Summary
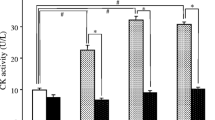
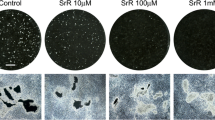
We have studied the effects of cyclosporine A (CsA) on basal and bovine parathyroid hormone (1–34) (bPTH)-stimulated bone resorption by osteoclasts in 24-hour cultures of chick long bone cells. At a high concentration (10 μg/ml), CsA had a cytotoxic effect on both osteoclasts and mononuclear cells in the culture. At 1 μg/ml, CsA inhibited basal and bPTH-stimulated bone resorption but was not cytotoxic over 24 hours. We also studied the binding of bPTH to the osteoblastic cell line, Saos-2, and chick long bone cells in suspension culture. CsA inhibited bPTH binding in Saos-2 in a dose-dependent manner; inhibition of binding was also observed in chick bone cells. The effects of CsA on osteoclast viability and resorptive function may be due to a direct effect on the osteoclasts and/or to an interaction with the nonosteoclastic cell population in the culture.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Borel JF, Feurer C, Gubler HU, Stahelin H (1976) Biological effects of cyclosporin A. Agents Actions 6:468–475
Shaw LM (1989) Advances in cyclosporin pharmacology, measurement and therapeutic monitoring. Clin Chem 35:1299–1308
Orcel P, Bielakoff J, Modrowski D, Miravet L, de Vernejoul MC (1989) Cyclosporin A induces in vivo inhibition of resorption and stimulation of formation of rat bone. J Bone Miner Res 4:387–391
Del Pozo E, Graeber M, Elford P, Payne T (1990) Regression of bone and cartilage loss in adjuvant arthritic rats after treatment with cyclosporin A. Arthritis Rheum 33:247–252
Dougados M, Awada H, Amor B (1988) Cyclosporin in rheumatoid arthritis: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study in 52 patients. Ann Rheum Dis 47:127–133
Mavsowitz C, Epstein S, Fallon M, Ismail F, Thomas S (1988) Cyclosporin A in vivo produces severe osteopenia in the rat: effect of dose and duration of administration. Endocrinology 123:2571–2577
Mavsowitz C, Epstein S, Ismail F, Fallon M, Thomas S (1989) Cyclosporin A in the oophorectomized rat: unexpected severe bone resorption. J Bone Miner Res 4:393–398
Stewart PJ, Green OC, Stern PH (1986) Cyclosporine A inhibits calcemic hormone-induced bone resorption in vitro. J Bone Miner Res 1:285–291
Klaushofer K, Hoffman O, Stewart PJ, Czerwenka E, Koller K, Peterlik M, Stern PH (1987) Cyclosporine A inhibits bone resorption in cultured neonatal mouse calveria. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 243:584–590
Stewart PJ, Stern PH (1989) Cyclosporins: correlation of immunosuppressive activity and inhibition of bone resorption. Calcif Tissue Int 45:222–226
Stewart PJ, Stern PH (1989) Interaction of cyclosporine A and calcitonin on bone resorption in vitro. Horm Metab Res 21:194–197
Lafferty KJ, Borel JF, Hodgkin P (1983) Cyclosporine A (CsA): models for the mechanism of action. Transplant Proc (suppl 1) 15:2230–2241
Hoffmann O, Klaushofer K, Gleispach H, Leis HJ, Luger T, Koller K, Peterlik M (1987) Gamma interferon inhibits basal and interleukin 1-induced prostaglandin production and bone resorption in neonatal mouse calveria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 143:38–43
Sabatini M, Boyce B, Aufdemorte T, Bonewald L, Mundy GR (1988) Infusion of recombinant human interleukins 1 alpha and 1 beta cause hypercalcemia in normal mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci 85:5235–5239
Dingle JT, Page-Thomas DP, Kings B, Bard DR (1987) In vivo studies of articular tissue damage mediated by catabolin/interleukin 1. Ann Rheum Dis 46:527–533
Espevik T, Figari IS, Shalaby MR Jr (1987) Inhibition of cytokine production by cyclosporin A and transforming growth factor beta. J Exp Med 166:571–576
Bertolini DR, Nedwin GE, Bringman TS, Smith DD, Mundy GR (1986) Stimulation of bone resorption and inhibition of bone formation in vitro by human tumour necrosis factor. Nature 319:516–518
