Abstract
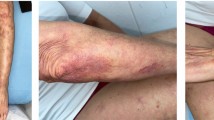
Candida spp. are the most common fungal pathogens isolated in immunocompromised hosts, particularly cancer patients. Numerous clinical manifestations of candidiasis have been recognized, including localized infection such as oropharyngeal candidasis or focal hepatic candidiasis, and disseminated infection resulting from hematogenous spread, with or without documented fungemia. Granulocytopenic patients are particularly at risk.Candida albicans is isolated in approximately 40 % of cases of fungemia, otherCandida spp. now also commonly being isolated. The rate of morbidity and mortality secondary to candidiasis is still significant despite numerous attempts to develop better diagnostic techniques, and more effective means of chemoprophylaxis and therapy. Currently, new antifungal agents and galenic preparations of amphotericin B are being evaluated with the aim of improving the prognosis of candidiasis in immunocompromised hosts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bodey, G. (ed.): Candidiasis: a growing concern. American Journal of Medicine 1984, 77: 1–48.
Edwards, J. E. Candida species. In: Mandell, G. L., Douglas, R. G., Bennett, J. E. (ed.): Principles and practice of infectious diseases. Wiley Medical, New York, 1985, p. 1435–1447.
Meunier, F. Fungal infections in the compromised host. In: Rubin, R. H., Young, L. S. (ed.): Clinical approach to infection in the compromised host. Plenum Medical, New York, 1988, p. 193–220.
Bennett, J. V. Incidence and nature of endemic and epidemic nosocomial infections. In: Bennett, J. V., Brachman, P. S. (ed.): Hospital infections. Little/Brown, Boston, 1979, p. 233–254.
Krick, J., Remington, J. Opportunistic fungal infection in patients with leukemia and lymphoma. Clinics in Haematology 1976, 5: 249–310.
Hawkins, C., Armstrong, D. Fungal infections in the immunocompromised host. Clinics in Haematology 1984, 13: 599–630.
Gold, J. W. M. Infectious complications of AIDS. In: Staquet, M., Hemmer, R., Baert, A. (ed.): Clinical aspects of AIDS and AIDS-related complex. University Press, Oxford, 1986, p. 93–100.
Butler, K. M., Baker, C. J. Candida: an increasingly important pathogen in the nursery. Pediatric Clinics of North America 1988, 35: 543–563.
Dupont, B., Drouhet, E. Cutaneous, occular and osteoarticular candidiasis in heroin addicts. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1985, 152: 577–591.
Wade, J. C., Schimpff, S. C. Epidemiology and prevention of infection in the compromised host. In: Rubin, R. H., Young, L. S. (ed.): Clinical approach to infection in the compromised host. Plenum Medical, New York, 1988, p. 5–40.
Aisner, J., Schimpff, S., Sutherland, J., Young, V., Wiernick, P. Torulopsis glabrata infections in patients with cancer: increasing incidence and relationship to colonization. American Journal of Medicine 1976, 61: 23–28.
Wingard, J., Merz, W., Saral, R. Candida tropicalis: a major pathogen in immunocompromised patients. Annals of Internal Medicine 1979, 91: 539–543.
Kiehn, T., Edwards, F., Armstrong, D. The prevalence of yeasts in clinical specimens from cancer patients. American Journal of Clinical Pathology 1980, 73: 518–521.
Meunier-Carpentier, F., Kiehn, T., Armstrong, D. Fungemia in the immunocompromised host: changing patterns, antigenemia, high mortality. American Journal of Medicine 1981, 1: 363–370.
Horn, R., Wong, B., Kiehn, T. E., Armstrong, D. Fungemia in a cancer hospital: changing frequency, earlier onset, and results of therapy. Reviews of Infectious Diseases 1985, 7: 646–655.
Bennett, J. E. Rapid diagnosis of candidiasis and aspergillosis. Reviews of Infectious Diseases 1987, 9: 398–402.
Sanford, G. R., Merz, W. G., Wingard, J. R., Sarache, P., Saral, R. The value of fungal surveillance cultures as predictors of systemic fungal infections. Journal of infectious Diseases 1980, 142: 503–509.
Schimpff, S. Surveillance cultures. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1981, 144: 81–84.
Kramer, B. S., Pizzo, P. A., Robichaud, K. J., Witesbsky, F., Wesley, R. Role of serial microbiologic surveillance and clinical evaluation in the management of cancer patients with fever and granulocytopenia. American Journal of Medicine 1982, 72: 561–568.
