Abstract
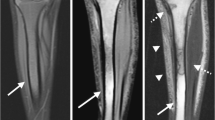
Thirteen patients with sickle cell disease (SCD) undergoing transfusion therapy and 8 control patients were examined by magnetic resonance imaging to discriminate bone marrow change due to iron deposition from hematologic marrow hyperplasia. Using T1-weighted spin echo images, only two subjects showed extremely low signal intensity marrow compatible with iron deposition. However, using T2-weighted fast spin echo images with fat suppression, cranial bone marrow in SCD patients with transfusion therapy showed considerably lower signal than that of controls. The main cause of marrow signal decrease in SCD patients with transfusion therapy was considered to be iron deposition due to repeated transfusion therapy rather than red marrow hyperplasia.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Okada Y, Aoki S, Barkovich AJ, Nishimura K, Norman D, Kjos BO, Brasch RC (1989) Cranial bone marrow in children: assessment of normal development with MR imaging. Radiology 171:161
Murayama S, Borne JA, Robinson AE, Onitsuka H, Hasuo K, Masuda K (1991) MR imaging of pediatric hematologic disorders. Acta Radiol 32:267
Mankad VN, Williams JP, Harpen MD, Manci E, Longenecker G, Moore RB, Shah A, Yang YM, Brogdon BG (1990) Magnetic resonance imaging of bone marrow in sickle cell disease: clinical hematologic, and pathologic, correlations. Blood 75:274
Sebes JI (1989) Diagnostic imaging of bone and joint abnormalities associated with sickle cell hemoglobinopathies. AJR 152:1153
Brasch RC, Wesbey GE Gooding CA, Koerper MA (1984) Magnetic resonance imaging of transfusional hemosiderosis complicating thalassemia major. Radiology 150:767
Rao VM, Fishman M, Mitchell DG, Steiner RM, Ballas SK, Axel L, Dalinka MK, Gefter W, Kressel HY (1986) Painful sickle cell crisis: bone marrow patterns observed with MR imaging. Radiology 161:211
Aoki S, Dillon WP, Barkovich AJ, Norman D (1989) Marrow conversion before pneumatization of the sphenoid sinus: assessment with MR imaging. Radiology 172:373
Kricun ME (1985) Red-yellow marrow conversion: its effect on the location of some solitary bone lesions. Skeletal Radiol 14:10
Cristy M (1981) Active bone marrow distribution as a function of age in humans. Phys Med Biol 26:389
Borrello JA, Chenevert TL, Meyer CR, Aisen AM, Glazer GM (1987) Chemical shift-based true water and fat images: regional phase correction of modified spin echo MR images. Radiology 164:531
Rosen RB, Fleming DM, Kushner DC, Zaner KS, Buxton RB, Bennet WP, Wismer GC, Brady TJ (1988) Hematologic bone marrow disorders: quantitative chemical shift MR imaging. Radiology 169:799
Schafer AI, Cheron RG, Dluhy R, Cooper B, Gleason RE, Soeldner JS, Bunn HF (1981) Clinical consequences of acquired transfusional iron overload in adults. N Engl J Med 304:319
Melki PS, Mulkern RV, Panych LS, Jolesz FA (1991) Comparing the FAISE method with conventional dual echo sequences. JMRI 1:319
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaneko, K., Humbert, J.H., Kogutt, M.S. et al. Iron deposition in cranial bone marrow with sickle cell disease: MR assessment using a fat suppression technique. Pediatr Radiol 23, 435–438 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02012442
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02012442