and myocardial injury during ischeamia and reperfusion: pathogenesis and therapeutic implica-tions.J. Am. Coll. Cardiol., 13, 450–459 (1989).
Gaudel, Y. and Duvelleroy, M. A., Role of oxygen radicals in cardiac injury due to reoxygenation.J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol., 16, 459–470 (1984).
Grover, G. J., McCullough, J. R., D'Alonzo, A. J., Sargent, C. A. and Atwal, K. S., Cardioprotective profile of the cardiac-selective ATP-sensitive potassium channel opener BMS-180448.J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol., 25, 40–50 (1995).
Grover, G. J., Sleph, P. G. and Dzwonczyk, S., Pharmacological profile of cromakalim in the treatment of myocardial ischemia in isolated rat hearts and anesthetized dogs.J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol., 16, 853–864 (1990).
Güldütuna, S., Zimmer, G., Imhof, M., Bhatt, S., You, T. and Leuschner, M., Molecular aspects of membrane stabilization by ursodeoxycholate.Gastroenterology, 104, 1736–1744 (1993).
Hara, A., Matsumura, H. and Abiko, Y., Lidocaine attenuates both mechanical and metbolic changes induced by hydrogen peroxide in the rat heart.Am. J. Physiol., 265, 1478–1485 (1993).
Hattori, Y., Murakami, Y., Hattori, S., Kuroda, H., Kasai, K. and Shimoda, S., Ursodeoxycholic acid inhibits the induction of nitric oxide synthase.Eur. J. Pharmacol., 300, 147–150 (1996).
Hearse, D. J., Humphrey, S. M., Nayler, W. G., Sale, A. and Border, Z., Ultrastructural damage associated with reoxygenation of anoxic myocardium.J. Mol. Cell Cardiol., 7, 315–324 (1975).
Hearse, D. J., Manning, A. S., Downey, J. M. and Yellen, D. M., Xanthine oxidase: a critical mediator of myocardial injury during ischaemia and reperfusion?Acta Physiol. Scand., 548, 65–74 (1986).
Hess, M. L. and Manson, N. H., Molecular oxygen: friend and foe-the role of the oxygen free radical system in the calcium paradox and ischemia/reperfusion injury.Mol. Cell Cardiol., 16, 969–989 (1984).
Josephson, R. A., Silverman, H. S. and Lakatta, E. G., Study of the mechanisms of hydrogen peroxide and hydroxyl free radical-induced cellular injury and calcium overload in cardiac myocytes.J. Biol. Chem., 266, 2354–2361 (1991).
Kokita, N. and Hara, A., Propofol attenuates hydrogen peroxide-induced mechanical and metabolic derangements in the isolated rat heart. Anesthesiology, 84, 117–127 (1996).
Lefer, A. M., Aoki, N. and Mulloy, D., Coronary endo-thelium-protective effects of defibrotide in ischaemia and reperfusion.Naunyn Schmiederberg's Arch. Pharmacol., 341, 246–250 (1990).
Lefer, A. M., Johnson, G., Ma, X. L., Tsao, P. S. and Thomas, G. R., Cardioprotective and endothelial protective effects of [Ala-IL8]77 in a rabbit model of myocardial ischaemia and reperfusion.Br. J. Pharmacol., 103, 1153–1159 (1991).
Lefer, A. M., Tsao, P. S., Lefer, D. J. and Ma, X. L. Role of endothelial dysfunction in the pathogenesis of reperfusion injury after myocardial ischemia.FASEB J., 5, 2029–2034 (1991).
Ljubuncic, P., Fuhrman, B., Oiknine, J., Aviram, M. and Bomzon, A., Effect of deoxycholic acid and ursodeoxycholic acid on lipid peroxidation in cultured macrophages.Gut, 39, 475–478 (1996).
Lucchesi, B. R. Myocardial ischemia, reperfusion and free radical injury.Am. J. Cardiol., 65, 141–231 (1990).
Lum, H. L., Barr, D. A., Shaffer, J. R., Cordon, R. J., Ezrin, A. M. and Malik, A. B., Reoxygenation of endothelial cells increases permeability by oxygen-dependent mechanisms.Ore. Res., 70, 991–998 (1992).
Maxwell, L. and Gavin, J. B., The role of post-ischaemic reperfusion in the development of microvascular imcompetence and ultrastructural damage in the myocardium.Basic Res. Cardiol., 86, 544–553 (1991).
McCord, J. M., Oxygen-derived free radicals in postishemic tissue injury.N. Engl. J. Med., 312, 159–163 (1985).
McFalls, E. O., Duncker, D. J., Krams, R., Ward, H., Gomick, C. and Verdouw, P. D., Endothelium dependent vasodilatation following brief ischaemia and reperfusion in anaesthetised swine.Cardiovasc. Res., 25, 659–665 (1991).
Nakaya, H., Tohse, N. and Kanno, M. Electrophysiological derangements induced by lipid peroxidation in cardiac tissue.Am. J. Physiol., 253, 1089–1097 (1987).
Ono, T., Nagasue, N., Kohno, H., Uchida, M., Takemoto, Y. Dhar, D. K. and Nakamura, T., Effect of taurourso-deoxycholic acid on bile flow and calcium excretion in ischemia-reperfusion injury of rat liver.J. Hepatology, 23, 582–590 (1995).
Pabla, R. and Curtis, M. J., Endogenous protection against reperfusion-induced ventricular fibrillation: role of neuronal versus nonneuronal sources of nitric oxide and species dependence in the rat versus rabbit isolated heart.J. Mol. Cell Cardiol., 28, 2097–2110 (1996).
Ro, J. Y., Cho, T. S. and Hong, S. S., The effects of cholates on smooth muscle strips and cardiac muscle.Kor. J. Pharmacol., 16, 41–50 (1986).
Sheridan, F. M., Dauber, I. M., McMurty, I. F., Lesnefsky, E. J. and Horwitz, L. D., Role of leukocytes in coronary vascular endothelial injury due to ischaemia and reperfusion.Cire. Res., 69, 1566–1574 (1991).
Simon, R. J. and Gregory, Y. H., Reperfusion injury: a review of the pathophysiology, clinical manifestations and therapeutic options.Int. J. Cardiol., 58, 95–117 (1997).
Steenbergen, C., Murphy, E., Watts, J. A. and London, R. E. Correlation between cystosolic free calcium, contracture, ATP and irreversible ischemic injury in perfused rat heart.Ore. Res., 66, 135–146 (1990).
Woodward, B. and Zakaria, M. V. M., Effect of some free radical scavengers on reperfusion induced arrhythmias in the isolated rat heart.J. Mol. Cell Cardiol., 84, 485–493 (1985).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, WY., Han, SH., Cho, TS. et al. Effect of ursodeoxycholic acid on ischemia/reperfusion injury in isolated rat heart. Arch Pharm Res 22, 479–484 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02979156
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02979156