Segre GV (1983) Amino terminal radioimmunoassay for human PTH. In: Frame B, Potts JT Jr (eds) Clinical disorders of bone and mineral metabolism. Excerpta Medica, Amsterdam, p 14
Arnett TR, Dempster DW (1987) A comparative study of disaggregated chick and rat osteoclasts in vitro: effects of clacitonin and prostaglandins. Endocrinology 120:602–608
Dempster DW, Murrills RJ, Horbert WR, Arnett TR (1987) Biological activity of chicken calcitonin: effects on neonatal rat and embryonic chick osteoclasts. J Bone Miner Res 2:443–447
Ryffel B, Donatsch P, Hiestand P, Mihatsch NJ (1986) PGE2 reduces nephrotoxicity and immunosuppression of cyclosporine in rats. Clin Nephrol (suppl 1) 25:S95-S99
Brown GP, Monik M, Hunninghake GW (1988) Fibroblast proliferation induced by silica-exposed human alveolar macrophages. Ann Rev Respir Dis 138:85–89
Martin TJ (1989) Bone cell physiology. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 18:833–858
Sasagawa K, Fujibayashi S, Okano K, Nawa C, Suzuki S, Kou S, Yamada Y, Someya K (1989) Different inhibitory actions of immunomodulating agents and immunosuppressive agents on bone resorption of mouse calvaria. Int J Immunopharmacol 11:953–959
Irschik E, Tilig H, Niederwieser D, Gastl G, Huber C, Margreiter R (1984) Cyclosporin blood levels do correlate with clinical complications. Lancet 2:692–693
Tropschug M, Barthelmess IB, Neupert W (1989) Sensitivity of cyclosporin A is mediated by cyclophilin in Neurospora crassa and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature 342:953–955
Zenatti M, Aupetit B, Ghazzi A, Schechter E, Michel A, Nataf V, Aymard P, Legrand JC (1988) Is the inhibition of oxidative phosphorylation chains in kidney mitochondria responsible for cyclosporine nephrotoxicity? Transplant Proc (suppl 3) 20:700–704
Fischer G, Wittman-Liebold B, Lang K, Kiefhaber T, Schmid FX (1989) Cyclophilin and peptidyl-prolyl cis-trans isomerase are probably identical proteins. Nature 337:476–478
Lang K, Schmid FX (1988) Protein-disulphide isomerase and prolyl isomerase act differently and independently as catalysts of protein folding. Nature 331:453–455
Nicchitta C, Kamoun M, Williamson JR (1985) Cyclosporin augments receptor-mediated cellular Ca2+ fluxes in isolated hepatocytes. J Biol Chem 260:13613–13618
Pfeilschifter J, Ruegg UT (1987) Cyclosporin augments angiotensin II-stimulated rise in intracellular free calcium in vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem J 248:883–887
Teti A, Blair HC, Schlesinger P, Grano M, Zambonin Zallone A, Kahn AJ, Tietelbaum SL, Hruska KA (1989) Extracellular protons acidify osteoclasts, reduce cytosolic calcium, and promote expression of cell-matrix attachment structures. J Clin Invest 84:773–780
Malgaroli A, Meldolesi J, Zambonin Zalone A, Teti A (1989) Control of cytosolic free calcium in rat and chicken osteoclasts. J Biol Chem 264:14342–14347
Datta H, Macintyre I, Zaidi M (1989) Inhibition by extracellular calcium of in vitro bone resorption by isolated rat osteoclasts. J Physiol 415:98P
Murrills RJ, Stein L, Horbert W, Dempster DW (1990) High extracellular calcium inhibits rat osteoclasts but does not potentiate the calcitonin response. J Bone Miner Res (suppl 2) 5:S148
Colombani PM, Robb A, Hess AD (1985) Cyclosporin A binding to calmodulin: a possible site of action on T lymphocytes. Science 228:337–339
Steinmuller DR (1989) Cyclosporin nephrotoxicity. Cleve Clin J Med 56:89–95
Dempster DW, Stein L, Horbert W, Chowdhury M, Hamada C, Murrills RJ (1990) Contrasting effects of glucocorticoids on rat and chick osteoclasts. J Bone Miner Res (suppl 2) 5:S95
Aubia J, Masramon J, Serrano S, Lloveras J, Marinoso LL (1988) Bone histology in renal transplant patients receiving cyclosporin. Lancet 1:1048
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chowdhury, M.H., Shen, V. & Dempster, D.W. Effects of cyclosporine a on chick osteoclastsIn vitro . Calcif Tissue Int 49, 275–279 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02556217
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02556217