Abstract
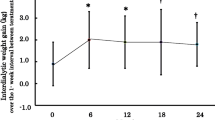
Ten children with chronic renal failure (CRF) were managed for 3 years using a strict low-protein and low-phosphorus diet supplemented by a mixture of the keto and amino forms of the essential amino acids and histidine (phase II). All of these children were previously managed for at least 2 years with a less rigorous diet of limited protein intake with no specific reduction of phosphorus (phase I). Energy, vitamin D, bicarbonate, phosphate binders and vitamin and mineral mixtures were added as required during both dietary phases. Data on dietary intake showed a significant fall in protein and phosphorus intake and a rise in calcium intake during phase II compared with phase I. Plasma calcium increased and phosphate fell, with an associated fall in intact parathyroid hormone levels. There was a marked improvement in urea creatinine ratios, which suggested an improved anabolic state. Cholesterol and triglyceride levels were improved. Height and weight velocity were increased, becoming significant after 3 years of phase II. Renal function deteriorated at a slower rate than predicted. The diet was well tolerated by the children, with fitness and school performance showing improvement. We conclude that long-term strict dietary management of children with CRF is feasible. Our data suggest an overall improvement in general health and an apparent reduction in the rate of deterioration of renal function.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brenner BM, Myer TW, Hostetter TH (1982) Dietary protein intake and the progressive nature of kidney disease. N Engl J Med 307: 652–659
Meyer TW, Lawrence WE, Brenner BM (1983) Dietary protein and the progression of renal disease. Kidney Int 24 [Suppl 16]: 243–247
Rosman JB, Donker AJM, Meyer S (1986) Two years experience with protein restriction in chronic renal failure. Contrib Nephrol 53: 109–120
El Nahas AM, Masters-Thomas A, Brady SA, Farrington K, Wilkinson V, Hilson AJW, Varghese Z, Moorhead JF (1984) Selective effect of low protein diet in chronic renal diseases. Br Med J 289: 1337–1341
Hostetter TH, Olsen JL, Rennke HG, Venkatachalan MA, Brenner BM (1981) Hyperfiltration in remnant nephrons, a potentially adverse response to renal ablation. Am J Physiol 241: 85–93
McCrory WW, Gertner JM, Burke FM, Pimental CT, Nemery RL (1987) Effects of dietary phosphate restriction in children with chronic renal failure. J Paediatr 111: 410–412
Kikuchi H, Matoushita L, Hirata K (1983) Improved dietary treatment with low protein and phosphorus restriction in uraemic rats. Kidney Int 24 [Suppl 16]: S254–258
Massry SG (1983) The toxic effects of parathyroid hormone in uraemia. Semin Nephrol 3: 306–328
Powell D, Bergstrom J, Dzurik R (1986) Toxins and inhibitors in chronic renal failure. Am J Kidney Dis 7: 292–299
Mak RH, Turner C, Haycock GB, Chantler C (1983) Secondary hyperparathyroidism and glucose intolerance in children with uraemia. Kidney Int 24: 128–133
Gin H, Aparicio M, Potaux L, Precigout V de, Bouchet JL, Aubertin J (1987) Low protein and low phosphorus diet in patients with chronic renal failure: influence on glucose tolerance and tissue insulin sensitivity. Metabolism 36: 1080–1085
Holliday M (1986) Nutritional therapy in renal disease. Kidney Int 30: S3–6
Jones R, Dalton N, Turner C, Start K, Haycock G, Chantler C (1983) Oral essential amino acid and ketoacid supplements in children with chronic renal failure. Kidney Int 24: 95–103
Adelaide Chidren's Hospital growth percentile charts (1982) Compiled from New South Wales Health Commission Publication (Jones, DL, Hemphill W, Meyers ESA, 1973)
Charts and Tables of Heights, Masses and Head Circumferences of Infants and Children (1975) Aust Dept Health Publ, p 13
Barrett TM, Broyer M, Chantler C, Gilli G, Guest G, Marti-Henneberg C, Preece MA, Rigden SPA (1986) Assessment of growth. Am J Kidney Dis 7: 340–346
Tanner JM, Whitehouse RH (1975) Revised standards for triceps and subscapular skinfolds in British children. Arch Dis Child 50: 142–145
Paul AA, Southgate DA (1978) McCance & Widdowson's, The composition of foods, 4th edn. HMSO, London
Wills RBH, Greenfield H (1989) Bibliography of composition of Australian foods. Food Australia 41: 902
Gruelich WW, Pyle SI (1966) Radiographic atlas of skeletal development of the hand and wrist, 2nd edn. Stanford University Press, Stanford, Calif.
Donath A (1971) The simultaneous determination in children of glomerular filtration rate and effective renal plasma flow by the single injection clearance technique. Acta Paediatr Scand 60: 512–520
Morris MC, Allanby CW, Toseland P, Haycock GB, Chantler C (1982) Evaluation of a height/plasma creatinine formula in the measurement of GFR. Arch Dis Child 57: 611–615
French CB, Genel M (1984) Pathophysiology of growth failure in chronic renal insufficiency. Kidney Int 30: 559–564
Southwood TR, Hogg RJ, Renen MJ van, Jureidini KF (1987) Growth velocity indexes. Med J Aust 147: 206
Jones RW, Dalton N, Start K, El Bishti MM, Chantler C (1980) Oral amino acid supplements in children with advanced chronic renal failure. Am J Clin Nutr 33: 1696–1792
Andreoli SP, Bergstein JM, Sherrard DJ (1984) Aluminium intoxication from aluminium-containing phosphate binders in children with azotemia not undergoing dialysis. N Engl J Med 310: 1079–1084
Mak RHK, Turner C, Powell H, Haycock GB, Chantler C (1985) Suppression of secondary hyperparathyroidism in children with chronic renal failure by high dose phosphate binders: calcium carbonate versus aluminium hydroxide. Br Med J 291: 623–627
Hruska KA, Martin K, Mennes P, Greenwalt A, Anderson C, Klahr S, Slatopolsky E (1977) Degradation of parathyroid hormone and fragment production by the isolated perfused dog kidney: the effect of glomerular filtration rate and perfusate CA++ concentrations. J Clin Invest 60: 501–510
Woolfield N, Haslam R, LeQuesne G, Chambers HM, Hogg R, Jureidini K (1988) Ultrasound diagnosis of nephrocalcinosis in preterm infants. Arch Dis Child 63: 86–88
Lucas PA, Meadows JH, Roberts DE, Coles GA (1986) The risks and benefits of a low protein-essential amino acid-keto acid diet. Kidney Int 29: 995–1003
Mitch WF, Walser M, Buffington GA, Lemann L (1976) A simple method of estimating progression o chronic renal failure. Lancet II: 1326–1328
Heidland A, Kuhl J, Rockel A, Heidbreder E (1978) Evaluation of essential amino acids and keto acids in uremic patients on low-protein diet. Am J Clin Nutr 31: 1784–1792
Walser M, LaFrance ND, Ward L, VanDuyn MA (1987) Progression of chronic renal failure in patients given ketoacids following amino acids. Kidney Int 32: 123–128
Arnold WC, Dansford D, Holliday MA (1983) Effects of caloric supplementation on growth in children with uraemia. Kidney Int 24: 205–209
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jureidini, K.F., Hogg, R.J., van Renen, M.J. et al. Evaluation of long-term aggressive dietary management of chronic renal failure in children. Pediatr Nephrol 4, 1–10 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00858428
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00858428