Summary
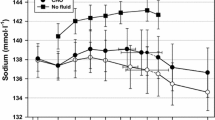
We investigated the effects of pedal speed on changes in plasma volume, electrolytes and protein during incremental exercise. Ten adult males participated in two, 30 minute incremental cycle ergometer exercise tests at room temperature (22° C, rh=56%). Exercise load was increased from 20 to 70% of peak\(\dot V_{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}} } \). Five minutes were spent at each of six stages which were equally spaced in exercise intensity. Subjects pedaled at 50 (50 RPM) and 90 (90 RPM) rev · min−1. Venous blood samples were drawn prior to exercise and during the last minute of each stage. Relative plasma volume changes showed a progressive hemoconcentration during the exercise. There were no significant differences due to pedal speed as plasma volume loss averaged −7.3% during exercise. [Na+], [Cl−], and [K+] increased significantly during exercise but were not influenced by pedal speed. Changes in plasma protein and albumin concentrations indicated that there was a loss of globulin from the vascular volume in both conditions and an addition of albumin to the plasma in 50 RPM. The difference in plasma albumin dynamics was possibly related to an effect of pedal speed on movement of fluid in the lymphatic vessels of the legs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boning D, Gonen Y, Maassen N (1984) Relationship between work load, pedal frequency, and physical fitness. Int J Sports Med 5:92–97
Convertino VA, Keil LC, Bernauer EM, Greenleaf JE (1981) Plasma volume, osmolality, vasopressin and renin activity during graded exercise in man. J Appl Physiol 50:123–128
Convertino VA, Keil LC, Greenleaf JE (1983) Plasma volume, renin, and vasopressin responses to graded exercise after training. J Appl Physiol 54:508–514
Costill DL, Branam L, Eddy D, Fink W (1974) Alterations in red cell volume following exercise and dehydration. J Appl Physiol 37:912–916
De Lanne R, Barnes JR, Brouha L (1958) Changes in concentration of plasma protein fractions during muscular work and recovery. J Appl Physiol 13:97–104
Dill DB, Costill DL (1974) Calculation of percentage changes in volume of blood, plasma, and red cells in dehydration. J Appl Physiol 37:247–248
Ekblom B (1970) Effect of physical training on circulation during prolonged severe exercise. Acta Physiol Scand 78:145–158
Faria I, Sjojaard G, Bonde-Petersen F (1982) Oxygen cost during different pedalling speeds for constant power output. J Sports Med 22:295–299
Gaebelein CJ, Senay LC jr (1982) Vascular volume dynamics during ergometer exercise at different menstrual phases. Eur J Appl Physiol 50:1–11
Greenleaf JE, van Beaumont W, Brock PJ, Morse JT, Mangseth GR (1979) Plasma volume and electrolyte shifts with heavy exercise in sitting and supine positions. Am J Physiol 236:R206-R214
Hagan RD, Diaz FJ, McMurray RG, Horvath SM (1980) Plasma volume changes related to posture and exercise. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 165:155–160
Hagberg JM, Mullin JP, Giese MD, Spitznagel E (1981) Effect of pedalling rate on submaximal exercise responses of competitive cyclists. J Appl Physiol 51:447–451
Harrison MH (1985) Effects of thermal stress and exercise on blood volume in humans. Physiol Rev 65:149–209
Harrison MH, Edwards RJ, Graveney MJ, Cochrane LA, Davies JA (1981) Blood volume and plasma protein responses to heat acclimation in humans. J Appl Physiol 50:597–604
Harrison MH, Edwards RJ, Leitch DR (1975) Effect of exercise and thermal stress on plasma volume. J Appl Physiol 39:925–931
Hughes EF, Turner SC, Brooks GA (1982) Effects of glycogen depletion and pedalling speed on “anaerobic threshold”. J Appl Physiol 52:1598–1607
Jones NL, McCartney N, Graham T, Spriet LL, Kowalchuk JM, Heigenhauser GJF, Sutton JR (1985) Muscle performance and metabolism in maximal isokinetic cycling at slow and fast speeds. J Appl Physiol 59:132–136
Kilburn KH (1966) Muscular origin of elevated plasma potassium during exercise. J Appl Physiol 21:675–678
Lollgen H, Graham T, Sjogaard G (1980) Muscle metabolites, force, and perceived exertion bicycling at varying pedal rates. Med Sci Sports Exerc 12:345–351
Lundvall J, Mellander S, Westling H, White T (1972) Fluid transfer between blood and tissue during exercise. Acta Physiol Scand 85:258–269
Melin B, Eclache JP, Geelen G, Annat G, Allevard AM, Jarsaillon E, Zebidi A, Legros JJ, Harib CG (1980) Plasma AVP, neurophysin, renin activity, and aldosterone during submaximal exercise performed until exhaustion in trained and untrained men. Eur J Appl Physiol 44:141–151
Nadel ER, Cafarelli E, Roberts MF, Wenger CB (1979) Circulatory regulation during exercise in different ambient temperatures. J Appl Physiol 46:430–437
Olszewski W, Engeset A, Jaeger PM, Sokolowski J, Theodorsen L (1977) Flow and composition of leg lymph in normal men during venous stasis, muscular activity and local hyperthermia. Acta Physiol Scand 99:149–155
Pivarnik JM, Goetting MP, Senay LC Jr (1986) The effects of body position and exercise on plasma volume dynamics. Eur J Appl Physiol 55:450–456
Pivarnik J, Kayrouz T, Senay LC Jr (1985) Plasma volume and protein content in progressive exercise: influence of cyclooxygenase inhibitors. Med Sci Sports Exerc 17:153–157
Pivarnik JM, Senay LC Jr (1986) Effects of exercise detraining and deacclimation to the heat on plasma volume dynamics. Eur J Appl Physiol 55:222–228
Schneeberger EE (1983) Proteins and vesicular transport in capillary endothelium. Fed Proc 42:2419–2424
Schultze HE, Heremans JF (1966) Molecular biology of human proteins. With special reference to plasma proteins. Nature and metabolism of extracellular proteins, vol 1. Elsevier, New York
Senay LC Jr, Fortney SM (1975) Untrained females: effects of submaximal exercise and heat on body fluids. J Appl Physiol 39:643–647
Senay LC Jr, Rogers G, Jooste P (1980) Changes in blood plasma during progressive treadmill and cycle exercise. J Appl Physiol 49:59–65
Senay LC Jr, Pivarnik JM (1985) Fluid shifts during exercise. In: Terjung RL (ed) Exercise and sport sciences reviews. MacMillan, New York, pp 335–387
Sjogaard G, Saltin B (1982) Extra- and intracellular water spaces in muscles of man at rest and with dynamic exercise. Am J Physiol 243:R271-R280
Smith EE, Guyton AC, Manning RD, White RJ (1976) Integrated mechanisms of cardiovascular response and control during exercise in the normal human. Prog Cardiovasc Dis 18:421–443
Van Beaumont W, Greenleaf JE, Juhos L (1972) Disproportional changes in hematocrit, plasma volume, and proteins during exercise and bed rest. J Appl Physiol 33:55–61
Winer BJ (1971) Statistical principles in experimental design. McGraw-Hill, New York, 2 ed
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported in part by Grants from the Theresa Monaco Endowment of the University of Houston College of Education and Nautilus Sports/Medical Industries
The constructive criticism of Dr. L. C. Senay, Jr. was sincerely appreciated.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pivarnik, J.M., Montain, S.J., Graves, J.E. et al. Alterations in plasma volume, electrolytes and protein during incremental exercise at different pedal speeds. Europ. J. Appl. Physiol. 57, 103–109 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00691247
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00691247