Bille, J., Stockman, L., Roberts, G. D., Horstmeier, C. D., Hestrup, D. M. Evaluation of a lysis-centrifugation system for recovery of yeasts and filamentous fungi from blood. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1983, 18: 469–471.
Kiehn, T., Wong, B., Edwards, F., Armstrong, D. Comparative recovery of bacteria and yeasts from lysis centrifugation and a conventional blood culture system. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1983, 18: 300–304.
Bille, J., Edson, R., Roberts, G. Clinical evaluation of the lysis centrifugation blood culture system for the detection of fungemia and comparison with a conventional biphasic broth blood culture system. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1984, 19: 126–128.
Edwards, J. E. Candida endophthalmitis. In: Remington, J. S., Swartz, M. N. (ed.): Current clinical topics in infectious diseases. Volume 3. McGraw Hill, New York, 1982, p. 381–397.
Murray, H., Fialk, M., Roberts, R. Candida arthritis: a manifestation of disseminated candidiasis. American Journal of Medicine 1976, 60: 587–595.
Noble, M., Lyne, E. Candida osteomyelitis and arthritis from hyperalimentation therapy. Journal of Bone and Joint Surgery 1974, 56, Supplement B: 825–829.
Meunier-Carpentier, F. Significance and clinical manifestations of fungemia. In: Klastersky, J. (ed.): Infections in cancer patients. Volume 10. Raven Press, New York, 1982, p. 141–155.
Torres-Rojas, J. R., Stratton, C. W., Sanders, C. V., Horsman, T. A., Hawley, H. B., Dascomb, H. E., Vial, L. J. Candidal suppurative peripheral thrombophlebitis. Annals of Internal Medicine 1982, 96: 431–435.
Walsh, T. J., Bustamente, C. I., Vlahov, D., Standiford, H. C. Candidal suppurative peripheral thrombophlebitis: recognition, prevention, and management. Infection Control 1986, 7: 16–22.
Whimbey, E., Kiehn, T. E., Brannon, P., Benezra, D., Armstrong, D. Bacteremia and fungemia in patients with neoplastic disease. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1987, 155: 1328–1330.
Eras, P., Goldstein, M., Sherlock, P. Candida infection of the gastrointestinal tract. Medicine 1972, 51: 367–379.
Meunier, F.: Fungal infections in AIDS. In: Staquet, M., Hemmer, R., Baert, A. (ed.): Clinical aspects of AIDS and AIDS-related complex. Oxford University Press, 1986, p. 101–105.
Aisner, J., Sickles, E., Schimpff, S., Young, V. M. Greene, W. H. Torulopsis glabrata pneumonitis in patients with cancer. Journal of the American Medical Association 1974, 230: 584–585.
Masur, H., Rosen, P., Armstrong, D. Pulmonary disease caused byCandida species. American Journal of Medicine 1977, 63: 914–925.
Tasjhjian, L. S., Abramson, J. S., Peacock, J. E. Focal hepatic candidiasis: a distinct clinical variant of candidiasis in immunocompromised patients. Reviews of Infectious Diseases 1984, 6: 689–703.
Haron, E., Feld, R., Tuffnell, P., Patterson, B., Hasselback, R., Matlow, A. Hepatic candidiasis: an increasing problem in immunocompromised patients. American Journal of Medicine 1987, 83: 17–26.
Thaler, M., Pastakia, B., Shawker, T. H., O'Leary, T., Pizzo, P. A. Hepatic candidiasis in cancer patients. The evolving picture of the syndrome. Annals of Internal Medicine 1988, 108: 88–100.
Marcucci, R., Whitelly, H., Armstrong, D. Common bile duct obstruction secondary to infection withCandida. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1978, 7: 490–492.
Schreiber, M., Black, L., Noah, Z., Shulman, S. T., Yoger, R., Venezio, S. R. Gallbladder candidiasis in a leukemic child. American Journal of Diseases of Children 1982, 136: 462–463.
Gordon, R., Simmons, B., Appelbaum, P., Aber, R. C. Intraabdominal abscess and fungemia caused byCandida krusei. Archives of Internal Medicine, 1980, 140: 1239–1240.
Solomkin, J., Flohr, A., Quie, P., Simmons, R. The role ofCandida in intraperitoneal infections. Surgery 1980, 88: 524–530.
