Summary
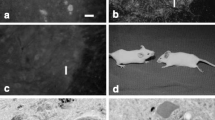
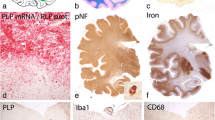
Sera from guinea pigs with acute or chronic relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE) were injected into the lumbosacral subarachnoid space of normal recipient rats. Seventeen of 37 sera induced demyelination in the CNS, and 27 of 37 sera caused demyelinated peripheral nerve fibers in the roots. The highest incidence of demyelinating activity of EAE sera was noted in those from donor animals sampled during the early chronic stage of the disease [40–100 days post sensitization (dps)]. Only few sera from animals sampled during the acute and subacute stage (10–40 dps) were able to induce demyelination. Sera from animals sampled between 100 and 200 dps showed a lower incidence of demyelinating activity as compared to those from the early chronic phase of the disease. There was no clear-cut correlation between the serum-demyelinating activity and the severity of the demyelinating disease in the donor animals. The patterns of demyelination in the central as well as peripheral nervous system of recipient animals were characterized by vesicular disruption of myelin or myelin stripping. Myelin degradation was performed mainly by macrophages. In the CNS some astrocytes also contained debris. Astrocytes increased in size, and mitosis of astrocytes was observed. Oligodendrocytes appeared to be unaffected. No demyelination was found when the sera from animals sensitized with CFA alone or with guinea pig liver tissue were injeted into the subarachnoid space of normal recipient rats.
Two possible mechanisms of demyelination are diseussed: Antibody-mediated complement-dependent and antibody-dependent cell-mediated demyelination.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Appel SH, Bornstein MB (1964) The application of tissue culture to the study of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. II. Serum factors, responsible for demyclination. J Exp Med 119:303–312
Ballin RHM, Thomas PK (1968) Electron-microscopic observations on demyelination and remyelination in experimental allergic neuritis. 1. Demyelination. J Neurol Sci 8:1–18
Bornstein MB, Appel SH (1961) The application of tissue culture to the study of experimental “allergic” encephalomyelitis. I. Patterns of demyelination. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 20:141–147
Brosnan CF, Stoner GL, Bloom BR, Wisniewski HM (1977) Studies on demyelination by activated lymphycytes in the rabbit eye. II. Antibody-dependent cell-mediated demyelination. J Immunol 118:2103–2110
Dal Canto MC, Wisniewski HM, Johnson AB, Brostoff SW, Raine CS (1975) Vesicular disruption of myelin in autoimmune demyelination. J Neurol Sci 24:313–319
Dubois-Dalq M, Niedieck B, Buyse M (1970) Action of anticerebroside sera on myelinated nervous tissue cultures. Pathol Eur 5:313–347
Fontana A, Grieder A, Arrenbrecht St, Grob P (1980a) In vitro stimulation of glia cells by a lymphocyte-produced factor. J Neurol Sci 46:55–62
Fontana A, Grieder A, Jost R, Balsiger S, Grob PJ (1980b) Gliastimmulating factor: Further analysis of secretion mechanisms. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr) 8:454
Fry JM, Weissbarth S, Lehrer GM, Bornstein MB (1974) Cerebroside antibody inhibits sulfatide synthesis and myelination and demyelinates in cord tissue cultures. Science 183:540–542
Grundke-Iqbal I, Lassmann H, Wisniewski HM (1980) Chronic relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis: Immunohistochemical studies. Arch Neurol 37:651–656
Jankovic B, Draskoci M, Janjic M (1965) Passive transfer of “allergic encephalomyelitis with antibrain serum, injected into the lateral ventricle of the brain. Nature 207:438–429
Kitz K, Lassmann H, Wisniewski HM (1981) Isolated leptomeninges of the spinal cord: An ideal tool to study inflammatory reaction in EAE. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) [Suppl] 7:179–181
Lampert PW (1965) Demyelination and remyelination in experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 24:371–385
Lampert PW (1969) Mechanism of demyelination in experimental allergic neuritis: Electron-microscopic studies. Lab Invest 20:127–138
Lampert PW, Kies MW (1967) Mechanism of demyelination in allergic encephalomyelitis of guinea pigs. An electronmicroscopic study. Exp Neurol 18:210–223
Lassmann H, Wisniewski HM (1979) Chronicrelapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Clinicopathological comparison with multiple selerosis. Arch Neurol 36:490–497
Lassmann H, Kitz K, Wisniewski HM (1980) Structural variability of demyelinating lesions in different models of subacute and chronic experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 51:191–201
Lebar R, Boutry JM, Vincent C, Robinaux R, Voisin GA (1976) Studies on autoimmune encephalomyelitis in the guinea pig. II. An in vitro investigation on the nature, properties and specificity of the serum demyelinating factor. J Immunol 116:1439–1446
Marburg O (1906) Die sogenannte „akute Multiple Sklerose”. Jahrb Psychiatrie 27:211–212
Mehta PD, Lassmann H, Wisniewski HM (1980) Immunoglobulin studies in chronic relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis (R+EAE). In: Boese A (ed) Search for the cause of multiple sclerosis and other chronic diseases of the central nervous system. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, pp 105–112
Oldstone MBA, Lampert PW (1979) Antibody-mediated complement-dependent lysis of virus-infect cells. Springer Semin Immunopathol 2:261–283
Paterson PY (1971) The demyelinating diseases. Clinical and experimental correlates. In: Samter M (ed) Immunological diseases. Little, Brown, Boston, pp 1269–1298
Perlmann H, Perlmann P, Schreiber RD, Müller-Eberhard HJ (1981) Interaction of target cell bound C3 bi and C3 d with human lymphocyte receptors. Enhancement of antibody-mediated cellular cytotoxicity. J Exp Med 153:1529–1603
Raine CS, Bornstein MB (1970) Experimental allergic encephalomyelitis: A light-and electron-microscopic study of remyelination and sclerosis in vitro. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 29:552–574
Saida K, Saida T, Brown MJ, Silberberg DH, Asbury AK (1978) Antiserum-mediated demyelination in vivo. A sequential study using intraneural injection of experimental allergic neuritis serum. Lab Invest 39:449–462
Saida T, Saida K, Brown MJ, Silberberg DH (1979a) Peripheral nerve demyelination induced by intraneural injection of experimental allergic encephalomyelitis serum. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 38:498–518
Saida K, Saida T, Brown MJ, Silberberg DH (1979b) In vivo demyelination induced by intraneural injection of antigalactocerebroside serum. Am J Pathol 95:99–119
Simon J, Simon O (1975) Effect of passive transfer of anti brain antibodies to a normal recipient. Exp Neurol 47:523–534
Snyder DH, Valsamis VD, Stone SH, Raine CS (1975) Progressive and reparatory events in chronic experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 34:209–221
Williams RM, Krakowka S, Koestner A (1980) In vivo demyelination by antimyelin antibodies. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 50:1–8
Wisniewski HM, Prineas J, Raine CS (1969) An ultrastructural study of experimental demyelination and remyelination in the peripheral and central nervous system. I. Acute experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Lab Invest 21:105–118
Wisniewski HM, Keith AB (1977) Chronic relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. An experimental model of multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 1:144–148
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported in part by the Fonds zur Förderung der wissenschaftlichen Forschung, Austria, Project No. S-25/07
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lassmann, H., Kitz, K. & Wisniewski, H.M. In vivo effect of sera from animals with chronic relapsing experimental allergic encephalomyelitis on central and peripheral myelin. Acta Neuropathol 55, 297–306 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00690994
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00690994