Abstract
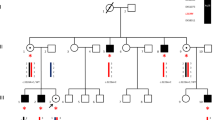
X-linked hydrocephalus-stenosis of the aqueduct of Sylvius sequence (H-SAS, MIM number 30007) is a rare genetic disorder characterized by hydrocephalus, macrocephaly, adducted thumbs, spasticity, agenesis of corpus callosum and mental retardation. We confirm here the localisation of the mutant gene on Xq (Xq 2.8) by linkage analysis in a 5-generation pedigree (maximum lod score of Z=4.57 at theta =0.04 with probe St14 at locus DXS52) and emphasise the phenotypic variability of the disease. Ventricular dilatation in affected males was either severe and diagnosed antenatally or moderate and consistent with a long survival with little or no macrocephaly. Since other X-linked syndromes of mental retardation with spasticity and flexion deformities of the thumbs have previously been shown to map to the Xq 2.8 region as well (e.g. MASA syndrome and spastic paraplegia), the present results raise the question of whether H-SAS syndrome, MASA syndrome and spastic paraplegia with mental retardation might represent different phenotypic expression of various mutations at the same locus.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- H-SAS:
-
hydrocephalus-stenosis of the aqueduct of Sylvius sequence
References
Bianchine JW, Lewis RC (1974) The MASA syndrome: a new heritable mental retardation syndrome. Clin Genet 5:298–306
Bickers DS, Adams RD (1949) Hereditary stenosis of the aqueduct of Sylvius as a cause of congenital hydrocephalus. Brain 72:246–262
Edwards JH (1961) The syndrome of sex-linked hydrocephalus. Arch Dis Child 36:486–493
Gareis FJ, Mason JD (1984) X-linked mental retardation associated with bilateral clasp anomaly. Am J Med Genet 17:333–338
Halliday J, Chow CW, Wallace D, Danks DM (1986) X-linked hydrocephalus: a survey of a 20 year period in Victoria, Australia. J Med Genet 23:23–31
Holmes LB, Nash A, Zurhein GM, Levin M, Opitz JM (1973) X-linked aqueductal stenosis: clinical and neuropathological findings in two families. Pediatrics 51:697–704
Kelley RI, Mennuti MT, Hickey WF, Zackai EH (1988) X-linked recessive aqueductal stenosis without macrocephaly. Clin Genet 33:390–394
Kenwrick S, Ionasescu V, Ionasescu G, Searby CH, King A, Dubowitz M, Davies KE (1986) Linkage studies of X-linked recessive spastic paraplegia using DNA probes. Hum Genet 73:264–266
Landrieu P, Ninane J, Ferrière G, Lyon G (1979) Aqueductal stenosis in X-linked hydrocephalus: a secondary phenomenon? Dev Med Child Neurol 21:637–642
Lathrop GM, Lalouel JM, Julier C, Ott J (1985) Multilocus linkage analysis in humans: detection of linkage and estimation of recombinaison. Am J Med Genet 37:482–495
Oberlé I, Kamerino G, Helig R, Grünebaum H, Casenave JP, Crappanzeno C, Mamicci PM, Mandel JL (1985) Genetic screening for hemophilia. A (classic hemophily) with a polymorphic DNA probe. N Engl J Med 312:682–686
Schrander-Stumpel C, Legius E, Fryns JP, Cassiman JJ (1990) MASA syndrome: new clinical features and linkage analysis using DNA probes. J Med Genet 27:688–692
Schrander-Stumpel C, Fryns JP, Legius E, Cassiman JJ (1990) X-linked complicated spastic paraplegia (McKusick 31290), MASA syndrome (McKusick 30925) and X-linked hydrocephaly due to congenital stenosis of the aqueduct of Sylvius (McKusick 30700): a variable expression of the same mutation at Xq28. In: Fryns JP (ed) Proceedings of the First European Meeting of Dysmorphology, pp 76–78
Viseskul C, Gilbert EF, Opitz JM (1975) X-linked hydrocephalus. Further observations. Z Kinderheilkd. 119:111–121
Willems PJ, Brouwer OF, Dijkstra I, Wilmink J (1987) X-linked hydrocephalus. Am J Med Genet 27:921–928
Willems PJ, Dijkstra I, Van der Auwera BJ, Vits L, Coucke P, Raeymaekers P, Van Broeckhoven C, Gonsalez GG, Freeman SB, Warren ST, Brouwer OF, Brunner HG, Renier WO, Van Elsen AF, Dumon JE (1990) Assignment of X-linked hydrocephalus to Xq28 by linkage analysis. Genomics 8:367–370
Winter RM, Davies KE, Bell MV, Huson SM, Patterson MN (1989) MASA syndrome: further clinical delineation and chromosomal localisation. Hum Genet 82:367–370
Yeatman GW (1984) Mental retardation clasped thumb syndrome. Am J Med Genet 17:339–344
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Serville, F., Lyonnet, S., Pelet, A. et al. X-linked hydrocephalus: Clinical heterogeneity at a single gene locus. Eur J Pediatr 151, 515–518 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01957757
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01957757