Eisenberg, E., Alpert, B., Weiss, R., Mittman, N., Soeiro, R. Rhodotorula rubra peritonitis in patients undergoing continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. American Journal of Medicine 1983, 75: 349–352.
Bayer, A. S., Blumenkrantz, M. J., Montgomerie, J. Z., Galpin, J. E., Coburn, J. W., Guze, L. B. Candida peritonitis: report of 22 cases and review of the English literature. American Journal of Medicine 1976, 61: 832–840.
Kerr, C. M., Perfect, J. R., Craven, P. C., Jorgensen, J. H., Drutz, D. J., Shelburne, J. D., Gallis, H. A., Gutman, R. A. Fungal peritonitis in patients on continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Annals of Internal Medicine 1983, 99: 334–337.
Boldus, R., Brown, R., Culp, D. Fungus balls in the renal pelvis. Radiology 1972, 102: 555–557.
Dembner, A., Pfister, R. Fungal infection of the urinary tract: demonstration by antegrade pyelography and drainage by percutaneous by nephrostomy. American Journal of Roentgenology 1977, 129: 415–418.
McDonald, D., Fagan, C. Fungus balls in the urinary bladder. American Journal of Roentgenology 1972, 114: 753–757.
Ellis, C., Spivack, M. The significance of candidemia. Annals of Internal Medicine 1967, 67: 511–522.
Goldberg, P., Kozinn, P., Wise, G., Nouri, N., Brooks, R. B. Incidence and significance of candiduria. Journal of the American Medical Association 1979, 241: 582–584.
Argyle, C., Schumann, G. B., Genack, L., Gregory, M. Identification of fungal casts in a patient with renal candidiasis. Human pathology 1984, 15: 480–481.
Gregory, M. C., Schumann, G. B., Schumann, J. L., Argyle, J. C. The clinical significance ofCandida casts. American Journal of Kidney Diseases 1984, 4: 179–184.
Bayer, A., Guze, L. Fungal arthritis. Candida arthritis: diagnostic and prognostic implications and therapeutic considerations. Seminars in Arthritis and Rheumatism 1978, 8: 142–150.
Fainstein, V., Gilmore, C., Hopfer, R. L., Maksymiuk, A., Bodey, G. P. Septic arthritis due toCandida species in patients with cancer: report of five cases and review of the literature. Reviews of Infectious Diseases 1982, 4: 78–85.
Gerster, J., Glauser, M., Delacretaz, F., Nguyen, T. Erosive candida arthritis in a patient with disseminated candidiasis. Journal of Rheumatology 1980, 7: 911–914.
Gathe, J. C., Harris, R. L., Garland, B., Bradshaw, M. W., Williams, T. W. Candida osteomyelitis: report of five cases and review of the literature. American Journal of Medicine 1987, 82: 927–937.
Lipton, S., Hickey, W., Morris, J., Loscalzo, J. Candidal infection in the central nervous system. American Journal of Medicine 1984, 76: 101–108.
Chesney, P. J., Justman, R. A., Bogdanowicz, W. M. Candida meningitis in new-born infants: a review and report of combined amphotericin B-flucytosine therapy. John Hopkins Medical Journal 1978, 142: 155–160.
Lilien, L. D., Ramamurthy, R. S., Pildes, R. S. Candida albicans meningitis in a premature neonate successfully treated with 5-fluorocytosine and amphotericin B: a case report and review of the literature. Pediatrics 1978, 61: 57–61.
Chmel, H. Candida albicans meningitis following lumbar puncture. American Journal of Medical Sciences 1973, 266: 465–467.
McLeod, R., Remington, J.: Fungal endocarditis. In: Rahimtoola, S. (ed.): Infective endocarditis Gunne Stratton, New York, 1978, p. 211–290.
Bennett, J. E. Antifungal agents. In: Mandell, G. L., Douglas, R. G., Bennett, J. E. (ed.): Principles and practice of infectious diseases. Wiley Medical, New York, 1985, p. 263–270.
Gigliotti, F., Shenep, J. L., Lott, L., Thornton, D. Induction of prostaglandin synthesis as the mechanism responsible for the chills and fever produced by infusing amphotericin B. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1987, 156: 784–789.
Stamm, A. M., Diasio, R. B., Dismukes, W. E., Shadomy, S., Cloud, C. A., Bowles, C. A., Karam, G. H., Espinel-Ingroff, A. Toxicity of amphotericin B plus flucytosine in 194 patients with cryptococcal meningitis. American Journal of Medicine 1987, 83: 236–242.
