Abstract
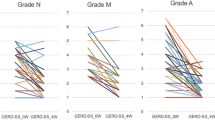
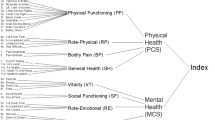
One thousand one hundred forty-five patients with acute erosive reflux esophagitis participating in an eight-week double-blind, multicenter study of lansoprazole 15 mg daily, lansoprazole 30 mg daily, omeprazole 20 mg daily, and placebo responded to a health-related quality of life (HRQoL) questionnaire at baseline and at two, four, and eight weeks. At baseline, there were no HRQoL differences among the four study groups. However, all three active treatment groups improved statistically significantly more than placebo on most HRQoL scales at each follow-up. There were no statistically significant differences among the three active treatment groups at week 2, although in most instances lansoprazole 30 mg showed slightly more improvement. After week 2, benefits in all the study groups leveled off and remained constant. Greater acid suppression appeared to result in greater improvement in terms of HRQoL.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Garnett WR: Efficacy, safety, and cost issues in managing patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Am J Hosp Pharm 50(suppl 1):S11-S18, 1993
Dobrilla G, Di Fede F: Treatment of gastroesophageal (acid) reflux with lansoprazole: an overview. Clin Ther 15(suppl B):2–13, 1993
Bate CM, Richardson PDI: Clinical and economic factors in the selection of drugs for gastroesophageal reflux disease. Pharmacoeconomics 3:94–99, 1993
DeVault KR, Castell DO: Current diagnosis and treatment of gastroesophageal reflux disease. Mayo Clin Proc 69:867–876, 1994
Sontag SJ, Hirschowitz BI, Holt S, Robinson MG, Behar J, Berenson MM, McCullough A, Ippoliti AF, Richter JE, Ahtaridis G, McCallum RW, Pambianco DJ, Vlahcevic RZ, Johnson DA, Collen MJ, Lyon DT, Humphries TJ, Cagliola A, Berman RS: Two doses of omeprazole versus placebo in symptomatic erosive esophagitis: The US multicenter study. Gastroenterology 102:109–118, 1992
Tolman KG, Sanders SW, Buchi KN: Gastric pH levels after 15 mg and 30 mg of lansoprazole and 20 mg omeprazole. Gastroenterology Suppl 106(4):A197, 1994
Jaeschke R, Guyatt GH, Cook D: Quality of life instruments in the evaluation of new drugs. Pharmacoeconomics 1:84–94, 1992
Patrick DL, Deyo RA: Generic and disease-specific measures in assessing health status and quality of life. Med Care 27(suppl):S217-S232, 1989
Revicki DA: Health-related quality of life in the evaluation of medical therapy for chronic illness. J Fam Pract 29:377–380, 1989
Stewart AL, Greenfield S, Hays RD, Wells K, Rogers WH, Berry SD, McGlynn EA, Ware JE, Jr: Functional status and well-being of patients with chronic conditions. Results from the Medical Outcomes Study. JAMA 262:907–913, 1989
Rush DR, Stelmach WJ, Young TL, Kirchdoerfer LJ, Scott-Lennox J, Holverson HE, Sabesin SM, Nicholas TA: Clinical effectiveness and quality of life with ranitidine vs placebo in gastroesophageal reflux disease patients: A clinical experience network (CEN) study. J Fam Pract 41:126–136, 1995
Dimenäs E, Glise H, Hallerbäck B, Hernqvist H, Svedlund J, Wiklund I: Quality of life in patients with upper gastrointestinal symptoms. An improved evaluation of treatment regimens? Scand J Gastroenterol 28:681–687, 1993
Glise H: Quality of life assessments in patients with peptic ulcer during treatment and follow-up. Scand J Gastroenterol 28(suppl 199):34–35, 1993
Hallerbäck B: Assessment of quality of life among patients with suspected duodenal ulcer. Scand J Gastroenterol 28(suppl 199):32–33, 1993
Korman MG: Quality of life in duodenal ulcer. Scand J Gastroenterol 28(suppl 199):28–31, 1993
McGee HM, O'Boyle CA, Hickey A, O'Malley K, Joyce CRB: Assessing the quality of life of the individual: The SEIQoL with a healthy and a gastroenterology unit population. Psychol Med 21:749–759, 1991
Chal KL, Stacey JH, Sacks GE: The effect of ranitidine on symptom relief and quality of life of patients with gastrooesophageal reflux disease. Br J Clin Pract 49:73–77, 1995
Stewart AL, Ware JE Jr (eds): Measuring Functioning and Well-Being. The Medical Outcomes Study Approach. Durham, North Carolina, Duke University Press, 1992
Stewart AL: Psychometric considerations in functional status instruments.In Functional Status Measurement in Primary Care. WONCA Classification Committee (ed). New York, Springer-Verlag, 1990
Ware JE Jr, Snow KK, Kosinski M, Gandek B: SF-36 Health Survey Manual and Interpretation Guide. Boston, Massachusetts, The Health Institute, New England Medical Center, 1993
Mathias SD, Fifer SK, Mazonson PD, Lubeck DP, Buesching DP, Patrick DL: Necessary but not sufficient: The effect of screening and feedback on outcomes of primary care patients with untreated anxiety. J Gen Intern Med 9:606–615, 1994
Dupuy HJ: The psychological general well-being (PGWB) index.In Assessment of Quality of Life in Clinical Trials of Cardiovascular Therapies. Wenger NK, Mattson ME, Furberg CF, Elinson J (eds). LeJacq Publishing Inc., 1984, pp 170–183
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This research was funded by TAP Holdings Inc., Deerfield, Illinois.
This study was presented in preliminary form for Digestive Disease Week, in San Diego, California, May 1995.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mathias, S.D., Castell, D.O., Elkin, E.P. et al. Health-related quality of life of patients with acute erosive reflux esophagitis. Digest Dis Sci 41, 2123–2129 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02071390
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02071390