Summary
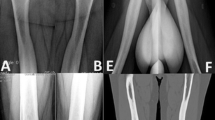
Pyknodysostosis is a rare form of sclerosing bone dysplasia with autosomal recessive inheritance. Affected members of two families were assessed as follows: three patients underwent densitometry measurements and bone scans; four patients underwent magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and an immunological investigation, as well as a detailed endocrinological and biochemical laboratory review. Densitometry measurements revealed values of up to 291% of age-matched normal controls; this increased bone density was mainly in the trabecular bone and not in the cortical bone. The MRI showed the cortex to be of normal thickness, whereas the increase in trabecular bone limited the space within the medullary canal. Bone scans and single photon emission computerized tomography in three patients showed an increased uptake of [99mTc]methylene diphosphonate of up to 538% of age-matched controls, which reflected the increased bone density. Monocyte function tests demonstrated a normal phagocytic capacity, but their killing activity was impaired. Interleukin-1 secretion was also impaired, which may point to the pathogenesis of the disease, in view of its function as an osteoclast activator and its role in bone resorption.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fairbank TJ (1976) Fairbank's atlas of general affections of the skeleton. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, p 96
Elmore SM (1967) Pyknodysostosis: a review. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 49A:153–162
Edelson JG, Suliman O, Gaiger R, On A (in press) Pyknodysostosis: orthopedic aspects with a presentation of fourteen new cases. Clin Orthop
Lehrer RI, Cline MJ (1969) Interaction ofCandida albicans with human leukocytes and serum. J Bacteriol 98:996–1004
Conlon PJ (1983) A rapid biologic assay for the detection of interleukin-1. J Immunol 131:1280–1282
Shuler SE (1963) Pyknodysostosis. Arch Dis Child 38:620–625
Emami-Ahari Z, Zarabi M, Javid B (1969) Pyknodysostosis. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 51B:307–312
Meredith SC, Simon MA, Laros GS, Jackson MA (1978) Pyknodysostosis: a clinical, pathological, and ultramicroscopic study of a case. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 60A:1122–1127
Kumar A (1988) Pyknodysostosis: case report. Int Orthop 12:261–263
Anegawa S, Bekki Y, Furukawa Y, Yokuta S, Torigeo R (1987) A case of pyknodysostosis: observation of the skull by CT scan. No To Shinkei 39:621–626
Van-Merkesteyn JP, Bras J, Vermereen JI, Van der Sar A, Statius-Van-Eps LW (1987) Osteomyelitis of the jaws in pyknodysostosis. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 16:615–619
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karkabi, S., Reis, N.D., Linn, S. et al. Pyknodysostosis: Imaging and laboratory observations. Calcif Tissue Int 53, 170–173 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01321833
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01321833