Drutz, D. J.: Newer antifungal agents and their use, including an update on amphotericin B and flucytosine. In: Remington, J. S., Swartz, M. N. (ed.): Current clinical topics in infectious diseases. Volume 3. McGraw-Hill, New York, 1980, p. 97–135.
Lopez-Berestein, G., Fainstein, V., Hopfer, R., Mehta, K., Sullivan, M. P., Keating, M., Rosenblum, M. G., Mehta, R., Luna, M., Hersh, E. M., Reuben, J., Juliano, R. L., Bodey, G. P. Liposomal amphotericin B for the treatment of systemic fungal infections in patients with cancer: a preliminary study. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1985, 151: 704–710.
Lopez-Berestein, G., Bodey, G. P., Frankel, L. S., Mehta, K. Treatment of hepatosplenic fungal infections with liposomal amphotericin B. Journal of Clinical Oncology 1987, 5: 310–317.
Sculier, J. P., Coune, A., Meunier, F., Brassinne, C., Laduron, C., Hollaert, C., Collette, N., Heymans, C., Klastersky, J. Pilot study of amphotericin B entrapped in sonicated liposomes in cancer patients with fungal infections. European Journal of Cancer and Clinical Oncology 1988, 24: 527–538.
Meunier, F., Sculier, J. P., Coune, A., Brassinne, C., Heymans, C., Laduron, C., Collette, N., Hollaert, C., Bron, D., Klastersky, J. Amphotericin B encapsulated in liposomes administered to cancer patients. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1988, 544: 598–610.
Guinet, R., Chanas, J., Goullier, A., Bonnefoy, G. Fatal septicemia due to amphotericin B-resistantCandida lusitaniae. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1983, 18: 433–444.
Pappagianis, D., Collins, M., Hector, R., Remington, J. Development of resistance to amphotericin B inCandida lusitaniae infecting a human. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1979, 16: 123–126.
Merz, W. G. Candida lusitaniae: frequency of recovery, colonization, infection, and amphotericin B resistance. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1984, 20: 1194–1195.
Merz, W., Sandford, G. Isolation and characterization of a polyene resistant variant ofCandida tropicalis. Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1979, 9: 677–680.
Dick, J. D., Merz, W. G., Saral, R. Incidence of polyene-resistant yeasts recovered from clinical specimens. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1980, 18: 158–163.
Powderly, W. G., Kobayashi, G. S., Herzig, G. P., Medoff, G. Amphotericin B-resistant yeast infection in severely immunocompromised patients. American Journal of Medicine 1988, 84: 826–832.
Dick, J. D., Rosengard, B. R., Merz, W. G., Stuart, R. K., Grover, M., Hutchins, v., Saral, R. Fatal disseminated candidiasis due to amphotericin B resistantCandida guillermondii. Annals of Internal Medicine 1985, 102: 67–68.
Seidenfeld, S. M., Cooper, B. H., Smith, J. W., Luby, J. P., Mackowiak, P. A. Amphotericin B tolerance: a characteristic ofCandida parapsilosis not shared by otherCandida species. Journal of Infectious Diseases 1983, 147: 116–119.
Stiller, R., Bennett, J., Scholer, H., Wall, M., Polal, A., Stevens, D. A. Susceptibility of 5-fluorocytosine and prevalence of serotype in 402Candida albicans isolates in the US. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1982, 22: 482–487.
Wingard, J. R. Prevention of fungal sepsis in patients with prolonged neutropenia: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of intravenous miconazole. American Journal of Medicine 1987, 83: 1103–1110.
Horsburgh, C., Kirkpatrick, C. Long-term therapy of chronic mucocutaneous candidosis with ketoconazole: experience with twenty-one patients. American Journal of Medicine 1983, 74: 23–29.
Fazio, R. A., Wickremesinghe, P. C., Arsura, E. L. Ketoconazole treatment of candida esophagitis: a prospective study of 12 cases. American Journal of Gastroenterology 1983, 78: 261–264.
Symoens, J., Moens, M., Dom, J., Sheijgrond, H., Dony, J., Schuermans, V., Legendre, R., Finsestine, N. An evaluation of two years of clinical experience with ketoconazole. Reviews of Infectious Diseases 1980, 2: 674–687.
Meunier, F. Serum fungistatic and fungicidal activity in volunteers receiving antifungal agents. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology 1986, 5: 103–109.
Daneshemend, T. Ketoconazole-cyclosporin interaction. Lancet, 1982, ii: 1342–1343.
Ferguson, R., Sutherland, D., Simmons, R., Najarian, J. S.: Ketoconazole, cyclosporin metabolism and renal transplantation Lancet, 1982, ii: 882–883.
Morgenstern, G., Powels, R., Robinson, B., McElwain, T. J. Cyclosporin interaction with ketoconazole and melphalan. Lancet, 1982, ii: 1342.
Pont, A., William, P., Azhar, S., Reitz, R. E., Bochra, C., Smith, E. R., Stevens, D. A. Ketoconazole blocks testosterone synthesis. Archives of Internal Medicine 1982, 142: 2137–2140.
Pont, A., William, P., Loose, D., Feldman, D., Reitz, R. E., Bochra, C., Stevens, D. A. Ketoconazole blocks adrenal steroids synthesis. Annals of Internal Medicine 1982, 97: 370–372.
Saag, M. S., Dismuskes, W. E. Azole antifungal agents: emphasis on new triazoles. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy, 1988, 32: 1–8.
Fromtling, R. A. Overview of medically important antifungal azole derivatives. Clinical Microbiological Reviews 1988, 147: 116–119.
Hay, R. J., Dupont, B., Graybill, J. R. (ed.): First International Symposium on Itraconazole. Reviews of Infectious Diseases 1987, 9, Supplement 1: S1–S152.
Meunier, F., Gerain, J., Snoeck, R., Libotte, F., Lambert, C., Ceuppens, A. M. Fluconazole therapy of orophyaryngeal candidiasis in cancer patients. In: Fromtling, R. A. (ed.): Recent trends in the discovery, development and evaluation of antifungal agents. J. R. Prouss, Barcelona, 1987, p. 169–174.
Dupont, B., Drouhet, E. Fluconazole in the management of oropharyngeal candidiasis in a predominantly HIV antibody-positive group of patients. Journal of Medical Veterinary Mycology 1988, 26: 67–71.
Pizzo, P. A., Robichaud, K. J., Gill, F. A., Witebsky, F. Empiric antibiotic and antifungal therapy for cancer patients with prolonged fever and granulocytopenia. American Journal of Medicine 1982, 72: 101–111.
Holleran, W. M., Wilbur, J. R., DeGregorio, M. G. Empiric amphotericin B therapy in patients with acute leukemia. Reviews of Infectious Diseases 1985, 7: 619–624.
Fainstein, V., Bodey, G. P., Elting, L., Maksymiuk, A., Keating, M., McCredie, K. B. Amphotericin B or ketoconazole therapy of fungal infections in neutropenic cancer patients. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 1987, 31: 11–15.
Meunier, F. Prevention of opportunistic mycoses in immunocompromised patients. Reviews of Infectious Diseases 1987, 9: 408–416.
Owens, M., Nightingale, C., Schweizer, R., Schauer, P., Dekker, P., Quintiliani, R. Prophylaxis of oral candidiasis with clotrimazole troches. Archives of Internal Medicine 1984, 144: 290–293.
Jones, P. G., Kauffmann, C. A., McAuliffe, L. S., Liepman, M. K., Bergman, A. G. Efficacy of ketoconazole versus nystatin in prevention of fungal infections in neutropenic patients. Archives of Internal Medicine 1984, 144: 549–551.
Meunier-Carpentier, F., Cruciani, M., Klastersky, J. Oral prophylaxis with miconazole or ketoconazole of invasive fungal disease in neutropenic cancer patients. European Journal of Cancer and Clinical Oncology 1983, 19: 43–48.
Estey, E., Maksymiuk, A., Smith, T., Fainstein, V., Keating, M., McCredie, K. B., Freireich, E. M., Bodey, G. P. Infection prophylaxis in acute leukemia. Archives of Internal Medicine, 1984, 144: 1562–1568.
Meunier, F., Leleux, A., Snoeck, R., Gérain, J., Lambert, C., Ceuppens, A. M. Chemoprophylaxis of fungal infections. In: Holmberg, K., Meyer, R. (ed.): Diagnosis and therapy of systemic fungal infections. Raven Press, New York, 1989, p. 167–177.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meunier, F. Candidiasis. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 8, 438–447 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01964058
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01964058